Risk management
Navigating Stock Market Dynamics: Strategies for Optimal Performance
Unveiling the Intricacies of Stock Market Performance
Embarking on the journey of understanding stock market performance is akin to navigating a complex financial landscape. This article aims to unravel the intricacies, providing insights into strategies for optimal performance and informed decision-making.
The Dynamics of Stock Market Performance: A Primer
Stock market performance encapsulates the ebbs and flows of financial markets, reflecting the collective sentiment of investors. Understanding the dynamics involves delving into factors such as company earnings, economic indicators, and global events. This multifaceted approach is essential for grasping the nuances of stock market behavior.
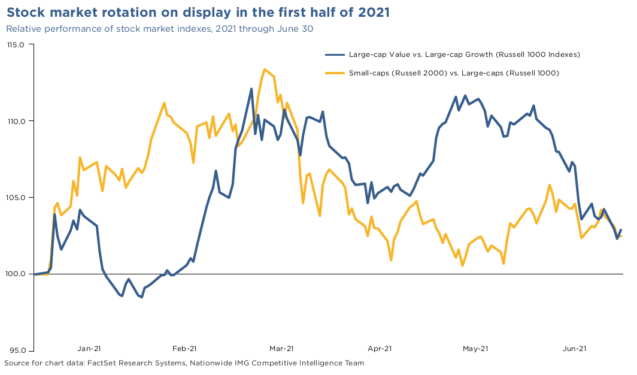
Bull and Bear Markets: Riding the Waves
Stock markets are often characterized by bull and bear markets, representing periods of growth and decline, respectively. Recognizing the signs of these market cycles is crucial for investors. During bull markets, optimism prevails, and stocks generally rise. In contrast, bear markets witness pessimism, with stock prices falling. Strategic decision-making hinges on accurately identifying these market phases.
Market Indices: Gauging Overall Performance
Market indices, such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average, serve as benchmarks for assessing stock market performance. They provide a snapshot of how a broad section of the market is faring. Monitoring these indices aids investors in making informed decisions, offering insights into overall market trends.
Volatility and Risk Management: Navigating Uncertainties
Volatility is an inherent aspect of stock market performance. Prices can experience significant fluctuations, creating both opportunities and risks. Successful investors employ risk management strategies to mitigate potential downsides. Diversification, setting stop-loss orders, and staying informed about market news are essential components of effective risk management.
Economic Indicators and Their Impact: Connecting the Dots
The interplay between stock market performance and economic indicators is profound. Factors like GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation influence investor confidence and, consequently, stock prices. A comprehensive understanding of these economic indicators enhances the ability to anticipate market movements.
Company Fundamentals: Digging Deeper for Long-Term Gains
Examining the fundamentals of individual companies is a cornerstone of successful stock market investing. Factors such as earnings per share, revenue growth, and debt levels offer insights into a company’s financial health. Long-term investors often focus on strong fundamentals, aiming for sustained growth over time.
Market Timing vs. Time in the Market: A Strategic Dilemma
A perennial dilemma for investors is whether to focus on market timing or time in the market. Market timing involves trying to predict the best moments to buy or sell stocks, while time in the market emphasizes the benefits of long-term investing. Striking a balance that aligns with individual risk tolerance and financial goals is paramount.
Behavioral Finance: Understanding Investor Psychology
Stock market performance is not solely dictated by economic factors; it is also deeply intertwined with investor psychology. Behavioral finance explores how emotions and cognitive biases influence financial decisions. Awareness of these psychological factors empowers investors to make rational choices and avoid succumbing to market hysteria.
Technological Advancements and Algorithmic Trading: Shaping the Future
The advent of technology has revolutionized stock market dynamics. Algorithmic trading,
Navigating Global Expansion: Effective Business Strategies

Navigating Global Expansion: Effective Business Strategies
Expanding a business globally presents both opportunities and challenges. In this article, we explore key strategies for successful global business expansion, guiding organizations through the intricate process of entering new markets and thriving on a global scale.
