GlobalEconomy
Navigating Consumer Confidence: Index Insights for Economic Trends
Navigating Consumer Confidence: Index Insights for Economic Trends
Understanding the Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) is vital for gauging economic sentiment and predicting market trends. In this exploration, we delve into the significance of the CCI and its impact on economic landscapes.
Defining the Consumer Confidence Index
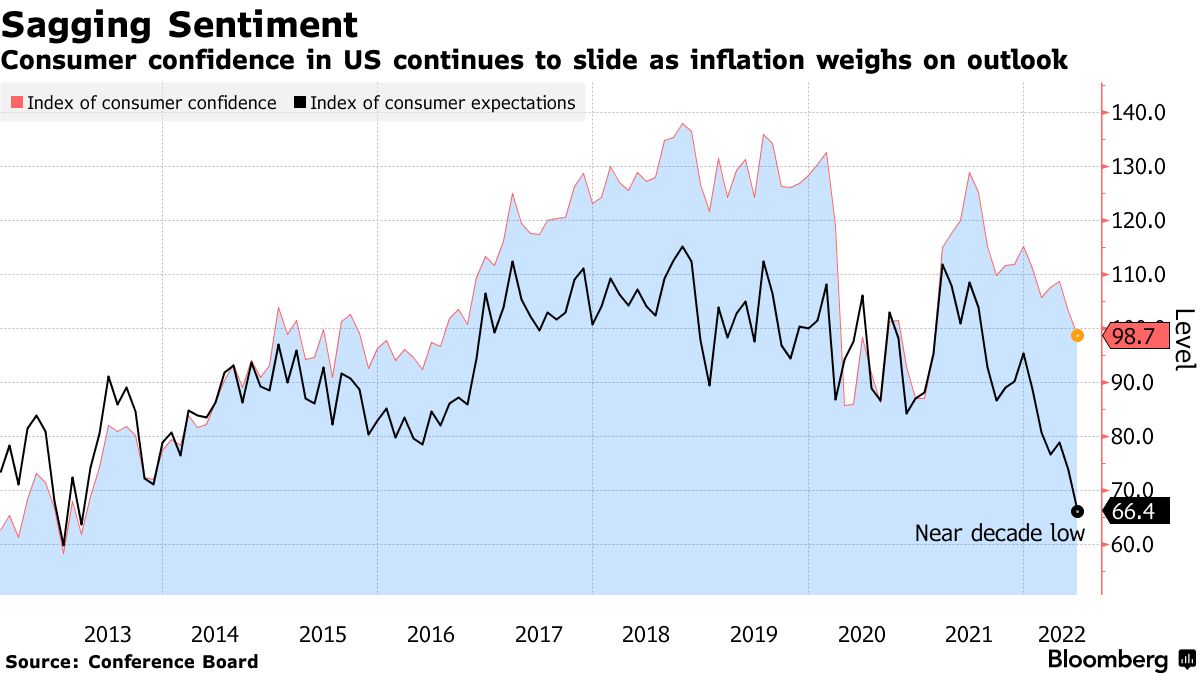
The Consumer Confidence Index is a key economic indicator that measures the confidence levels of consumers regarding current and future economic conditions. It is compiled through surveys that assess consumers’ perceptions of the economy, employment prospects, and their personal financial situations. A high CCI reflects positive consumer sentiment, while a low index may indicate economic concerns.
CCI Components and Their Influence
To explore the latest insights into the Consumer Confidence Index, visit vexhibits.com. The CCI comprises two main components: the Present Situation Index, reflecting current economic conditions, and the Expectations Index, gauging consumers’ outlook for the future. Understanding the interplay between these components provides a nuanced view of consumer sentiment and its potential impact on economic behavior.
Consumer Confidence and Spending Patterns
Consumer confidence is closely linked to consumer spending patterns. High confidence levels often translate into increased spending, as consumers feel optimistic about the economy and their financial stability. On the contrary, low confidence may lead to cautious spending, impacting retail, manufacturing, and overall economic growth. Monitoring the CCI assists businesses and policymakers in anticipating shifts in consumer behavior.
