MonetaryPolicy
Navigating USA’s Monetary Policy for Economic Stability
Navigating USA’s Monetary Policy for Economic Stability
Monetary policy in the United States is a dynamic and influential force, shaping the nation’s economic landscape. This article delves into the intricate world of USA’s monetary policy, exploring its components, objectives, and impact on fostering economic stability.
The Federal Reserve’s Mandate
At the heart of monetary policy in the USA is the Federal Reserve, commonly known as the Fed. Endowed with the responsibility of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates, the Fed plays a crucial role in steering the nation’s economic course. This mandate underscores the importance of a balanced and resilient economy.
Interest Rates and the Money Supply
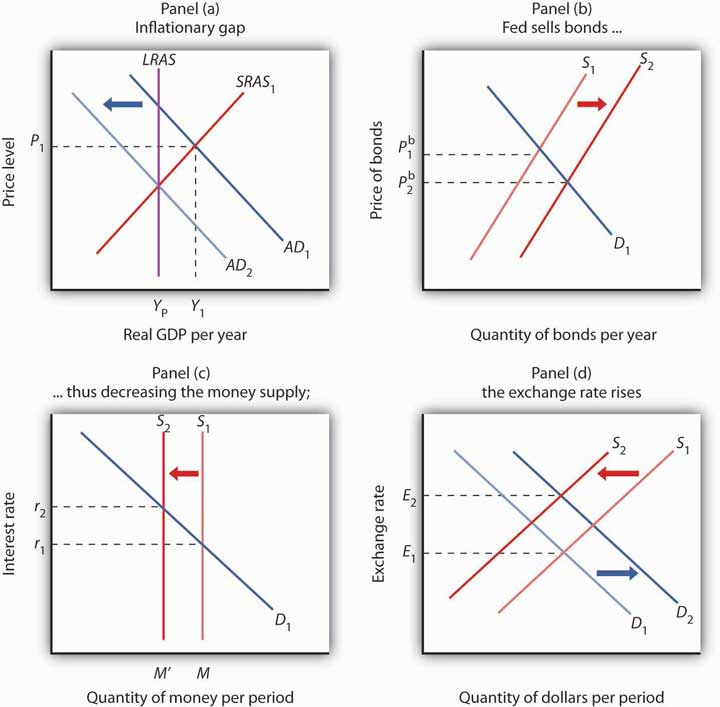
One of the primary tools in the Fed’s toolkit is the management of interest rates. By influencing short-term interest rates, the Fed aims to control the money supply and, consequently, economic activity. Lowering interest rates encourages borrowing and spending, stimulating economic growth, while raising rates can help cool down an overheated economy and control inflation.
Inflation Targeting
Maintaining price stability is a key objective of USA’s monetary policy. The Fed employs an inflation targeting approach, striving to keep inflation at a moderate and predictable level. This commitment to price stability contributes to a more predictable economic environment, fostering consumer and investor confidence.
Employment and Economic Output
The pursuit of maximum employment is another critical aspect of USA’s monetary policy. The Fed seeks to create conditions that support job growth and reduce unemployment to levels consistent with a healthy and thriving economy. By carefully managing interest rates and economic stimuli, the Fed aims to strike a balance that fosters sustainable employment.
Quantitative Easing and Unconventional Tools
In times of economic stress or crisis, the Fed may resort to unconventional tools like quantitative easing (QE). This involves the central bank purchasing financial assets to inject liquidity into the financial system. Such measures aim to lower long-term interest rates, stimulate borrowing, and support economic recovery during challenging periods.
Communication and Forward Guidance
Effective communication is a cornerstone of USA’s monetary policy. The Fed provides regular statements and reports, offering insights into its decisions and economic outlook. Forward guidance, indicating the likely future path of interest rates, is a communication tool used to guide market expectations and influence economic behavior.
Global Considerations and Exchange Rates
The interconnected nature of the global economy means that USA’s monetary policy has implications beyond its borders. Changes in interest rates and monetary policies can influence exchange rates, impacting international trade and financial markets. The Fed must consider global economic conditions in its decision-making process.
Challenges in Achieving Policy Goals
Despite the Fed’s best efforts, challenges arise in achieving all aspects of its mandate simultaneously. Balancing the objectives of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates requires careful calibration, and external factors such as geopolitical events and global economic shifts can complicate the task.
Adapting to Economic Uncertainty
The ever-changing nature of the economy demands adaptability in monetary policy. The Fed must be agile in responding
Balancing Act: Navigating US Fiscal Policy Challenges
Balancing Act: Navigating US Fiscal Policy Challenges
As the United States continues to navigate complex economic landscapes, its fiscal policy plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s financial trajectory. This article delves into the intricate web of challenges and considerations involved in managing US fiscal policy and the implications for economic stability and growth.
Foundation of Economic Management
US fiscal policy, often overseen by government agencies and policymakers, forms the foundation of economic management. It involves decisions related to taxation, government spending, and borrowing, collectively influencing the overall economic health of the nation. Striking the right balance in these areas is crucial for maintaining stability and fostering sustainable economic growth.
The Dual Role of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy serves a dual role in economic management. During periods of economic downturn, the government may implement expansionary fiscal policies, such as tax cuts and increased spending, to stimulate economic activity. Conversely, during times of overheating and inflationary pressures, contractionary fiscal policies may be employed to cool down the economy. This delicate dance requires precision to avoid unintended consequences.
Taxation Strategies and Economic Impact
One of the key components of US fiscal policy is taxation. Decisions related to tax rates, deductions, and credits have direct implications for businesses and individuals. Striking a balance between providing necessary government revenue and avoiding stifling economic activity is a constant challenge. Effective tax policies aim to encourage investment, job creation, and overall economic prosperity.
Government Spending Priorities
Determining government spending priorities is a critical aspect of fiscal policy. Allocation of funds to areas such as infrastructure, education, healthcare, and defense reflects national priorities. Striking a balance between addressing immediate needs and making long-term investments is essential. Efficient and targeted government spending can spur economic growth, create jobs, and enhance the overall well-being of the population.
Debt Management and Fiscal Responsibility
Managing the national debt is a perpetual challenge within the realm of fiscal policy. While borrowing can be a tool for financing essential initiatives, an unsustainable debt burden can lead to economic instability. Striking a balance between leveraging debt for strategic investments and ensuring fiscal responsibility is essential to avoid long-term economic consequences.
Global Economic Considerations
The interconnectedness of the global economy adds another layer of complexity to US fiscal policy. Economic decisions made in the United States have ripple effects worldwide. Coordinating fiscal policies with international economic conditions is crucial for maintaining stability and fostering collaborative solutions to global challenges.
Inflationary Pressures and Monetary Policy Coordination
Balancing fiscal policy with monetary policy is vital for economic stability. Inflationary pressures, influenced by fiscal decisions, require coordination with the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies. Effective collaboration ensures a harmonized approach to managing interest rates, money supply, and overall economic conditions.
Challenges in Times of Crisis
During times of crisis, such as a recession or a global pandemic, the challenges facing US fiscal policy become more pronounced. Rapid response mechanisms, such as stimulus packages and targeted interventions, must be deployed to mitigate economic downturns. Striking the right balance between