Market Research: The Foundation of Global Expansion
Before embarking on global expansion, thorough market research is essential. Understanding the target market’s demographics, consumer behavior, and cultural nuances provides valuable insights. This foundational knowledge informs decision-making and helps tailor strategies to meet the specific demands of diverse markets.
Localization: Adapting to Cultural Differences
Cultural sensitivity is critical in global business expansion. Localization involves adapting products, services, and marketing strategies to suit the cultural preferences and norms of each target market. Respectful integration ensures that the business resonates with local audiences, fostering acceptance and trust.
Strategic Partnerships: Leveraging Local Expertise
Establishing strategic partnerships with local businesses or experts is a powerful strategy for global expansion. These partnerships provide invaluable insights into the local business landscape, regulatory environment, and consumer behavior. Leveraging local expertise enhances the organization’s ability to navigate unfamiliar territories successfully.
Legal Compliance: Navigating Regulatory Challenges
Global expansion brings with it a myriad of regulatory challenges. From compliance with local laws to understanding international trade regulations, businesses must navigate complex legal landscapes. Investing in legal counsel and staying abreast of regulatory changes is crucial to ensuring a smooth and lawful expansion process.
Risk Management: Anticipating and Mitigating Challenges
Expanding globally involves inherent risks. Effective risk management strategies anticipate potential challenges and outline mitigation plans. Businesses must identify geopolitical, economic, and operational risks to develop contingency plans that safeguard the continuity and success of global operations.
Technology Integration: Streamlining Global Operations
Technology plays a pivotal role in global business expansion. Integrating advanced technologies for communication, project management, and data analytics streamlines global operations. This ensures efficient collaboration among teams across different time zones and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
Talent Acquisition and Development: Building a Global Team
A successful global expansion requires a skilled and diverse workforce. Businesses should focus on talent acquisition strategies that attract individuals with a deep understanding of local markets. Additionally, investing in ongoing training and development programs ensures that the global team remains adaptive and competitive.
Financial Management: Adapting to Currency and Market Fluctuations
Fluctuations in currency and market conditions are inherent to global expansion. Implementing robust financial management strategies, including hedging against currency risks and regularly assessing market conditions, safeguards the financial stability of the business during global operations.
Customer-Centric Approach: Building Global Relationships
Maintaining a customer-centric approach is paramount in global expansion. Building strong relationships with customers across diverse cultures requires attentiveness to customer needs, personalized service, and responsiveness to feedback. A positive customer experience fosters brand loyalty and advocacy on a global scale.
Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation: Staying Agile
Global business environments are dynamic, requiring organizations to remain agile. Continuous evaluation of strategies, market conditions, and performance metrics is essential. This ongoing assessment enables businesses to adapt quickly to changes, capitalize on emerging
Governance Excellence: Corporate Best Practices Unveiled
Governance Excellence: Corporate Best Practices Unveiled
Corporate governance is the bedrock of effective management and ethical business conduct. This article delves into the best practices that companies can adopt to ensure robust corporate governance, fostering transparency, accountability, and sustained success.
Defining Corporate Governance
At its core, corporate governance encompasses the mechanisms, processes, and relations by which companies are directed and controlled. It involves balancing the interests of a company’s many stakeholders, such as shareholders, management, customers, financiers, government, and the community. Defining the principles that guide these relationships is fundamental to good governance.
Transparency and Open Communication
One of the foundational pillars of corporate governance is transparency. Openly sharing information about a company’s strategies, financial performance, risks, and decision-making processes builds trust with stakeholders. Transparent communication fosters an environment where shareholders and other stakeholders feel informed and engaged in the company’s direction.
Board of Directors: Composition and Independence
A key aspect of effective corporate governance lies in the composition and independence of the board of directors. Having a diverse board with a mix of skills, experience, and backgrounds contributes to well-informed decision-making. Independence ensures that the board can act objectively in the best interests of the company without undue influence.
