Technological advancements
Financial Market Analysis: Navigating Trends and Strategies

Introduction:
The financial markets are dynamic ecosystems influenced by various factors. In this exploration, we delve into the significance of financial market analysis, providing insights into how individuals and businesses can navigate trends and strategies for informed decision-making.
Understanding Market Trends: The Foundation of Analysis:
Financial market analysis begins with understanding market trends. By examining price movements, trading volumes, and historical patterns, analysts can identify trends that shape market behavior. This foundational step allows investors to anticipate potential shifts and align their strategies accordingly.
Fundamental Analysis: Evaluating Financial Health:
Fundamental analysis focuses on assessing the intrinsic value of financial instruments. This involves examining financial statements, economic indicators, and company performance. By evaluating the underlying factors that impact an asset’s value, investors can make informed decisions about buying or selling.
Technical Analysis: Charting Patterns for Insights:
Technical analysis involves studying price charts and applying statistical techniques to forecast future price movements. Analysts use tools such as trendlines, moving averages, and candlestick patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Technical analysis complements fundamental analysis, providing a holistic view of market dynamics.
Risk Management Strategies: Mitigating Uncertainties:
Financial market analysis extends to risk management strategies. Understanding potential risks is crucial for protecting investments. Analysts assess factors such as market volatility, geopolitical events, and economic indicators to develop risk mitigation plans that align with investment goals.
Market Sentiment Analysis: Gauging Investor Psychology:
Market sentiment analysis involves evaluating the mood and behavior of investors. This includes monitoring social media, news sentiment, and surveys to gauge overall market sentiment. Understanding investor psychology helps in anticipating market shifts and identifying potential buying or selling opportunities.
Global Economic Analysis: The Interconnected Financial Landscape:
Financial markets are interconnected on a global scale. Analysts conduct global economic analysis to assess how geopolitical events, trade policies, and economic trends in one region impact markets worldwide. This broader perspective is essential for comprehensive financial market analysis.
Technological Advancements in Analysis: Embracing Innovation:
The landscape of financial market analysis is evolving with technological advancements. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics play a significant role in processing vast amounts of data and extracting actionable insights. Embracing innovation is essential for staying competitive in modern markets.
Algorithmic Trading: Executing Strategies with Precision:
Algorithmic trading, driven by complex mathematical models and algorithms, is a key trend in financial market analysis. This automated approach allows for precise execution of trading strategies, leveraging speed and accuracy to capitalize on market opportunities. Traders use algorithms to analyze data and execute trades swiftly.
Educational Resources for Analysis Proficiency: Empowering Investors:
Proficiency in financial market analysis is empowered by educational resources. Investors and analysts can access courses, webinars, and research materials to enhance their analytical skills. Continuous learning is crucial in adapting to changing market dynamics and refining analysis techniques.
Exploring Financial Market Analysis:
For in-depth insights into financial market analysis and strategies, visit vexhibits.com. Explore a curated collection of resources, market trends, and expert analyses that empower individuals and businesses in making informed financial decisions.
Conclusion:
Navigating Unemployment Rate Trends: Insights for Today’s Economy
Deciphering Unemployment Rate Trends: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding the nuances of unemployment rate trends is crucial in navigating the complex terrain of today’s economy. This article delves into the intricacies of this economic indicator, shedding light on its impact and providing insights for individuals and policymakers alike.
The Unemployment Rate Unveiled: Defining the Metric
The unemployment rate is a key economic indicator that reflects the percentage of the labor force without employment. This metric serves as a thermometer for the job market, providing a snapshot of economic health. Examining its trends allows for a deeper understanding of the dynamics shaping the workforce landscape.
Historical Perspectives: Tracing the Evolution of Unemployment
To comprehend the present, it is essential to glance back at the historical context of unemployment rate trends. Examining patterns over time reveals the resilience of economies in overcoming challenges and adapting to changing circumstances. Historical perspectives offer valuable insights for shaping effective policies and responses.
Economic Downturns and Surges: Unraveling Cause and Effect
Unemployment rate trends often mirror economic downturns and surges. During times of recession, the rate tends to rise as businesses cut costs and reduce their workforce. Conversely, economic upturns see a decline in unemployment as businesses expand, creating more job opportunities. Understanding this cause-and-effect relationship is crucial for anticipating economic shifts.
Impact on Communities: Beyond Numbers to Real Lives
Behind every unemployment rate is a human story. The impact of job loss extends beyond statistical figures, affecting individuals, families, and entire communities. Exploring the human aspect of unemployment emphasizes the importance of proactive measures to mitigate its effects, such as job training programs and social support systems.
Government Policies and Interventions: Balancing Act for Stability
Policymakers play a pivotal role in influencing unemployment rate trends through economic interventions. Government policies, such as fiscal stimulus packages and job creation initiatives, aim to stabilize the job market during challenging times. Analyzing the effectiveness of these interventions is crucial for shaping future economic strategies.
Global Influences: Unemployment in a Connected World
In an era of globalization, unemployment rate trends are not isolated within national borders. Global economic factors, trade relationships, and geopolitical events can have a significant impact on local job markets. Understanding these interconnected influences provides a more comprehensive view for policymakers and businesses alike.
Technological Advancements: Shaping the Future of Employment
The rise of technology introduces a dynamic element to unemployment rate trends. Automation, artificial intelligence, and evolving job requirements contribute to a shifting employment landscape. Adapting to these changes requires forward-thinking strategies to ensure the workforce remains equipped with the skills demanded by emerging industries.
Education and Skill Development: Building Resilience
In the face of evolving employment trends, education and skill development become paramount. Empowering individuals with the right skills not only enhances their employability but also contributes to overall economic resilience. Investments in education and training programs play a crucial role in aligning the workforce with the demands of a rapidly changing job market.
Charting the Course Forward: Utilizing Insights for Progress
As we navigate
Industrial Momentum: Manufacturing Output in the USA

Driving Economic Engines: Manufacturing Output in the USA
The manufacturing sector serves as a barometer for a nation’s economic health, and understanding the nuances of manufacturing output in the USA is crucial. This article explores the dynamics, trends, and implications of manufacturing output, shedding light on its significance in the broader economic landscape.
Economic Pillar: Manufacturing’s Integral Role
Manufacturing holds a foundational role in the USA’s economic framework. Beyond creating products, it generates employment, fosters innovation, and contributes significantly to the country’s GDP. Analyzing manufacturing output provides insights into the overall economic pulse and the sector’s resilience.
Cyclical Nature: Manufacturing in Economic Cycles
Manufacturing output often mirrors economic cycles. During periods of expansion, production tends to rise, driving economic growth. Conversely, in downturns, reduced consumer demand may lead to production slowdowns. Recognizing the cyclical nature of manufacturing output is key for economic planners and businesses alike.
Global Interconnectedness: International Trade Impact
The USA’s manufacturing output is intricately linked to global trade. The demand for American-made goods on the international stage influences production levels. Trade policies, tariffs, and geopolitical shifts play a role in shaping the trajectory of manufacturing output and its contribution to the balance of trade.
Technological Advancements: Industry 4.0 Transformations
The advent of Industry 4.0, marked by technological advancements like automation, IoT, and artificial intelligence, has transformed manufacturing processes. Understanding how these technologies impact output efficiency, product innovation, and overall competitiveness is vital for staying abreast of industry trends.
Employment Landscape: Manufacturing Jobs and Skills
Changes in manufacturing output have direct implications for employment. While technological advancements may enhance productivity, they also impact labor requirements. Examining the evolving employment landscape within manufacturing sheds light on the skills needed in the industry and potential workforce challenges.
Supply Chain Resilience: Lessons from Disruptions
Recent global disruptions have underscored the importance of supply chain resilience. Manufacturing output can be significantly affected by disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, or unforeseen crises. Evaluating strategies to enhance supply chain resilience is paramount for the manufacturing sector.
Environmental Sustainability: Balancing Production and Impact
Manufacturing output has environmental implications, from resource consumption to waste generation. The industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Analyzing how manufacturers balance production needs with environmental impact and the adoption of eco-friendly initiatives is crucial for a sustainable future.
Government Policies: Shaping Manufacturing Landscape
Government policies play a substantial role in shaping the manufacturing landscape. Tax incentives, trade agreements, and regulations can influence output levels. Understanding the impact of policy changes provides insights into the potential trajectory of manufacturing output and its broader economic consequences.
Visit Manufacturing Output in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For those seeking in-depth insights into manufacturing output in the USA, visit Manufacturing Output in the USA. The curated analysis and information provided can empower businesses, policymakers, and individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the manufacturing sector.
In conclusion, manufacturing output is a multifaceted economic indicator that goes beyond production numbers. It reflects technological
Empowering Excellence: Business Education and Training Programs

Empowering Excellence: Business Education and Training Programs
Business education and training programs play a pivotal role in shaping the skills and competencies of professionals across industries. In this article, we delve into the significance of these programs, exploring how they empower individuals and contribute to the overall success of businesses.
The Evolving Landscape of Business Education
The landscape of business education has evolved significantly, adapting to the changing needs of the corporate world. Modern business education programs go beyond traditional classroom settings, incorporating online courses, workshops, and experiential learning opportunities. This evolution ensures that professionals receive diverse and dynamic education experiences.
