EconomicImpact
Navigating Tariffs: Trade Wars’ Economic Impact
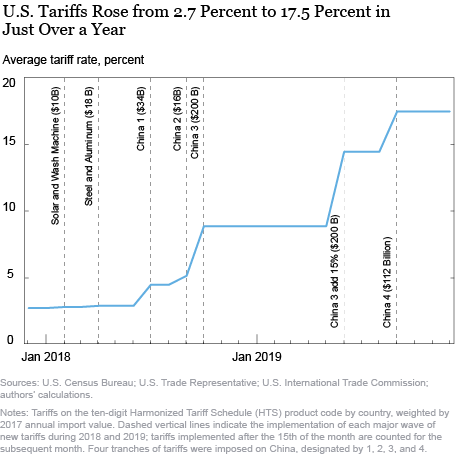
Navigating Tariffs: Trade Wars’ Economic Impact
Tariffs, often used as a tool in trade wars, have far-reaching implications for the global economy. This article delves into the intricate dynamics of tariffs and explores the profound economic impact of trade wars on nations, businesses, and consumers.
Understanding Tariffs as Trade Tools
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, designed to protect domestic industries or address trade imbalances. While they can be used strategically, the imposition of tariffs often triggers a chain reaction of consequences that reverberate through the interconnected web of global trade.
Trade Wars: The Escalation of Tariff Strategies
Trade wars involve tit-for-tat tariff escalations between nations, creating a hostile economic environment. The strategic use of tariffs as a negotiating tool can quickly devolve into a full-fledged trade war, where each side aims to protect its economic interests but risks damaging the global trade ecosystem in the process.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
One of the primary effects of tariffs and trade wars is the disruption of global supply chains. As tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, businesses may face higher production costs, leading to reevaluations of supply chain strategies. This realignment can result in delays, increased prices for consumers, and challenges for industries heavily dependent on international sourcing.
Economic Consequences for Nations
Nations engaged in trade wars often experience economic consequences. Retaliatory tariffs can lead to reduced exports, negatively affecting industries that heavily rely on international markets. Additionally, the overall economic uncertainty generated by trade wars can hinder investment and economic growth.
Business Strategies in the Face of Tariffs
Businesses must adapt to the changing landscape of tariffs and trade wars. Strategies may involve diversifying suppliers, renegotiating contracts, or absorbing some of the increased costs. Navigating these challenges requires agility and a keen understanding of the evolving trade environment.
Consumer Impact: Higher Prices and Economic Uncertainty
Tariffs, by increasing the cost of imported goods, often translate into higher prices for consumers. This impact is felt across various sectors, from electronics to everyday goods. Moreover, the uncertainty created by trade wars can influence consumer confidence, potentially leading to changes in spending patterns and economic behavior.
Negotiation and Diplomacy: Seeking Resolution
As nations grapple with the economic fallout of trade wars, the importance of negotiation and diplomacy becomes evident. Seeking resolution through diplomatic channels can mitigate the long-term damage inflicted by tariffs. Multilateral cooperation and trade agreements may offer avenues for resolving disputes and restoring economic stability.
The Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), play a crucial role in addressing trade disputes and providing a framework for negotiation. Engaging with these organizations helps establish rules and norms, fostering a more predictable and stable global trade environment.
Strategies for Mitigating Tariff Impact
To navigate the impact of tariffs and trade wars, businesses and nations may adopt various strategies. These include diversifying markets, investing in domestic industries, and actively participating in diplomatic efforts to find mutually beneficial resolutions. Strategic planning is essential for mitigating the
Navigating US Economic Impact: Trade Agreements Unveiled
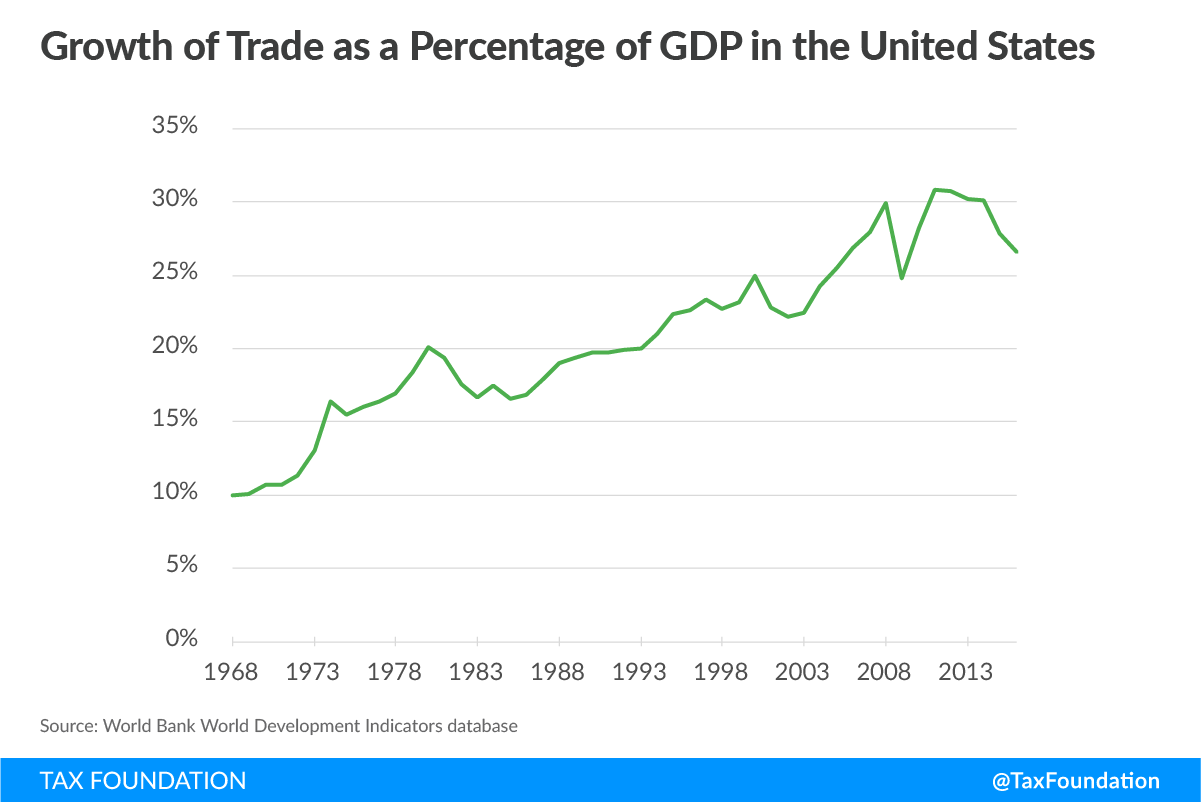
Navigating US Economic Impact: Trade Agreements Unveiled
Trade agreements play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States, influencing industries, job markets, and overall economic health. In this exploration, we unveil the intricate dynamics of trade agreements affecting the US economy.
The Cornerstone of Global Trade Relations
Trade agreements serve as the cornerstone of global trade relations, and the United States actively engages in negotiations to secure favorable terms with its key trading partners. These agreements define the rules and conditions under which goods and services are exchanged, impacting the competitiveness of American businesses in the international market.
