Innovation
Optimizing Corporate Profits: Strategies for Success
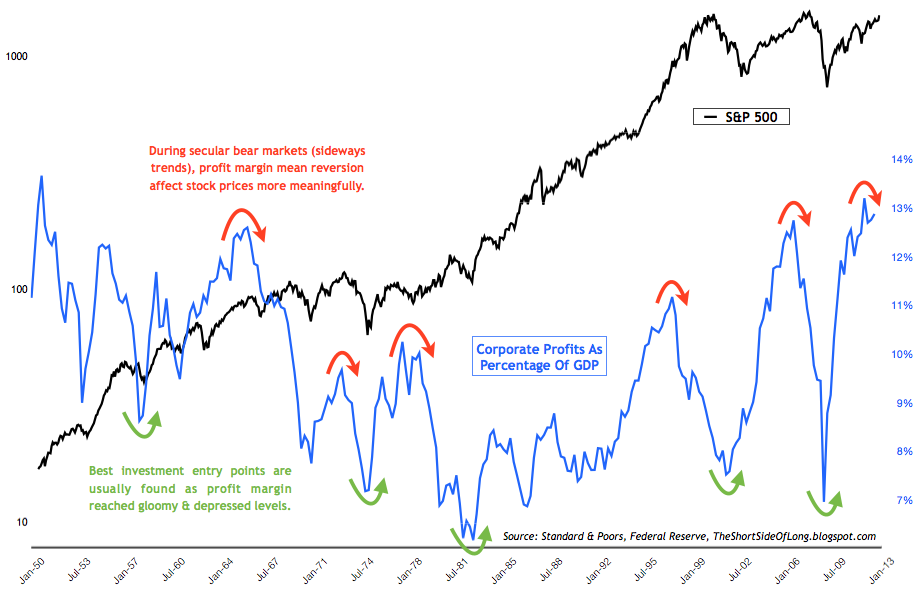
Navigating the Terrain: Strategies for Optimizing Corporate Profits in the USA
Corporate profits in the USA are a vital metric reflecting the financial health and success of businesses. This article delves into the intricacies of corporate profits, exploring strategies that companies employ to thrive in the competitive landscape.
Understanding Corporate Profits: Beyond the Bottom Line
Corporate profits encompass the net earnings of a business after deducting expenses. This financial metric serves as a barometer for a company’s performance and competitiveness. Understanding the components that contribute to corporate profits provides insights into the dynamics of a firm’s financial success.
Market Dynamics: Adapting to Competitive Realities
In a dynamic business environment, companies must navigate market forces to optimize their profits. This involves strategic positioning, effective marketing, and staying attuned to consumer trends. Companies that adapt swiftly to market dynamics are better positioned to capitalize on opportunities and enhance their profitability.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlining Processes for Success
Operational efficiency plays a pivotal role in maximizing corporate profits. Streamlining internal processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation contribute to cost savings. Companies that prioritize operational efficiency can allocate more resources to revenue-generating activities, positively impacting their bottom line.
Innovation and Product Development: Fuelling Profitable Growth
Innovative products and services are key drivers of corporate profits. Companies that invest in research and development, stay ahead of technological trends, and consistently bring innovative solutions to the market are positioned for sustained profitability. Innovation fosters differentiation and customer loyalty, contributing to long-term financial success.
Cost Management: Balancing Act for Financial Health
Effective cost management is a crucial aspect of optimizing corporate profits. This involves prudent expense control, negotiating favorable supplier agreements, and exploring opportunities for cost-sharing or outsourcing. Striking a balance between cost reduction and maintaining quality is paramount for sustainable financial health.
Global Expansion: Tapping into International Markets
Many successful companies optimize their profits by expanding beyond domestic borders. International markets offer new opportunities for revenue generation. However, global expansion requires careful consideration of cultural nuances, regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics. Companies that navigate these complexities effectively can unlock new avenues for profit growth.
Financial Planning and Investment: Strategic Allocation of Resources
Strategic financial planning and investment are instrumental in optimizing corporate profits. Companies must allocate resources judiciously, considering both short-term financial goals and long-term sustainability. Prudent investment decisions, whether in technology, infrastructure, or talent, contribute to enhanced profitability over time.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Balancing Profit and Purpose
In the modern business landscape, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is increasingly intertwined with profitability. Companies that actively engage in socially responsible practices often enjoy enhanced brand reputation, customer loyalty, and employee satisfaction. Balancing profit goals with a commitment to social and environmental responsibility is a strategy for sustained success.
