Skill Development Initiatives.
Demographic Shifts: Navigating Economic Effects
Demographic Shifts: Navigating Economic Effects
Demographic changes have far-reaching implications on the economic landscape, influencing various aspects from labor markets to consumer behavior. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate relationship between demographic shifts and their economic effects.
Population Aging and Labor Dynamics
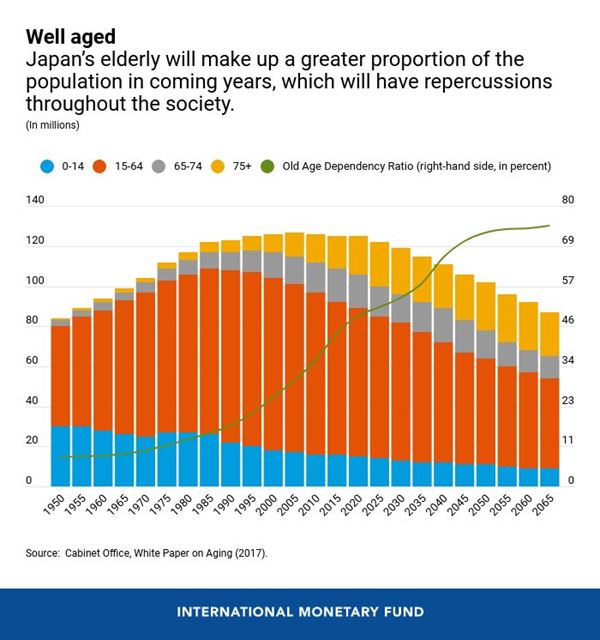
One of the prominent demographic changes is the aging population in many developed nations. This shift has significant implications for the labor force. As the proportion of older individuals increases, there is a potential decline in the workforce, affecting productivity and posing challenges for sustaining economic growth. Governments and businesses must adapt by implementing policies and practices that accommodate an aging workforce.
Consumer Spending Patterns and Market Trends
Demographic changes influence consumer spending patterns, shaping market trends and industries. For instance, an aging population may contribute to increased demand for healthcare services and products, while a younger demographic might drive trends in technology and entertainment. Businesses need to stay attuned to these shifting dynamics to effectively target their products and services to evolving consumer preferences.
Impact on Social Security and Pension Systems
The aging demographic poses challenges to social security and pension systems. With a larger proportion of retirees relative to the working population, there is increased strain on pension funds and government-sponsored retirement programs. Governments and private institutions must reassess and adapt these systems to ensure sustainability and adequacy for future generations.
Urbanization and Economic Development
Demographic changes often coincide with urbanization trends. As people migrate to urban centers in search of better opportunities, cities become hubs for economic activity. Urbanization contributes to increased productivity, innovation, and economic development. Policymakers need to manage the associated challenges, such as infrastructure demands and housing needs, to harness the economic benefits of urbanization.
Technological Adoption and Workforce Transformation
Demographic shifts influence the technological landscape as different age groups exhibit varying levels of technological adoption. Younger generations, for example, tend to be early adopters of new technologies. This demographic trait drives innovation and can reshape industries. Businesses must align their strategies with the technological preferences of their target demographics to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Fertility Rates and Economic Growth Prospects
Changes in fertility rates impact a nation’s economic growth prospects. Low fertility rates may lead to an aging population and a shrinking workforce, posing challenges for sustained economic expansion. Governments may implement policies to incentivize family formation and support population growth as a strategy to mitigate these economic challenges.
Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace
Demographic changes also highlight the importance of diversity and inclusion in the workplace. A diverse workforce, representing various demographic groups, brings a wealth of perspectives and ideas, fostering innovation and creativity. Businesses that prioritize diversity are better positioned to navigate demographic shifts and capitalize on the strengths of a varied workforce.
Global Migration and Economic Contributions
International migration patterns significantly impact the economic landscape. Migration brings a mix of skills, talents, and cultural influences to host countries, contributing to economic dynamism. However, it also presents challenges related to integration and social
Economic Impact of Evolving Labor Laws

Introduction:
The landscape of labor laws is undergoing significant transformations globally, ushering in a new era with profound economic implications. In this article, we explore the far-reaching effects of changes in labor laws on various aspects of the economy.
Labor Market Dynamics and Flexibility:
Changes in labor laws impact the dynamics of the labor market, introducing flexibility or rigidity depending on the nature of the reforms. Such shifts influence how businesses hire, manage, and retain their workforce, contributing to broader economic trends.
Impact on Wage Structures and Income Inequality:
Wage structures are intricately tied to labor laws, and changes can have implications for income distribution. Reforms that address wage gaps and promote fair compensation contribute to a more equitable society, fostering economic stability.
Employment Rates and Job Security:
Evolving labor laws can influence employment rates and job security. Striking the right balance is crucial to avoid unintended consequences such as reduced hiring or job insecurity. A stable employment environment is essential for sustained economic growth.
Entrepreneurship and Regulatory Compliance:
Changes in labor laws can impact entrepreneurship by altering the regulatory landscape. Entrepreneurs must navigate these changes, ensuring compliance while fostering an environment that encourages business innovation and growth.
Employee Benefits and Workplace Culture:
Labor laws often dictate employee benefits and workplace culture. Reforms in this area can affect businesses’ costs and employees’ satisfaction, influencing overall workplace dynamics and, consequently, economic productivity.
Collective Bargaining and Labor Unions:
The relationship between labor laws and collective bargaining is pivotal. Changes can impact the power dynamics between employers and labor unions, shaping working conditions and influencing economic negotiations within various industries.
Training and Skill Development Initiatives:
Labor laws play a role in shaping training and skill development initiatives. Reforms that encourage workforce upskilling contribute to a more skilled and adaptable labor force, fostering innovation and economic competitiveness.
Gig Economy and Freelance Work:
With the rise of the gig economy, changes in labor laws impact the classification of workers and the nature of freelance work. Adapting regulations to the evolving work landscape is crucial for sustaining economic growth in this sector.
Global Talent Mobility and Economic Competitiveness:
Labor laws influence global talent mobility, impacting a nation’s economic competitiveness. Attracting and retaining skilled professionals contributes to innovation and economic growth, positioning countries on the global stage.
Linking Economic Effects to Informed Decision-Making:
For a deeper exploration of the economic effects of changes in labor laws and strategies for informed decision-making, visit vexhibits.com. Discover insights into navigating the evolving labor landscape and ensuring economic resilience amid regulatory changes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic effects of changes in labor laws are multifaceted, influencing labor market dynamics, income distribution, employment rates, entrepreneurship, workplace culture, collective bargaining, skill development, the gig economy, global talent mobility, and overall economic competitiveness. As labor laws continue to evolve, businesses and policymakers must collaborate to strike a balance that fosters a fair and dynamic labor environment, contributing to sustained economic growth.