Job Markets and Industry Impact
One of the most direct consequences of trade agreements is their impact on job markets and industries within the United States. Depending on the terms negotiated, certain industries may experience growth due to increased exports, while others may face challenges from heightened international competition. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike.
Bilateral vs. Multilateral Agreements
The nature of trade agreements can vary, ranging from bilateral agreements between two nations to more complex multilateral agreements involving multiple countries. Bilateral agreements offer a targeted approach, addressing specific issues between two trading partners. Multilateral agreements, on the other hand, involve a broader scope, impacting a network of nations and fostering interconnected global trade.
Impact on Small and Large Businesses
Trade agreements have different implications for small and large businesses within the United States. While large corporations may have the resources to navigate complex international trade regulations, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may face challenges. Trade agreements that support SMEs can contribute to a more inclusive and dynamic economic landscape.
Tariffs, Duties, and Market Access
Key components of trade agreements include negotiations on tariffs, duties, and market access. The reduction or elimination of tariffs promotes the free flow of goods and services, fostering economic growth. Ensuring favorable market access for American products abroad is equally essential, enabling businesses to reach new consumers and expand their global footprint.
Strategic Alliances and Geopolitical Considerations
Trade agreements are not merely economic instruments; they also carry significant geopolitical implications. Forming strategic alliances through trade can strengthen diplomatic ties and influence geopolitical dynamics. Understanding the interconnectedness of economic and geopolitical considerations is crucial for policymakers as they navigate complex international relations.
Trade Agreements and Regulatory Harmonization
Harmonizing regulatory frameworks is a key aspect of modern trade agreements. Aligning standards and regulations facilitates smoother trade flows, reduces barriers, and enhances overall efficiency. For the United States, participating in agreements that promote regulatory coherence ensures that American businesses can compete on a level playing field globally.
Challenges and Controversies
Trade agreements are not without challenges and controversies. Debates often arise over issues such as job displacement, environmental standards, and the protection of intellectual property. Balancing the interests of various stakeholders and addressing concerns is a delicate process that requires a nuanced approach to negotiations.
Digital Trade and Emerging Trends
As the world becomes increasingly digital, trade agreements are adapting to address
Streamlining Operations: The Importance of Accounting Software in Tribal Casinos

Key Takeaways:
- Insight into the technological advancements in tribal casino management.
- Understanding the role of specialized software in enhancing casino operational efficiency.
- Exploration of critical features to look for in casino accounting software.
- Discussion on how such software fits into broader financial systems.
The Roles of Software in Casino Management
With the intricate nature of tribal casino financials, it’s essential to have a solid system for management and accountability. Enter the modern era where software not only aids in surveillance and security but also underpins the financial aspects of casino operations. Like those offered by market leaders, including Arctic IT, high-quality accounting software is the backbone of tribal casino management. These platforms, specifically designed for the unique needs of tribal gaming, have revolutionized what it means to keep a casino functioning and thriving. Ensuring transparency, compliance, and efficiency, these systems are the unsung heroes that handle the complex web of transactions with ease and agility. Management can track earnings, payouts, and expenditures with unparalleled precision through automation and real-time processing, reshaping what we expect from casino accounting practices.