Visit Corporate Profits in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For those seeking in-depth insights into optimizing corporate profits in the USA, visit Corporate Profits in the USA. The curated analysis and information provided can empower businesses with the knowledge needed to navigate the intricacies of profit optimization
Cloud Computing Unleashed: Empowering Business Agility

Introduction:
In the era of digital transformation, cloud computing has become a cornerstone for businesses seeking agility, scalability, and efficiency. This article explores the transformative power of cloud computing, its impact on business operations, and how organizations can harness this technology to drive innovation and achieve competitive advantages.
Cloud Computing for Businesses Link:
Discover the potential of Cloud Computing for Businesses here. Explore how businesses can leverage the cloud for enhanced agility and innovation.
Enhancing Business Agility:
Cloud computing enables businesses to embrace agility by providing on-demand access to computing resources. This flexibility allows organizations to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand, fostering agility in responding to market changes and seizing new opportunities.
Scalability for Growing Needs:
One of the key benefits of cloud computing is its inherent scalability. As businesses grow, their computing needs evolve. Cloud services offer the ability to scale resources effortlessly, ensuring that businesses can meet increased demands without the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware.
Cost-Efficiency and Resource Optimization:
Cloud computing introduces a cost-efficient paradigm, replacing traditional capital-intensive IT infrastructure with a pay-as-you-go model. This not only reduces upfront costs but also allows businesses to optimize their resources by paying only for the services they consume.
Global Accessibility and Collaboration:
The cloud breaks down geographical barriers, enabling global accessibility and collaboration. With data and applications stored in the cloud, teams can collaborate seamlessly from different locations, enhancing productivity and fostering innovation through diverse perspectives.
Data Security and Compliance:
Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures, often surpassing what individual businesses can implement. These providers adhere to strict compliance standards, ensuring that businesses can store and process sensitive data securely while meeting regulatory requirements.
Innovation Through Cloud Services:
Cloud computing is a catalyst for innovation. Businesses can leverage a plethora of cloud services, including machine learning, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics, to gain insights, automate processes, and drive innovation across various industries.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
Cloud computing acts as a robust disaster recovery solution. With data stored in the cloud, businesses can swiftly recover from data loss or system failures. This ensures business continuity, reduces downtime, and safeguards critical operations.
Adopting a Hybrid Cloud Approach:
Many businesses adopt a hybrid cloud approach, combining public and private cloud solutions to meet their specific needs. This flexibility allows organizations to balance the benefits of public cloud scalability with the security and control of a private cloud for sensitive operations.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies:
While the benefits of cloud computing are significant, businesses must address challenges such as data privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, and potential disruptions. Implementing robust risk management and mitigation strategies ensures a smooth transition to the cloud while safeguarding against potential pitfalls.
Future Trends and Continuous Evolution:
Cloud computing is a dynamic field, and its evolution continues. As businesses embark on their cloud journey, staying informed about emerging trends, such as edge computing and serverless architectures, allows them to remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Conclusion:
Economic Impact of Evolving Healthcare Laws
Introduction:
The intersection of healthcare and economics is a critical nexus that significantly influences the well-being of societies. This article delves into the intricate web of economic consequences arising from changes in healthcare laws, exploring how policy shifts can ripple through financial systems.
Financial Impact on Healthcare Institutions:
Changes in healthcare laws inevitably lead to a financial impact on healthcare institutions. Hospitals, clinics, and other providers must navigate evolving regulations, often requiring adjustments to operational structures and financial strategies to maintain stability.
Insurance Dynamics and Affordability:
One of the primary economic consequences involves the dynamics of health insurance. Alterations in healthcare laws can affect the affordability and accessibility of insurance plans. This, in turn, influences consumer spending patterns, impacting both individuals and the broader economy.
Innovation and Investment in Healthcare:
Healthcare laws play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape for innovation and investment in the medical field. Policy changes can either spur or hinder advancements, affecting not only the healthcare sector but also industries connected to medical research and technology.
Employer-Sponsored Healthcare and Labor Market Dynamics:
The economic ramifications extend to the employer-sponsored healthcare model. Changes in healthcare laws can influence labor market dynamics as businesses adjust to new compliance requirements, potentially impacting employment patterns and overall workforce management.
