Investor confidence
Economic Impact of Evolving Healthcare Laws
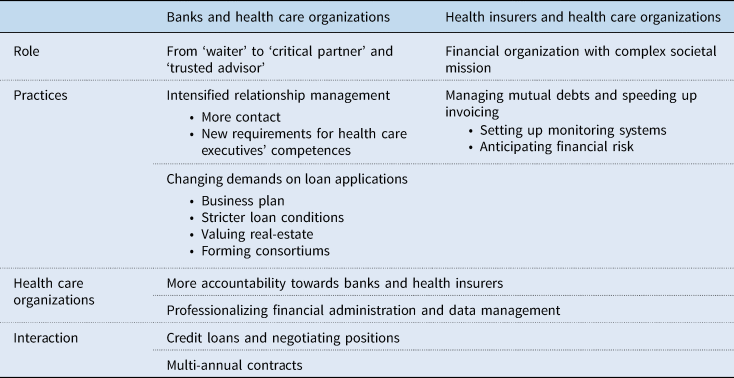
Introduction:
The intersection of healthcare and economics is a critical nexus that significantly influences the well-being of societies. This article delves into the intricate web of economic consequences arising from changes in healthcare laws, exploring how policy shifts can ripple through financial systems.
Financial Impact on Healthcare Institutions:
Changes in healthcare laws inevitably lead to a financial impact on healthcare institutions. Hospitals, clinics, and other providers must navigate evolving regulations, often requiring adjustments to operational structures and financial strategies to maintain stability.
Insurance Dynamics and Affordability:
One of the primary economic consequences involves the dynamics of health insurance. Alterations in healthcare laws can affect the affordability and accessibility of insurance plans. This, in turn, influences consumer spending patterns, impacting both individuals and the broader economy.
Innovation and Investment in Healthcare:
Healthcare laws play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape for innovation and investment in the medical field. Policy changes can either spur or hinder advancements, affecting not only the healthcare sector but also industries connected to medical research and technology.
Employer-Sponsored Healthcare and Labor Market Dynamics:
The economic ramifications extend to the employer-sponsored healthcare model. Changes in healthcare laws can influence labor market dynamics as businesses adjust to new compliance requirements, potentially impacting employment patterns and overall workforce management.
Public Health Initiatives and Government Expenditure:
Shifts in healthcare laws often coincide with adjustments in public health initiatives. Governments may need to reallocate resources, affecting public expenditure. Understanding the balance between public health priorities and economic considerations is crucial for sustainable policy development.
Pharmaceutical Industry and Drug Pricing:
The pharmaceutical industry is intricately linked to healthcare laws, particularly concerning drug pricing and market regulations. Changes in legislation can impact pharmaceutical companies’ profitability and influence the cost of medications for consumers, with wide-ranging economic implications.
Healthcare Access Disparities and Socioeconomic Factors:
Economic consequences also manifest in healthcare access disparities. Changes in healthcare laws can exacerbate or alleviate existing socioeconomic disparities in healthcare access, contributing to broader societal economic inequalities.
Technological Integration and Healthcare Costs:
Advancements in healthcare technology are often driven or hindered by legislative changes. The integration of new technologies can influence healthcare costs, posing challenges or opportunities for cost containment and efficiency within the healthcare system.
Investor Confidence in Healthcare Markets:
Investors closely monitor healthcare laws due to the substantial impact on the financial performance of healthcare-related companies. Changes in regulations can sway investor confidence, affecting market valuations and investment decisions within the healthcare sector.
Linking Economic Consequences to Informed Decision-Making:
For a comprehensive understanding of the economic consequences of changes in healthcare laws and strategies for informed decision-making, explore vexhibits.com. Delve into the nuances of healthcare policy impact on financial systems and discover ways to navigate these changes for economic resilience.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic consequences of changes in healthcare laws are far-reaching, influencing healthcare institutions, insurance dynamics, innovation, labor markets, public health initiatives, pharmaceuticals, healthcare access, technology integration, and investor confidence. Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced approach, considering both the healthcare and economic aspects
Economic Resilience Amid Shifting Immigration Laws

Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of global affairs, changes in immigration laws can have a profound impact on the economic resilience of nations. This article explores the intricate relationship between economic stability and the evolving policies surrounding immigration.
Adaptation in Workforce Dynamics:
One key aspect of economic resilience lies in the adaptation of workforce dynamics. Changes in immigration laws often lead to shifts in labor availability. Businesses must navigate these changes strategically to ensure a resilient and capable workforce.
Innovation and Skill Diversification:
Immigration has historically been a source of innovation and skill diversification. Restrictive immigration laws can limit the influx of diverse talents, potentially stifling innovation. Economic resilience necessitates finding alternative avenues to foster creativity and skill diversity.