Key Features of Casino Accounting Software
Key to an excellent casino accounting system are the features it provides. Imagine a system where every chip, every spin of the slots, and each deal of the cards is meticulously recorded with pinpoint accuracy. This is the level of detail that cutting-edge casino accounting platforms offer. In evaluating software options, it’s crucial to look beyond the basics and toward comprehensive functionalities: real-time financial tracking, relentless fraud detection systems, and an innate ability to break down even the most complex jackpot structures. Real-time reporting tools become invaluable in internal audits, operational reviews, and strategic planning sessions. Coupled with complete regulatory compliance modules and asset management mechanisms, these systems aren’t just about keeping the books in check but empowering tribal casinos to maximize their financial performance and security. The software’s ability to combine disparate economic data points creates a unified financial narrative that drives more brilliant and informed operational decisions.
Improving Audit and Regulatory Compliance
Casinos, particularly those operated by tribal entities, navigate a challenging regulatory environment. Diligently adhering to rules and protocols is critical, and the right casino accounting software makes this complex task more manageable. A proactive system records transactions, highlights discrepancies, flags potential issues for further review, and ensures every penny is accounted for according to the strictest standards. With dynamic software solutions, the otherwise daunting audits and regulatory compliance tasks become streamlined, taking the burden off human managers and minimizing human error. It becomes easier for tribal casinos to stay abreast of the shifting tides of legal and financial regulations, updating their processes to maintain uninterrupted compliance, ultimately safeguarding their operations against possible legal repercussions and monetary penalties.
Integration with Other Systems
In the current digital environment, the interoperability of systems within a casino’s infrastructure is not just a feature but a necessity. The pinnacle of casino accounting software lies in its robust standalone features and its ability to integrate neatly with …
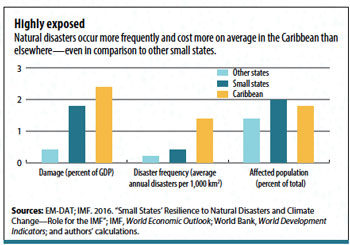
Weathering Calamity: Economic Impact of Natural Disasters
Weathering Calamity: Economic Impact of Natural Disasters
Natural disasters have the power to reshape landscapes and communities, leaving a profound and lasting impact on economies worldwide. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate web of consequences that unfold when nature’s fury collides with economic systems.
The Immediate Toll on Infrastructure
Natural disasters, be they hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, wreak havoc on infrastructure. Roads, bridges, and utilities are often damaged or destroyed, disrupting transportation and communication networks. The immediate economic toll involves the costs of emergency response, rescue operations, and the subsequent need for reconstruction. These impacts strain local and national economies, diverting resources from other essential areas.
Disruption to Businesses and Supply Chains
The economic repercussions of natural disasters extend to businesses and supply chains. Disruptions in manufacturing, distribution, and transportation impede the flow of goods and services. Businesses may face closures, production halts, and supply shortages, leading to financial losses. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that disruptions in one region can have ripple effects throughout the supply chain.
Job Losses and Unemployment
The aftermath of natural disasters often brings about job losses and increased unemployment. Businesses forced to shut down or scale back operations may lay off workers, contributing to a sudden spike in unemployment rates. This not only impacts individuals and families but also poses challenges for the broader economy as consumer spending decreases, further dampening economic activity.
Insurance Costs and Financial Strain
The economic impact of natural disasters extends to the insurance industry, which faces substantial claims for property damage and loss. The surge in claims can lead to increased insurance costs for individuals and businesses, putting financial strain on both. In some cases, the rising costs may lead to insurance unavailability, leaving communities vulnerable to future disasters.
Government Spending and Fiscal Challenges
Governments bear a significant economic burden in the aftermath of natural disasters. Emergency response efforts, infrastructure rebuilding, and assistance to affected communities require substantial financial resources. The strain on public finances can lead to budgetary deficits, increased debt, or the reallocation of funds from other essential services, creating long-term fiscal challenges.
Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
Natural disasters can devastate agricultural sectors, affecting food production and supply. Crop and livestock losses contribute to food shortages, leading to increased prices and food insecurity. The agricultural fallout also impacts the livelihoods of farmers, creating a ripple effect on rural economies and exacerbating economic challenges in already vulnerable regions.
Tourism and Economic Downturn
Regions heavily dependent on tourism often experience a sharp economic downturn following natural disasters. Damage to attractions, infrastructure, and the overall perception of safety can deter tourists, leading to a decline in revenue for businesses reliant on the tourism industry. The economic repercussions extend beyond tourism-related sectors to impact the broader local economy.
Rebuilding and Stimulating Economic Recovery
While natural disasters bring immense challenges, they also present opportunities for economic revitalization. The rebuilding phase necessitates investments in construction, infrastructure, and technology. Governments, businesses, and communities can work together to stimulate