Environmental Impact
Driving Business Success Through Sustainable Practices

Driving Business Success Through Sustainable Practices
In the contemporary business landscape, sustainability has evolved from a buzzword to a fundamental driver of success. As companies recognize the impact of their operations on the environment and society, integrating sustainable practices has become imperative for long-term viability.
The Triple Bottom Line: People, Planet, and Profit
Embracing sustainability means adopting a holistic approach that goes beyond financial gains. The triple bottom line concept, focusing on people, planet, and profit, serves as a guiding principle. Companies are now realizing that success isn’t solely measured by financial performance but also by the positive influence they exert on communities and the environment.
Reducing Environmental Footprint
One of the key pillars of business sustainability is the reduction of environmental impact. Companies are actively seeking ways to minimize their carbon footprint, enhance energy efficiency, and optimize resource usage. Implementing eco-friendly practices not only aligns businesses with global environmental goals but also appeals to an increasingly conscientious consumer base.
Social Responsibility: Beyond Profit Motives
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) has evolved into a powerful tool for companies to demonstrate their commitment to social issues. Engaging in philanthropy, supporting local communities, and fostering diversity and inclusion are integral components of sustainable business practices. Beyond profit motives, companies are recognizing their role as responsible global citizens.
Economic Viability of Sustainability
Contrary to the misconception that sustainability comes at a high cost, businesses are discovering the economic benefits of sustainable practices. Investing in renewable energy sources, efficient supply chain management, and waste reduction not only aligns with environmental goals but also contributes to long-term cost savings. Sustainable initiatives are increasingly viewed as strategic investments for future profitability.
Embracing Innovation for Sustainable Solutions
Innovation plays a pivotal role in driving sustainable practices. Companies are leveraging technology to develop innovative solutions that address environmental and social challenges. From adopting renewable energy sources to implementing circular economy models, businesses are realizing that sustainable innovation is not only a necessity but also a source of competitive advantage.
Consumer Preferences Driving Change
Consumer preferences are evolving, with an increasing number of individuals opting for products and services from socially and environmentally responsible companies. As awareness grows, consumers are making informed choices, influencing businesses to align with their values. Sustainable practices are no longer a mere differentiator but a key factor in gaining and maintaining customer loyalty.
The Role of Stakeholders in Sustainability
Stakeholders, including employees, investors, and regulatory bodies, play a crucial role in promoting sustainability. Companies are recognizing the importance of transparent communication and engagement with stakeholders to build trust and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts ensure a comprehensive approach to addressing challenges and fostering a culture of sustainability.
Business Sustainability Practices: A Call to Action
As businesses navigate the complexities of the modern world, the call to action for integrating sustainable practices becomes more urgent. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about embracing a mindset that prioritizes the well-being of the planet, its inhabitants, and future generations.
Driving Change with Business Sustainability Practices
Global Conflicts’ Economic Fallout: Navigating Consequences
