Government Expenditure
Healthcare Policies: Unraveling Economic Impact
Healthcare Policies: Unraveling Economic Impact
As nations grapple with the complexities of healthcare policies, the economic repercussions are profound. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between healthcare policies and their wide-ranging impact on economic landscapes.
The Interplay Between Public Health and Economic Stability
Healthcare policies are intricately linked to public health outcomes, and a healthy population is fundamental to economic stability. Policies that prioritize preventive care, vaccination programs, and disease management contribute to a productive workforce and reduce the economic burden of widespread illness. Investing in public health infrastructure becomes an essential component of fostering long-term economic resilience.
Government Expenditure and Budgetary Considerations
The implementation of healthcare policies often requires substantial government expenditure. Funding public healthcare initiatives impacts national budgets, requiring policymakers to strike a delicate balance between meeting healthcare needs and maintaining fiscal responsibility. Economic sustainability hinges on efficient allocation and management of healthcare resources within the broader financial framework.
Impact on Businesses and Workforce Productivity
Healthcare policies exert a direct influence on businesses and workforce productivity. Accessible and affordable healthcare can enhance employee well-being, reduce absenteeism, and improve overall productivity. Conversely, policies that create barriers to healthcare access may result in a less healthy and less productive workforce, ultimately affecting the economic output of businesses and the nation.
Innovations in Healthcare and Economic Growth
Investments in healthcare policies that foster innovation have the potential to drive economic growth. Advances in medical research, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare technologies not only improve health outcomes but also create jobs, stimulate industries, and position nations as leaders in the global healthcare market. A robust healthcare innovation ecosystem contributes to economic competitiveness.
Healthcare Policies and Insurance Markets
The structure of healthcare policies significantly influences insurance markets. Policies that promote universal coverage or implement insurance mandates impact the dynamics of the insurance industry. Striking a balance between expanding coverage and maintaining market competition requires careful consideration to ensure both economic viability and widespread access to healthcare services.
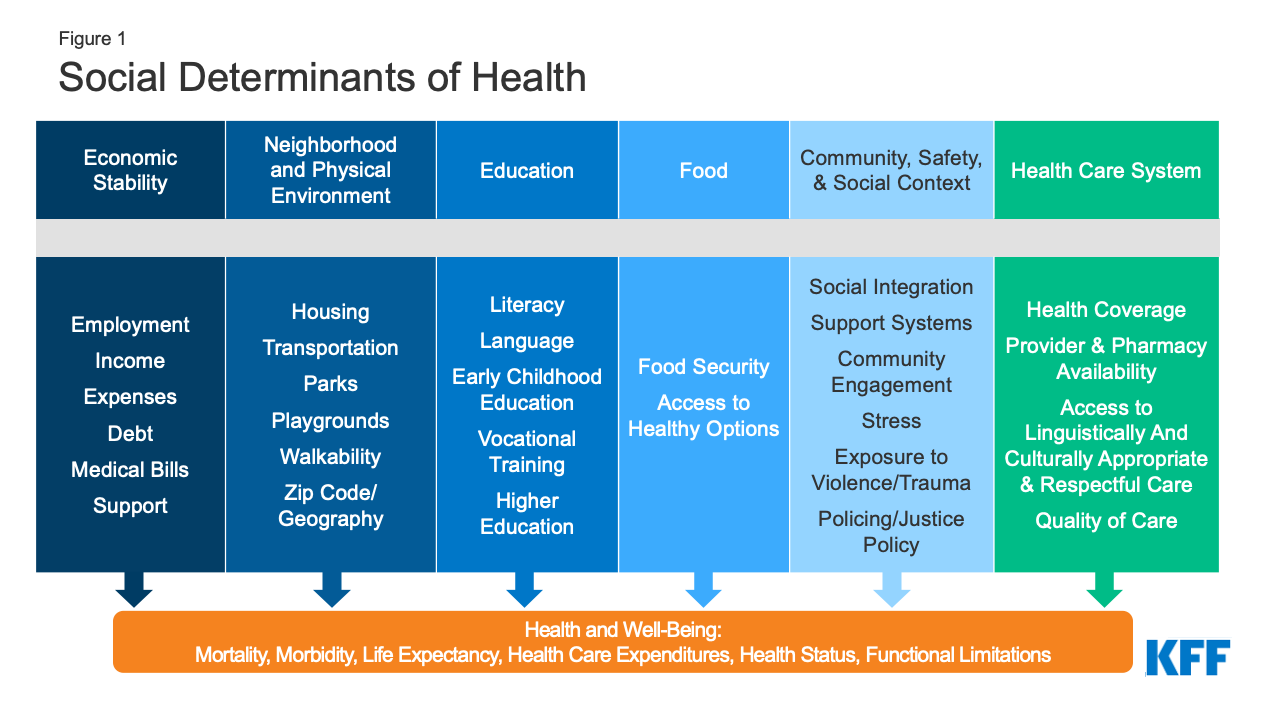
Social Determinants of Health and Economic Disparities
Healthcare policies play a crucial role in addressing social determinants of health, such as income, education, and housing. Policies that address these determinants not only improve health outcomes but also contribute to reducing economic disparities. By tackling root causes, healthcare policies become a tool for promoting a more equitable and economically inclusive society.