Ethical Leadership and Code of Conduct
Ethical leadership sets the tone for corporate culture. Establishing and promoting a strong code of conduct helps guide employees, management, and directors in making ethical decisions. Companies that prioritize ethical behavior not only foster a positive work environment but also enhance their reputation and credibility in the eyes of stakeholders.
Risk Management and Compliance
A robust corporate governance framework includes effective risk management and compliance measures. Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks are essential components of governance. Compliance with laws and regulations ensures that the company operates within legal boundaries, reducing the likelihood of legal issues that could impact its reputation and financial stability.
Shareholder Rights and Engagement
Protecting shareholder rights is fundamental to good governance. Establishing mechanisms for shareholder engagement, such as regular meetings and voting opportunities, allows shareholders to voice their opinions and influence important decisions. Engaging with shareholders creates a sense of ownership and aligns their interests with the long-term success of the company.
Vexhibits: Exemplifying Corporate Governance
Explore how Vexhibits exemplifies corporate governance best practices. By prioritizing transparency, ethical leadership, and stakeholder engagement, Vexhibits showcases a commitment to effective governance, contributing to its success in the exhibition and events industry.
Performance Evaluation and Accountability
Regular performance evaluations of the board, executives, and committees are crucial for accountability. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting objective assessments ensures that individuals and teams are held accountable for their responsibilities. Accountability is a cornerstone of effective corporate governance.
Long-Term Strategic Planning
Corporate governance extends beyond day-to-day operations; it involves planning for the long-term sustainability of the company. Aligning strategic goals with the interests of stakeholders ensures that the company is well-positioned for future success. Long-term planning involves anticipating challenges, adapting to market trends, and staying agile in a dynamic business landscape.
Adaptability and Continuous
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges: Innovative Solutions
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges: Innovative Solutions
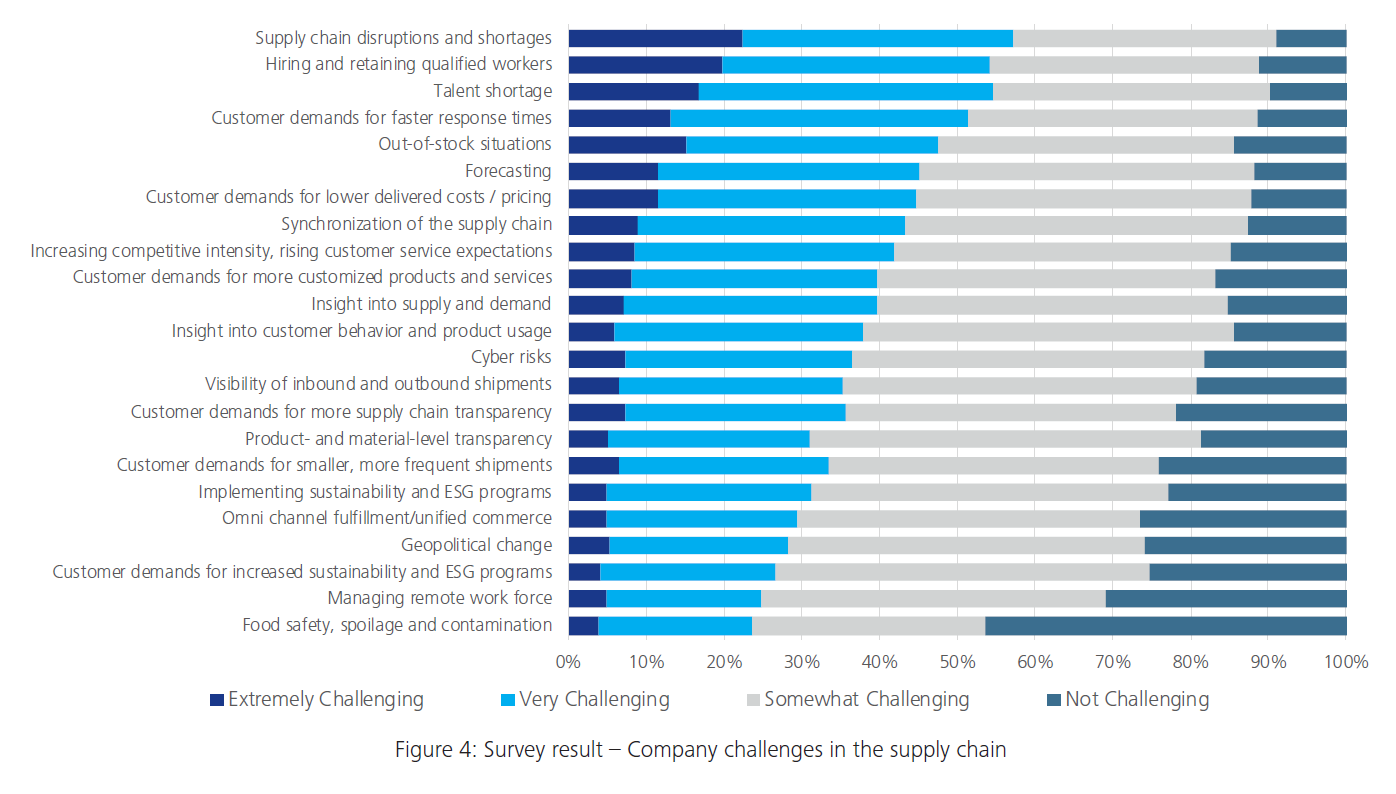
The global supply chain is facing unprecedented disruptions, requiring businesses to reassess and adapt to ensure continuity and resilience. In this article, we explore the challenges posed by supply chain disruptions and innovative solutions to navigate through these turbulent times.
Understanding Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions can arise from various factors, including natural disasters, geopolitical events, and unforeseen economic challenges. The interconnected nature of global supply chains means that a disruption in one part of the world can have cascading effects across industries. The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly highlighted the vulnerability of supply chains to unexpected shocks.
