Infrastructure Development
Foreign Investments: Shaping Economic Dynamics

Foreign Investments: Shaping Economic Dynamics
Foreign investments wield a transformative influence on the economic landscapes of nations, ushering in opportunities, challenges, and a complex interplay of global forces. This exploration navigates the multifaceted impact of foreign investments, unraveling the intricate tapestry that shapes the economic dynamics of both host and investor countries.
Attracting Capital: The Catalyst for Economic Growth
Foreign investments serve as a powerful catalyst for economic growth, injecting much-needed capital into host countries. Whether through foreign direct investment (FDI) in physical assets or portfolio investment in financial instruments, the influx of capital fosters job creation, infrastructure development, and the expansion of industries. This financial infusion propels economic activities, contributing to enhanced productivity and national prosperity.
Technological Transfer and Innovation Acceleration
Beyond financial capital, foreign investments facilitate the transfer of technology and knowledge. Multinational corporations often bring advanced technologies and innovative practices to host countries. This technological exchange not only elevates local industries but also fosters a culture of innovation. The absorption of new technologies can catalyze the development of domestic capabilities, positioning host countries at the forefront of global industries.
Job Creation and Employment Opportunities
A prominent impact of foreign investments is the creation of job opportunities. As businesses expand operations or new enterprises emerge, the demand for labor intensifies. Host countries benefit from increased employment rates, leading to improved standards of living, enhanced consumer spending, and a more robust local economy. Foreign investments thus play a pivotal role in addressing unemployment challenges and promoting inclusive economic growth.
Infrastructure Development and Capacity Building
Foreign investors often contribute to infrastructure development in host countries. Whether through direct investments in energy projects, transportation networks, or communication systems, these initiatives bolster the host nation’s infrastructure. The improvement in infrastructure not only supports the operations of foreign businesses but also enhances the overall economic competitiveness and connectivity of the host country.
Risks and Challenges: Navigating the Downsides
While foreign investments bring about numerous benefits, they also pose risks and challenges. Dependency on foreign capital can create vulnerabilities, particularly in times of economic downturns or global financial crises. Host countries need to carefully navigate the balance between attracting foreign investments and safeguarding their economic sovereignty.
Economic Diversification and Resilience
Foreign investments contribute to economic diversification by introducing new industries and sectors. This diversification is crucial for building economic resilience, reducing dependence on a single industry or market. A diversified economy is better equipped to withstand external shocks and adapt to changing global economic dynamics, fostering long-term stability.
Impact on Exchange Rates and Trade Balances
The flow of foreign investments influences exchange rates and trade balances. Large-scale investments can impact a host country’s currency value, affecting export competitiveness. Additionally, the injection of capital may lead to changes in trade balances as increased economic activities and demand for imports accompany foreign investment inflows. Managing these dynamics becomes essential for maintaining a stable economic environment.
Government Policies and Regulatory Frameworks
Host countries play a pivotal role in shaping the economic impact of foreign investments through well-crafted
Driving Prosperity: Transportation Industry’s Economic Impact
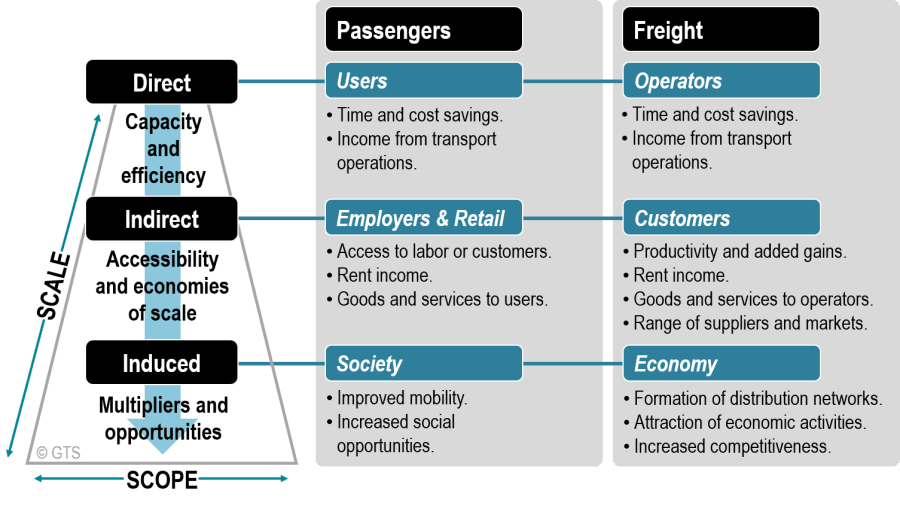
Driving Prosperity: The Interconnected Role of the Transportation Industry in Economic Growth
The transportation industry serves as a backbone for economic development, playing a pivotal role in connecting markets, facilitating trade, and driving overall prosperity. This article delves into the intricate relationship between the transportation industry and economic growth.
Foundations of Economic Connectivity
The transportation industry forms the bedrock of economic connectivity, providing the essential infrastructure that enables the movement of goods, services, and people. Efficient transportation networks are fundamental to fostering regional and global economic integration, opening avenues for trade and commerce.
Trade Facilitation and Global Markets Access
One of the primary contributions of the transportation industry to economic growth is its role in trade facilitation. Efficient transportation systems reduce the cost and time involved in moving goods, making it easier for businesses to access global markets. This connectivity encourages international trade, leading to increased economic activities and expanded opportunities for businesses.
Job Creation and Workforce Mobility
Investments in the transportation sector contribute significantly to job creation. From constructing and maintaining infrastructure to operating transportation services, the industry generates employment opportunities across various skill levels. Additionally, a well-developed transportation network enhances workforce mobility, allowing individuals to access a broader range of job opportunities.
Supply Chain Optimization and Efficiency
The transportation industry plays a critical role in supply chain optimization. Businesses rely on efficient transportation networks to streamline the movement of raw materials and finished products. Optimized supply chains contribute to cost savings, reduce lead times, and enhance overall operational efficiency, fostering a conducive environment for economic growth.
Infrastructure Development and Economic Stimulus
Investments in transportation infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, ports, and airports, have a direct impact on economic stimulus. These projects not only create immediate employment opportunities but also contribute to long-term economic growth by improving connectivity, reducing transportation costs, and attracting further investments.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The integration of technology within the transportation industry is driving innovation and further contributing to economic growth. From the implementation of smart transportation systems to the development of electric and autonomous vehicles, technological advancements enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and position the industry as a catalyst for a technologically advanced economy.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Initiatives
As the transportation industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability. Green initiatives, such as the adoption of electric vehicles and the promotion of public transportation, contribute to reducing the industry’s carbon footprint. A sustainable transportation sector aligns with global environmental goals while fostering economic growth.
Regional Development and Accessibility
Well-connected transportation networks are instrumental in promoting regional development. Areas with robust infrastructure tend to attract businesses, investments, and tourism, leading to balanced regional growth. Accessibility, facilitated by efficient transportation, opens up opportunities for previously marginalized regions to participate in economic activities.
Resilience in the Face of Challenges
The transportation industry’s resilience is evident in its ability to adapt to challenges. Whether overcoming disruptions in supply chains, addressing congestion issues, or navigating economic uncertainties, the industry’s adaptability ensures the continuity of essential