Global Healthcare Policies and Economic Competitiveness
On the global stage, healthcare policies influence economic competitiveness. Nations with robust healthcare systems are often more attractive to businesses and skilled professionals. A healthy population contributes to a more productive and stable workforce, enhancing a nation’s overall economic competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Economic Challenges of Healthcare Policy Implementation
While healthcare policies aim to improve overall well-being, their implementation can pose economic challenges. The cost of implementing new policies, potential resistance from various stakeholders, and the need for ongoing adjustments can strain financial resources. Effective policy implementation requires careful consideration of economic implications and strategies to mitigate potential challenges.
Pandemics and the Urgency of Adaptive Policies
The COVID-19 pandemic has
Economic Impact of Social Regulation Changes
Introduction:
In recent times, societies have witnessed a profound transformation in social regulations, prompting a ripple effect on the economic landscape. These changes, born out of evolving societal norms and governmental policies, carry substantial economic consequences that merit exploration.
Shifts in Employment Dynamics:
One of the primary facets of the economic impact revolves around alterations in employment dynamics. As social regulations adapt, businesses must reassess their workforce structures. These shifts can influence job creation, job security, and overall labor market stability.
Entrepreneurial Landscape:
Changes in social regulations often mold the entrepreneurial landscape. New regulations may either foster innovation or pose challenges to emerging businesses. Understanding the interplay between social regulations and entrepreneurship is crucial for predicting economic trends.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends:
Social regulations shape consumer behavior by influencing their preferences and values. This, in turn, has a direct impact on market trends. Businesses must stay attuned to these shifts to align their strategies with evolving consumer demands.
Government Expenditure and Social Welfare Programs:
As social regulations evolve, so does government expenditure. Changes in policies related to social welfare programs can significantly affect the allocation of public funds. Understanding these changes is essential for evaluating the broader economic impact on society.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Compliance:
The nexus between technological advancements and regulatory compliance is pivotal. Innovations may be driven by the need to adhere to new social regulations, presenting opportunities for growth in certain sectors. Conversely, industries lagging behind in compliance may face economic challenges.
Global Economic Integration:
Social regulations are not confined to national boundaries; they contribute to the broader trend of global economic integration. Understanding the global implications of these changes is imperative for businesses engaged in international trade.
Investor Confidence and Market Volatility:
Fluctuations in social regulations can impact investor confidence and market volatility. Investors keenly observe regulatory changes, as they can signal economic shifts. A transparent regulatory environment often enhances investor confidence and contributes to a more stable market.
Environmental Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility:
Modern social regulations increasingly emphasize environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility. Businesses aligning with these values may experience economic benefits through enhanced brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Linking Economic Impact to Social Responsibility:
Recognizing the symbiotic relationship between economic impact and social responsibility is crucial. Businesses that embrace social responsibility initiatives tend to fare better in the long run. For a deeper understanding of this interplay, explore the Economic impact of changes in social regulations at vexhibits.com.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic impact of changes in social regulations is multifaceted, influencing employment, entrepreneurship, consumer behavior, government expenditure, technology, global integration, investor confidence, and corporate responsibility. Navigating these dynamics requires a proactive approach from businesses and policymakers alike. As societal norms continue to evolve, understanding and adapting to the economic consequences of social regulatory changes will be integral to sustained growth and development.