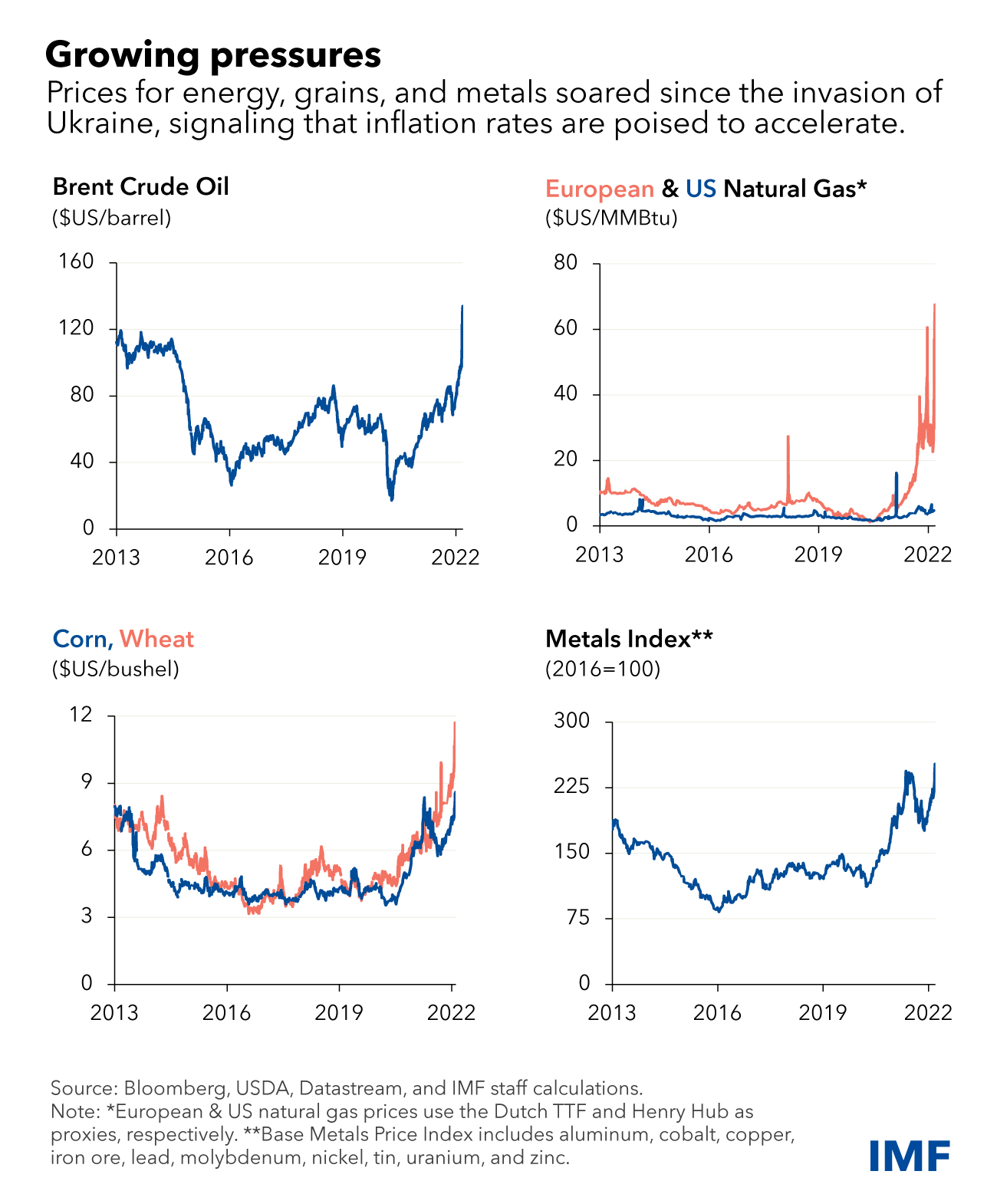
Global Conflicts’ Economic Fallout: Navigating Consequences
The echoes of global conflicts reverberate far beyond the battlefield, leaving a lasting imprint on the economic landscape. This exploration delves into the intricate web of economic consequences triggered by global conflicts and the challenges nations face in navigating their aftermath.
Destruction of Infrastructure and Economic Assets
One of the immediate economic consequences of global conflicts is the widespread destruction of infrastructure and economic assets. Wars often result in the bombing of vital transportation networks, factories, and communication systems. Rebuilding these structures requires significant financial resources, diverting funds that could be invested in economic development and growth.
Displacement and Humanitarian Costs
Global conflicts force millions to flee their homes, creating a massive refugee crisis with profound economic implications. The displaced population often strains resources in host countries, leading to increased demand for humanitarian aid. The costs of providing shelter, healthcare, and basic necessities to refugees contribute to a significant economic burden on both the affected and assisting nations.
Impact on Global Trade and Commerce
Global conflicts disrupt the flow of international trade and commerce, affecting economies worldwide. Trade routes may be compromised, and sanctions imposed on belligerent nations can lead to economic isolation. The resulting decline in global trade adversely impacts businesses, disrupts supply chains, and hampers economic growth in both conflict zones and beyond.
Shifts in Geopolitical Alliances and Trade Relationships
The aftermath of global conflicts often reshapes geopolitical alliances and trade relationships. Former allies may become adversaries, leading to realignments in international trade partnerships. Nations may need to adapt their economic strategies to navigate changing political dynamics, potentially leading to economic isolation or the forging of new alliances.
Debt Accumulation and Economic Strain
Financing global conflicts frequently involves taking on substantial amounts of debt. The accumulation of war-related debt places a severe strain on a nation’s economy. Servicing this debt diverts funds from essential public services, infrastructure development, and social programs, hindering long-term economic stability and growth.
Economic Inequality and Social Disparities
The economic consequences of global conflicts exacerbate existing inequalities and contribute to social disparities. War disrupts employment opportunities, leading to increased unemployment rates. Disruptions in education and healthcare further deepen societal divides, creating lasting economic challenges that persist long after the conflict has ended.
Environmental Degradation and Economic Impact
Global conflicts often result in environmental degradation due to factors like pollution, deforestation, and the use of destructive weaponry. The long-term economic impact of environmental damage is substantial, affecting agriculture, biodiversity, and public health. Mitigating these environmental consequences requires significant investment and poses additional economic challenges.
Reconstruction Efforts and Economic Recovery
Post-conflict reconstruction efforts are crucial for economic recovery. Rebuilding infrastructure, restoring social services, and creating a stable environment for businesses are essential components of recovery plans. The effectiveness of these efforts influences the speed and success of economic recovery in the aftermath of global conflicts.
Psychological Impact and Productivity Challenges
Beyond the physical destruction, global conflicts leave a lasting psychological impact on individuals and societies. Mental health challenges, trauma, and