Employment and Income Dynamics
Consumer confidence is heavily influenced by employment and income dynamics. Favorable job markets and rising incomes contribute to positive sentiment, boosting the CCI. Conversely, job losses, wage stagnation, or economic uncertainties can lead to a decline in confidence. Recognizing the relationship between employment trends and the CCI provides valuable insights into broader economic health.
CCI as a Leading Economic Indicator
The Consumer Confidence Index is often considered a leading economic indicator, providing early signals of economic trends. High confidence levels may precede periods of economic growth, while a sudden drop in the CCI could signal a potential economic downturn. Analysts, investors, and policymakers closely monitor the CCI to make informed decisions and respond proactively to emerging economic conditions.
Impact on Financial Markets
Changes in consumer confidence can have a significant impact on financial markets. Positive CCI readings may lead to increased investment in stocks, as investors anticipate strong economic performance. Conversely, a drop in consumer confidence may result in market volatility and adjustments to investment portfolios. Understanding these market dynamics is crucial for investors navigating the ever-changing financial landscape.
Government and Central Bank Response
Government and central bank policymakers closely track the Consumer Confidence Index to inform their decisions. High confidence levels may influence policy decisions aimed at sustaining economic growth, such as interest rate adjustments or stimulus measures. Conversely, a decline in confidence may prompt policymakers to implement measures to boost consumer sentiment and economic activity.
Global Comparisons and Economic Benchmarks
To explore innovative solutions at the intersection of Consumer Confidence Index trends, visit vexhibits.com. The CCI provides a basis for global comparisons, allowing analysts to assess
Balancing Act: Navigating US Fiscal Policy Challenges
Balancing Act: Navigating US Fiscal Policy Challenges
As the United States continues to navigate complex economic landscapes, its fiscal policy plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s financial trajectory. This article delves into the intricate web of challenges and considerations involved in managing US fiscal policy and the implications for economic stability and growth.
Foundation of Economic Management
US fiscal policy, often overseen by government agencies and policymakers, forms the foundation of economic management. It involves decisions related to taxation, government spending, and borrowing, collectively influencing the overall economic health of the nation. Striking the right balance in these areas is crucial for maintaining stability and fostering sustainable economic growth.
The Dual Role of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy serves a dual role in economic management. During periods of economic downturn, the government may implement expansionary fiscal policies, such as tax cuts and increased spending, to stimulate economic activity. Conversely, during times of overheating and inflationary pressures, contractionary fiscal policies may be employed to cool down the economy. This delicate dance requires precision to avoid unintended consequences.
Taxation Strategies and Economic Impact
One of the key components of US fiscal policy is taxation. Decisions related to tax rates, deductions, and credits have direct implications for businesses and individuals. Striking a balance between providing necessary government revenue and avoiding stifling economic activity is a constant challenge. Effective tax policies aim to encourage investment, job creation, and overall economic prosperity.
Government Spending Priorities
Determining government spending priorities is a critical aspect of fiscal policy. Allocation of funds to areas such as infrastructure, education, healthcare, and defense reflects national priorities. Striking a balance between addressing immediate needs and making long-term investments is essential. Efficient and targeted government spending can spur economic growth, create jobs, and enhance the overall well-being of the population.
Debt Management and Fiscal Responsibility
Managing the national debt is a perpetual challenge within the realm of fiscal policy. While borrowing can be a tool for financing essential initiatives, an unsustainable debt burden can lead to economic instability. Striking a balance between leveraging debt for strategic investments and ensuring fiscal responsibility is essential to avoid long-term economic consequences.
Global Economic Considerations
The interconnectedness of the global economy adds another layer of complexity to US fiscal policy. Economic decisions made in the United States have ripple effects worldwide. Coordinating fiscal policies with international economic conditions is crucial for maintaining stability and fostering collaborative solutions to global challenges.
Inflationary Pressures and Monetary Policy Coordination
Balancing fiscal policy with monetary policy is vital for economic stability. Inflationary pressures, influenced by fiscal decisions, require coordination with the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies. Effective collaboration ensures a harmonized approach to managing interest rates, money supply, and overall economic conditions.
Challenges in Times of Crisis
During times of crisis, such as a recession or a global pandemic, the challenges facing US fiscal policy become more pronounced. Rapid response mechanisms, such as stimulus packages and targeted interventions, must be deployed to mitigate economic downturns. Striking the right balance between