Impact on Businesses: From Delays to Shortages
The repercussions of supply chain disruptions are felt by businesses of all sizes. From delays in production and distribution to shortages of critical components, the disruptions can lead to increased costs, revenue loss, and potential damage to a company’s reputation. Businesses must proactively address these challenges to stay afloat in the face of uncertainty.
Technological Integration for Enhanced Visibility
One of the innovative solutions to supply chain disruptions is the integration of advanced technologies for enhanced visibility. Businesses are leveraging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, blockchain, and real-time analytics to gain insights into their supply chains. This increased visibility allows for better risk assessment, early detection of potential disruptions, and informed decision-making.
Diversification and Redundancy Strategies
To mitigate the impact of disruptions, businesses are adopting diversification and redundancy strategies. This involves diversifying supplier networks, sourcing materials from multiple regions, and maintaining safety stock levels. By spreading risk across different suppliers and geographic locations, businesses can enhance their resilience to unforeseen disruptions.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaboration
Collaboration is becoming a key component of supply chain resilience. Establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers, logistics providers, and other stakeholders creates a network of support. Collaborative efforts enable the sharing of information, resources, and expertise, fostering a more agile and responsive supply chain ecosystem.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making is paramount in navigating supply chain disruptions. Businesses are leveraging big data analytics to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential risks. The use of predictive analytics enables businesses to proactively respond to changes in market conditions and supply chain dynamics.
Supply Chain Transparency and Ethical Sourcing
Transparency in the supply chain is gaining prominence as companies and consumers alike prioritize ethical sourcing. Businesses are investing in technologies that provide end-to-end visibility, allowing consumers to trace the origins of products. Ethical sourcing practices not only build trust with consumers but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
Reskilling the Workforce for Agility
The human element plays a crucial role in navigating supply chain disruptions. Businesses are reskilling their workforce to enhance agility and adaptability. Cross-training employees, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and investing in skills relevant to supply chain management contribute to a more versatile and resilient workforce.
Investment in Robust Risk Management Strategies
Supply chain disruptions necessitate a reevaluation and enhancement of risk management strategies. Businesses