Tailoring Education to Industry Demands
One of the key strengths of business education programs is their ability to tailor curricula to meet industry demands. These programs focus on providing practical, real-world skills that are directly applicable to the challenges professionals face in their respective fields. This alignment between education and industry needs enhances the relevance and effectiveness of the learning experience.
Professional Development: Beyond Academic Degrees
Business education and training programs contribute significantly to professional development. While academic degrees are essential, specialized training programs offer targeted skill enhancement. Whether it’s mastering a new software, improving leadership abilities, or gaining insights into emerging industry trends, these programs empower professionals to stay competitive and relevant.
Leadership Training: Nurturing Tomorrow’s Leaders
Effective leadership is a cornerstone of successful businesses. Business education programs, particularly those focused on leadership training, play a crucial role in nurturing tomorrow’s leaders. These programs emphasize strategic thinking, decision-making skills, and the ability to navigate complex business landscapes, preparing individuals to take on leadership roles with confidence.
Adapting to Technological Advancements
In the era of rapid technological advancements, staying abreast of the latest tools and innovations is vital for professionals. Business education and training programs integrate technology into their curricula, ensuring that individuals are not only familiar with current technologies but are also equipped to leverage them for enhanced productivity and efficiency.
Entrepreneurial Education: Fostering Innovation
Entrepreneurial education programs contribute to fostering innovation and a spirit of entrepreneurship. These programs guide individuals through the intricacies of starting and running a business, providing insights into market dynamics, risk management, and creative problem-solving. Empowering individuals with entrepreneurial skills drives innovation within organizations.
Soft Skills Development: Enhancing Interpersonal Competence
In addition to technical expertise, business education programs emphasize the development of soft skills. Effective communication, teamwork, adaptability, and emotional intelligence are integral components of these programs. Enhancing interpersonal competence is essential for professionals to collaborate seamlessly and contribute positively to their work environments.
Global Perspective: Navigating the International Business Arena
As businesses operate on a global scale, having a comprehensive understanding of international markets and cultures is imperative. Business education and training programs with a global focus provide individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the complexities of the international business arena, fostering a global mindset among professionals.
Networking Opportunities: Building Professional Connections
Business education programs offer invaluable networking opportunities. Whether through collaborative projects, industry events, or alumni networks, these
Economic Impact of Social Regulation Changes
Introduction:
In recent times, societies have witnessed a profound transformation in social regulations, prompting a ripple effect on the economic landscape. These changes, born out of evolving societal norms and governmental policies, carry substantial economic consequences that merit exploration.
Shifts in Employment Dynamics:
One of the primary facets of the economic impact revolves around alterations in employment dynamics. As social regulations adapt, businesses must reassess their workforce structures. These shifts can influence job creation, job security, and overall labor market stability.
Entrepreneurial Landscape:
Changes in social regulations often mold the entrepreneurial landscape. New regulations may either foster innovation or pose challenges to emerging businesses. Understanding the interplay between social regulations and entrepreneurship is crucial for predicting economic trends.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends:
Social regulations shape consumer behavior by influencing their preferences and values. This, in turn, has a direct impact on market trends. Businesses must stay attuned to these shifts to align their strategies with evolving consumer demands.
Government Expenditure and Social Welfare Programs:
As social regulations evolve, so does government expenditure. Changes in policies related to social welfare programs can significantly affect the allocation of public funds. Understanding these changes is essential for evaluating the broader economic impact on society.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Compliance:
The nexus between technological advancements and regulatory compliance is pivotal. Innovations may be driven by the need to adhere to new social regulations, presenting opportunities for growth in certain sectors. Conversely, industries lagging behind in compliance may face economic challenges.
Global Economic Integration:
Social regulations are not confined to national boundaries; they contribute to the broader trend of global economic integration. Understanding the global implications of these changes is imperative for businesses engaged in international trade.
Investor Confidence and Market Volatility:
Fluctuations in social regulations can impact investor confidence and market volatility. Investors keenly observe regulatory changes, as they can signal economic shifts. A transparent regulatory environment often enhances investor confidence and contributes to a more stable market.
Environmental Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility:
Modern social regulations increasingly emphasize environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility. Businesses aligning with these values may experience economic benefits through enhanced brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Linking Economic Impact to Social Responsibility:
Recognizing the symbiotic relationship between economic impact and social responsibility is crucial. Businesses that embrace social responsibility initiatives tend to fare better in the long run. For a deeper understanding of this interplay, explore the Economic impact of changes in social regulations at vexhibits.com.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic impact of changes in social regulations is multifaceted, influencing employment, entrepreneurship, consumer behavior, government expenditure, technology, global integration, investor confidence, and corporate responsibility. Navigating these dynamics requires a proactive approach from businesses and policymakers alike. As societal norms continue to evolve, understanding and adapting to the economic consequences of social regulatory changes will be integral to sustained growth and development.