Impact on Industries and Economic Sectors:
Different industries are affected in varying degrees by changes in immigration laws. Some sectors rely heavily on immigrant labor. Understanding the sector-specific impact is crucial for devising resilient economic strategies that account for potential labor shortages or skill gaps.
Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth:
Immigrants often play a vital role in entrepreneurship and economic growth. Restrictive immigration policies can hamper the influx of entrepreneurial minds, impacting innovation and job creation. Building economic resilience requires fostering an environment that encourages immigrant entrepreneurs.
Global Competitiveness and Talent Retention:
Nations with flexible and welcoming immigration policies often attract top global talent. Changes in immigration laws can influence a country’s global competitiveness. To maintain economic resilience, countries must balance the need for talent retention with evolving immigration regulations.
Supply Chain Resilience and Immigration Policies:
Supply chains are intricately connected to the labor force, and changes in immigration laws can disrupt these chains. Businesses need to assess and enhance supply chain resilience to mitigate potential economic shocks resulting from immigration policy changes.
Investor Confidence and Economic Stability:
Investors closely monitor immigration policies as they impact workforce stability and overall economic conditions. Maintaining investor confidence requires transparent policies that provide a sense of stability amid changing immigration laws.
Social and Cultural Contributions:
Beyond the economic aspects, immigrants often contribute significantly to the social and cultural fabric of a nation. Recognizing these contributions is essential for fostering a resilient and cohesive society that can adapt to changing immigration laws without compromising unity.
Linking Economic Resilience to Immigration Policy:
For a deeper exploration of the strategies to build economic resilience in the face of changing immigration laws, visit vexhibits.com. Understand the crucial interplay between immigration policies and economic stability, and discover proactive measures to fortify your nation’s economic resilience.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, economic resilience in the face of changing immigration laws requires a holistic approach. From workforce adaptation and innovation to sector-specific considerations and cultural contributions, nations must navigate these changes with foresight. By understanding the symbiotic relationship between immigration policies and economic stability, countries can forge a path that ensures resilience and sustainable growth in the evolving global landscape.
Economic Impact of Social Regulation Changes
Introduction:
In recent times, societies have witnessed a profound transformation in social regulations, prompting a ripple effect on the economic landscape. These changes, born out of evolving societal norms and governmental policies, carry substantial economic consequences that merit exploration.
Shifts in Employment Dynamics:
One of the primary facets of the economic impact revolves around alterations in employment dynamics. As social regulations adapt, businesses must reassess their workforce structures. These shifts can influence job creation, job security, and overall labor market stability.
Entrepreneurial Landscape:
Changes in social regulations often mold the entrepreneurial landscape. New regulations may either foster innovation or pose challenges to emerging businesses. Understanding the interplay between social regulations and entrepreneurship is crucial for predicting economic trends.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends:
Social regulations shape consumer behavior by influencing their preferences and values. This, in turn, has a direct impact on market trends. Businesses must stay attuned to these shifts to align their strategies with evolving consumer demands.
Government Expenditure and Social Welfare Programs:
As social regulations evolve, so does government expenditure. Changes in policies related to social welfare programs can significantly affect the allocation of public funds. Understanding these changes is essential for evaluating the broader economic impact on society.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Compliance:
The nexus between technological advancements and regulatory compliance is pivotal. Innovations may be driven by the need to adhere to new social regulations, presenting opportunities for growth in certain sectors. Conversely, industries lagging behind in compliance may face economic challenges.
Global Economic Integration:
Social regulations are not confined to national boundaries; they contribute to the broader trend of global economic integration. Understanding the global implications of these changes is imperative for businesses engaged in international trade.
Investor Confidence and Market Volatility:
Fluctuations in social regulations can impact investor confidence and market volatility. Investors keenly observe regulatory changes, as they can signal economic shifts. A transparent regulatory environment often enhances investor confidence and contributes to a more stable market.
Environmental Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility:
Modern social regulations increasingly emphasize environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility. Businesses aligning with these values may experience economic benefits through enhanced brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Linking Economic Impact to Social Responsibility:
Recognizing the symbiotic relationship between economic impact and social responsibility is crucial. Businesses that embrace social responsibility initiatives tend to fare better in the long run. For a deeper understanding of this interplay, explore the Economic impact of changes in social regulations at vexhibits.com.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic impact of changes in social regulations is multifaceted, influencing employment, entrepreneurship, consumer behavior, government expenditure, technology, global integration, investor confidence, and corporate responsibility. Navigating these dynamics requires a proactive approach from businesses and policymakers alike. As societal norms continue to evolve, understanding and adapting to the economic consequences of social regulatory changes will be integral to sustained growth and development.