Public Health Initiatives and Government Expenditure:
Shifts in healthcare laws often coincide with adjustments in public health initiatives. Governments may need to reallocate resources, affecting public expenditure. Understanding the balance between public health priorities and economic considerations is crucial for sustainable policy development.
Pharmaceutical Industry and Drug Pricing:
The pharmaceutical industry is intricately linked to healthcare laws, particularly concerning drug pricing and market regulations. Changes in legislation can impact pharmaceutical companies’ profitability and influence the cost of medications for consumers, with wide-ranging economic implications.
Healthcare Access Disparities and Socioeconomic Factors:
Economic consequences also manifest in healthcare access disparities. Changes in healthcare laws can exacerbate or alleviate existing socioeconomic disparities in healthcare access, contributing to broader societal economic inequalities.
Technological Integration and Healthcare Costs:
Advancements in healthcare technology are often driven or hindered by legislative changes. The integration of new technologies can influence healthcare costs, posing challenges or opportunities for cost containment and efficiency within the healthcare system.
Investor Confidence in Healthcare Markets:
Investors closely monitor healthcare laws due to the substantial impact on the financial performance of healthcare-related companies. Changes in regulations can sway investor confidence, affecting market valuations and investment decisions within the healthcare sector.
Linking Economic Consequences to Informed Decision-Making:
For a comprehensive understanding of the economic consequences of changes in healthcare laws and strategies for informed decision-making, explore vexhibits.com. Delve into the nuances of healthcare policy impact on financial systems and discover ways to navigate these changes for economic resilience.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic consequences of changes in healthcare laws are far-reaching, influencing healthcare institutions, insurance dynamics, innovation, labor markets, public health initiatives, pharmaceuticals, healthcare access, technology integration, and investor confidence. Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced approach, considering both the healthcare and economic aspects
Fostering Economic Growth Through Education Initiatives

Fostering Economic Growth Through Education Initiatives
In today’s rapidly evolving global landscape, the intersection of education and economic development plays a pivotal role in shaping the future. As nations strive for progress and prosperity, investing in education emerges as a catalyst for sustainable economic growth. This article explores the intricate relationship between education and economic development, shedding light on the transformative power of well-crafted educational initiatives.
The Foundation of Prosperity
Education serves as the bedrock of a prosperous society. It empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate an increasingly complex world. A well-educated workforce is not only more adept at addressing contemporary challenges but also more capable of driving innovation and productivity, two key factors that fuel economic development.
Empowering the Workforce
One of the primary ways education contributes to economic development is by empowering the workforce. A highly skilled and knowledgeable workforce is essential for industries to thrive and remain competitive in the global marketplace. As technological advancements continue to reshape industries, a workforce equipped with up-to-date skills becomes a valuable asset, attracting investments and fostering economic sustainability.
Closing the Skills Gap
The ever-changing demands of the job market highlight the importance of education in addressing the skills gap. By aligning educational curricula with industry needs, educational institutions can play a crucial role in producing graduates with the skills required by the workforce. This proactive approach not only benefits individuals seeking employment but also strengthens the economic fabric by ensuring a skilled and adaptable workforce.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Education fosters an environment conducive to entrepreneurship and innovation, both integral components of economic development. A well-rounded education system encourages creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills—qualities essential for driving entrepreneurial ventures. By supporting an entrepreneurial culture, education becomes a catalyst for job creation and economic diversification.
Investment in Infrastructure
Robust education systems often attract investments in infrastructure. Nations recognizing the value of education are more likely to invest in schools, colleges, and research institutions. These investments not only enhance the quality of education but also create construction jobs and stimulate economic activity in the short term, laying the groundwork for long-term development.
Global Competitiveness
In an interconnected world, global competitiveness is a key driver of economic success. A nation’s education system plays a pivotal role in determining its standing in the global arena. A well-educated workforce enhances a country’s competitiveness by contributing to research, development, and innovation, ultimately attracting international investments and fostering economic growth.
The Role of Technology in Education
The integration of technology in education further amplifies its impact on economic development. Technologically literate individuals are better equipped to adapt to the evolving demands of the digital age. Educational initiatives that embrace technology not only prepare students for the future job market but also contribute to the growth of the technology sector, a potent driver of economic development.
Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of education on economic development are evident, challenges such as accessibility, affordability, and quality persist. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort
