Global expansion
Optimizing Corporate Profits: Strategies for Success
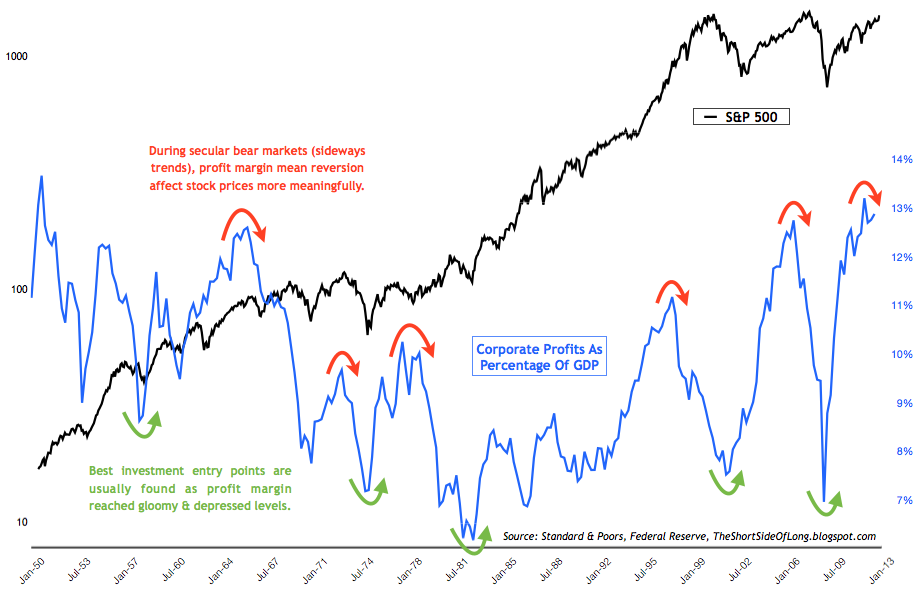
Navigating the Terrain: Strategies for Optimizing Corporate Profits in the USA
Corporate profits in the USA are a vital metric reflecting the financial health and success of businesses. This article delves into the intricacies of corporate profits, exploring strategies that companies employ to thrive in the competitive landscape.
Understanding Corporate Profits: Beyond the Bottom Line
Corporate profits encompass the net earnings of a business after deducting expenses. This financial metric serves as a barometer for a company’s performance and competitiveness. Understanding the components that contribute to corporate profits provides insights into the dynamics of a firm’s financial success.
Market Dynamics: Adapting to Competitive Realities
In a dynamic business environment, companies must navigate market forces to optimize their profits. This involves strategic positioning, effective marketing, and staying attuned to consumer trends. Companies that adapt swiftly to market dynamics are better positioned to capitalize on opportunities and enhance their profitability.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlining Processes for Success
Operational efficiency plays a pivotal role in maximizing corporate profits. Streamlining internal processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation contribute to cost savings. Companies that prioritize operational efficiency can allocate more resources to revenue-generating activities, positively impacting their bottom line.
Innovation and Product Development: Fuelling Profitable Growth
Innovative products and services are key drivers of corporate profits. Companies that invest in research and development, stay ahead of technological trends, and consistently bring innovative solutions to the market are positioned for sustained profitability. Innovation fosters differentiation and customer loyalty, contributing to long-term financial success.
Cost Management: Balancing Act for Financial Health
Effective cost management is a crucial aspect of optimizing corporate profits. This involves prudent expense control, negotiating favorable supplier agreements, and exploring opportunities for cost-sharing or outsourcing. Striking a balance between cost reduction and maintaining quality is paramount for sustainable financial health.
Global Expansion: Tapping into International Markets
Many successful companies optimize their profits by expanding beyond domestic borders. International markets offer new opportunities for revenue generation. However, global expansion requires careful consideration of cultural nuances, regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics. Companies that navigate these complexities effectively can unlock new avenues for profit growth.
Financial Planning and Investment: Strategic Allocation of Resources
Strategic financial planning and investment are instrumental in optimizing corporate profits. Companies must allocate resources judiciously, considering both short-term financial goals and long-term sustainability. Prudent investment decisions, whether in technology, infrastructure, or talent, contribute to enhanced profitability over time.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Balancing Profit and Purpose
In the modern business landscape, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is increasingly intertwined with profitability. Companies that actively engage in socially responsible practices often enjoy enhanced brand reputation, customer loyalty, and employee satisfaction. Balancing profit goals with a commitment to social and environmental responsibility is a strategy for sustained success.
Visit Corporate Profits in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For those seeking in-depth insights into optimizing corporate profits in the USA, visit Corporate Profits in the USA. The curated analysis and information provided can empower businesses with the knowledge needed to navigate the intricacies of profit optimization
Navigating Global Expansion: Effective Business Strategies

Navigating Global Expansion: Effective Business Strategies
Expanding a business globally presents both opportunities and challenges. In this article, we explore key strategies for successful global business expansion, guiding organizations through the intricate process of entering new markets and thriving on a global scale.
Market Research: The Foundation of Global Expansion
Before embarking on global expansion, thorough market research is essential. Understanding the target market’s demographics, consumer behavior, and cultural nuances provides valuable insights. This foundational knowledge informs decision-making and helps tailor strategies to meet the specific demands of diverse markets.
Localization: Adapting to Cultural Differences
Cultural sensitivity is critical in global business expansion. Localization involves adapting products, services, and marketing strategies to suit the cultural preferences and norms of each target market. Respectful integration ensures that the business resonates with local audiences, fostering acceptance and trust.
Strategic Partnerships: Leveraging Local Expertise
Establishing strategic partnerships with local businesses or experts is a powerful strategy for global expansion. These partnerships provide invaluable insights into the local business landscape, regulatory environment, and consumer behavior. Leveraging local expertise enhances the organization’s ability to navigate unfamiliar territories successfully.
Legal Compliance: Navigating Regulatory Challenges
Global expansion brings with it a myriad of regulatory challenges. From compliance with local laws to understanding international trade regulations, businesses must navigate complex legal landscapes. Investing in legal counsel and staying abreast of regulatory changes is crucial to ensuring a smooth and lawful expansion process.
Risk Management: Anticipating and Mitigating Challenges
Expanding globally involves inherent risks. Effective risk management strategies anticipate potential challenges and outline mitigation plans. Businesses must identify geopolitical, economic, and operational risks to develop contingency plans that safeguard the continuity and success of global operations.
Technology Integration: Streamlining Global Operations
Technology plays a pivotal role in global business expansion. Integrating advanced technologies for communication, project management, and data analytics streamlines global operations. This ensures efficient collaboration among teams across different time zones and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
Talent Acquisition and Development: Building a Global Team
A successful global expansion requires a skilled and diverse workforce. Businesses should focus on talent acquisition strategies that attract individuals with a deep understanding of local markets. Additionally, investing in ongoing training and development programs ensures that the global team remains adaptive and competitive.
Financial Management: Adapting to Currency and Market Fluctuations
Fluctuations in currency and market conditions are inherent to global expansion. Implementing robust financial management strategies, including hedging against currency risks and regularly assessing market conditions, safeguards the financial stability of the business during global operations.
Customer-Centric Approach: Building Global Relationships
Maintaining a customer-centric approach is paramount in global expansion. Building strong relationships with customers across diverse cultures requires attentiveness to customer needs, personalized service, and responsiveness to feedback. A positive customer experience fosters brand loyalty and advocacy on a global scale.
Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation: Staying Agile
Global business environments are dynamic, requiring organizations to remain agile. Continuous evaluation of strategies, market conditions, and performance metrics is essential. This ongoing assessment enables businesses to adapt quickly to changes, capitalize on emerging
Sharing Economy’s Economic Impact: A Comprehensive Analysis
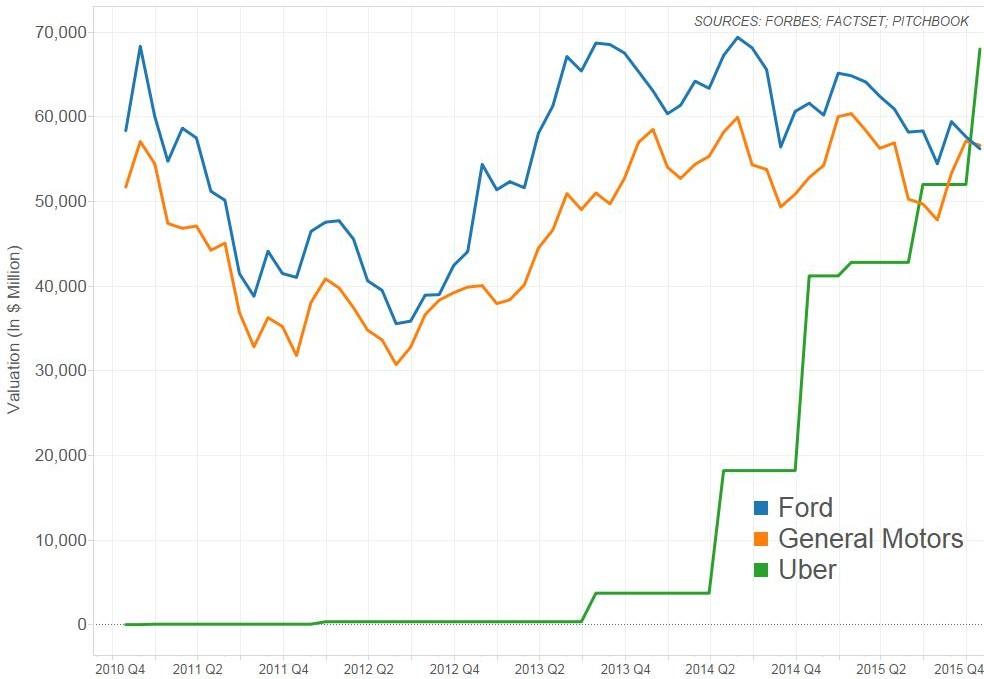
Sharing Economy’s Economic Impact: A Comprehensive Analysis
The emergence of the sharing economy has revolutionized traditional business models, bringing forth a myriad of economic implications that ripple across industries. This exploration delves into the multifaceted economic dynamics of the sharing economy, shedding light on both its positive and challenging effects on businesses, consumers, and the broader economic landscape.
Redefining Consumer Behavior and Expenditure Patterns
The sharing economy has redefined how consumers access goods and services, altering traditional expenditure patterns. With the rise of platforms facilitating peer-to-peer transactions, consumers increasingly opt for shared access over ownership. This shift has economic implications, impacting industries like transportation and accommodation, as consumers prioritize experiences over possessions, altering the demand for certain products and services.
Job Creation and Gig Economy Opportunities
One of the notable economic implications of the sharing economy is the creation of job opportunities within the gig economy. Platforms connecting individuals for tasks such as ride-sharing, freelance work, and short-term rentals empower individuals to monetize their assets and skills. While this opens avenues for flexible employment, it also brings challenges related to job security, benefits, and regulatory considerations.
Impact on Traditional Industries and Market Disruption
The sharing economy has disrupted traditional industries, challenging established business models. Sectors like hospitality, taxi services, and retail have faced intensified competition from sharing economy platforms. This disruption sparks economic debates as it raises questions about fair competition, regulatory frameworks, and the adaptability of traditional industries to evolving market dynamics.
Regulatory Challenges and Government Response
The rapid growth of the sharing economy has posed regulatory challenges for governments worldwide. Balancing innovation with consumer protection and fair competition requires nuanced approaches. Governments grapple with establishing regulatory frameworks that ensure safety, tax compliance, and fair labor practices without stifling the economic potential of sharing economy platforms.
Economic Inclusion and Access to Services
The sharing economy fosters economic inclusion by providing access to services that might be otherwise unaffordable or unavailable. Ride-sharing, co-working spaces, and peer-to-peer lending platforms democratize access, empowering individuals who may have been excluded from certain services in traditional models. This economic inclusion aspect has both positive societal and economic impacts.
Asset Utilization and Environmental Sustainability
From shared rides to accommodation, the sharing economy optimizes asset utilization, promoting environmental sustainability. By maximizing the use of existing resources, the sharing economy contributes to reduced waste and environmental impact. This economic benefit aligns with growing consumer preferences for eco-friendly practices and positions sharing economy platforms as contributors to sustainable development.
Data Privacy Concerns and Trust Dynamics
The sharing economy heavily relies on data-driven transactions, raising concerns about data privacy and trust. Economic implications arise as consumers grapple with the trade-off between convenience and the protection of their personal information. Building and maintaining trust become crucial for the sustained success of sharing economy platforms, with economic consequences tied to their ability to address privacy concerns.
Market Monopolization and Anti-Competitive Practices
As certain sharing economy platforms grow in prominence, concerns about market monopolization and anti-competitive practices emerge. Economic implications include reduced