Driving Prosperity: Transportation Industry’s Economic Impact
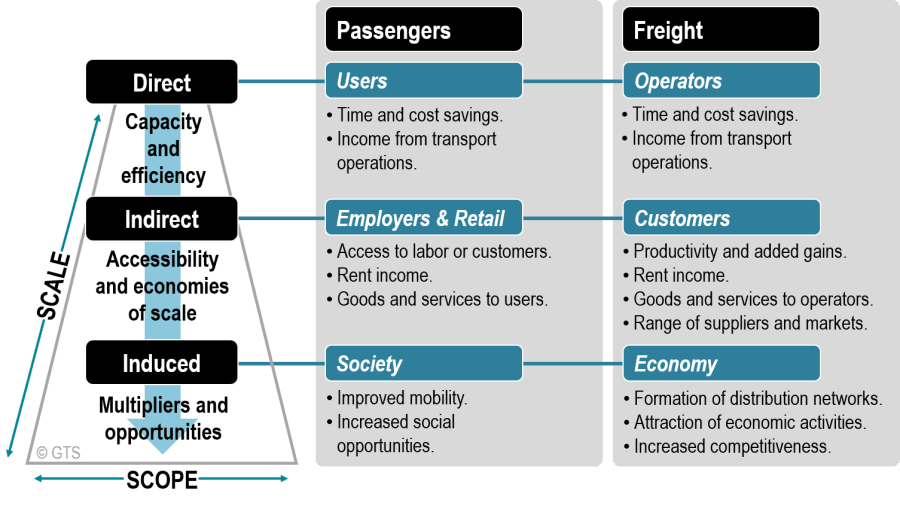
Driving Prosperity: The Interconnected Role of the Transportation Industry in Economic Growth
The transportation industry serves as a backbone for economic development, playing a pivotal role in connecting markets, facilitating trade, and driving overall prosperity. This article delves into the intricate relationship between the transportation industry and economic growth.
Foundations of Economic Connectivity
The transportation industry forms the bedrock of economic connectivity, providing the essential infrastructure that enables the movement of goods, services, and people. Efficient transportation networks are fundamental to fostering regional and global economic integration, opening avenues for trade and commerce.
Trade Facilitation and Global Markets Access
One of the primary contributions of the transportation industry to economic growth is its role in trade facilitation. Efficient transportation systems reduce the cost and time involved in moving goods, making it easier for businesses to access global markets. This connectivity encourages international trade, leading to increased economic activities and expanded opportunities for businesses.
Job Creation and Workforce Mobility
Investments in the transportation sector contribute significantly to job creation. From constructing and maintaining infrastructure to operating transportation services, the industry generates employment opportunities across various skill levels. Additionally, a well-developed transportation network enhances workforce mobility, allowing individuals to access a broader range of job opportunities.
Supply Chain Optimization and Efficiency
The transportation industry plays a critical role in supply chain optimization. Businesses rely on efficient transportation networks to streamline the movement of raw materials and finished products. Optimized supply chains contribute to cost savings, reduce lead times, and enhance overall operational efficiency, fostering a conducive environment for economic growth.
Infrastructure Development and Economic Stimulus
Investments in transportation infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, ports, and airports, have a direct impact on economic stimulus. These projects not only create immediate employment opportunities but also contribute to long-term economic growth by improving connectivity, reducing transportation costs, and attracting further investments.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The integration of technology within the transportation industry is driving innovation and further contributing to economic growth. From the implementation of smart transportation systems to the development of electric and autonomous vehicles, technological advancements enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and position the industry as a catalyst for a technologically advanced economy.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Initiatives
As the transportation industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability. Green initiatives, such as the adoption of electric vehicles and the promotion of public transportation, contribute to reducing the industry’s carbon footprint. A sustainable transportation sector aligns with global environmental goals while fostering economic growth.
Regional Development and Accessibility
Well-connected transportation networks are instrumental in promoting regional development. Areas with robust infrastructure tend to attract businesses, investments, and tourism, leading to balanced regional growth. Accessibility, facilitated by efficient transportation, opens up opportunities for previously marginalized regions to participate in economic activities.
Resilience in the Face of Challenges
The transportation industry’s resilience is evident in its ability to adapt to challenges. Whether overcoming disruptions in supply chains, addressing congestion issues, or navigating economic uncertainties, the industry’s adaptability ensures the continuity of essential

