Economic impact
Housing Horizon: Unveiling Real Estate Market Trends

Housing Horizon: Unveiling Real Estate Market Trends
The real estate market is a dynamic landscape influenced by various factors, from economic shifts to societal changes. This article delves into the current trends shaping the real estate market, offering insights into what homebuyers, sellers, and investors can expect in the ever-evolving housing horizon.
Economic Impact on Housing
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping real estate trends. Economic downturns or upswings directly influence housing demand and affordability. As economies recover from global challenges, such as the recent pandemic, real estate markets respond with shifts in pricing, mortgage rates, and overall market activity.
Remote Work and Housing Preferences
The rise of remote work has brought about a paradigm shift in housing preferences. Homebuyers are increasingly prioritizing spaces that accommodate remote work needs. This has led to a surge in demand for homes with dedicated offices, outdoor spaces, and enhanced connectivity, reshaping the criteria for an ideal home.
Urban vs. Suburban Dynamics
The dynamics between urban and suburban living have experienced notable changes. While urban areas historically held appeal for their proximity to amenities and workplaces, the pandemic has driven a surge in suburban demand. Homebuyers seek larger properties, green spaces, and a quieter lifestyle, prompting a reevaluation of urban living priorities.
Sustainability and Green Features
Sustainability has become a focal point in real estate trends. Homebuyers increasingly prioritize eco-friendly features, energy-efficient appliances, and environmentally conscious designs. The integration of sustainable practices not only aligns with environmental concerns but also enhances property values and attracts a growing segment of environmentally conscious buyers.
Technology Integration in Real Estate
The integration of technology is transforming the real estate industry. Virtual tours, augmented reality, and online platforms are becoming standard tools for property viewing and transactions. Technology streamlines processes, enhances property marketing, and offers a more accessible and efficient experience for both buyers and sellers.
Affordability Challenges and Solutions
Affordability remains a persistent challenge in many real estate markets. Skyrocketing home prices and limited inventory pose barriers for aspiring homebuyers. Addressing affordability challenges requires innovative solutions, such as government initiatives, community land trusts, and collaborative efforts between stakeholders to create more inclusive housing opportunities.
Market Trends in Commercial Real Estate
Commercial real estate is also experiencing shifts in response to changing business landscapes. The rise of remote work has influenced office space demand, with companies reevaluating their space requirements. Retail spaces are adapting to e-commerce trends, and industrial properties are in high demand due to the growth of online shopping and distribution needs.
Vexhibits: Navigating Real Estate Trends
Explore how Vexhibits navigates and adapts to real estate trends. By staying attuned to market dynamics, Vexhibits showcases a commitment to providing spaces that align with evolving housing preferences and emerging trends.
Financial Considerations and Mortgage Trends
Financial considerations, including mortgage trends, significantly impact the real estate market. Mortgage rates, lending policies, and government incentives influence homebuying decisions. Understanding these financial dynamics is crucial for both buyers and sellers, shaping their strategies in response to prevailing market
Healthcare Policies: Unraveling Economic Impact
Healthcare Policies: Unraveling Economic Impact
As nations grapple with the complexities of healthcare policies, the economic repercussions are profound. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between healthcare policies and their wide-ranging impact on economic landscapes.
The Interplay Between Public Health and Economic Stability
Healthcare policies are intricately linked to public health outcomes, and a healthy population is fundamental to economic stability. Policies that prioritize preventive care, vaccination programs, and disease management contribute to a productive workforce and reduce the economic burden of widespread illness. Investing in public health infrastructure becomes an essential component of fostering long-term economic resilience.
Government Expenditure and Budgetary Considerations
The implementation of healthcare policies often requires substantial government expenditure. Funding public healthcare initiatives impacts national budgets, requiring policymakers to strike a delicate balance between meeting healthcare needs and maintaining fiscal responsibility. Economic sustainability hinges on efficient allocation and management of healthcare resources within the broader financial framework.
Impact on Businesses and Workforce Productivity
Healthcare policies exert a direct influence on businesses and workforce productivity. Accessible and affordable healthcare can enhance employee well-being, reduce absenteeism, and improve overall productivity. Conversely, policies that create barriers to healthcare access may result in a less healthy and less productive workforce, ultimately affecting the economic output of businesses and the nation.
Innovations in Healthcare and Economic Growth
Investments in healthcare policies that foster innovation have the potential to drive economic growth. Advances in medical research, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare technologies not only improve health outcomes but also create jobs, stimulate industries, and position nations as leaders in the global healthcare market. A robust healthcare innovation ecosystem contributes to economic competitiveness.
Healthcare Policies and Insurance Markets
The structure of healthcare policies significantly influences insurance markets. Policies that promote universal coverage or implement insurance mandates impact the dynamics of the insurance industry. Striking a balance between expanding coverage and maintaining market competition requires careful consideration to ensure both economic viability and widespread access to healthcare services.
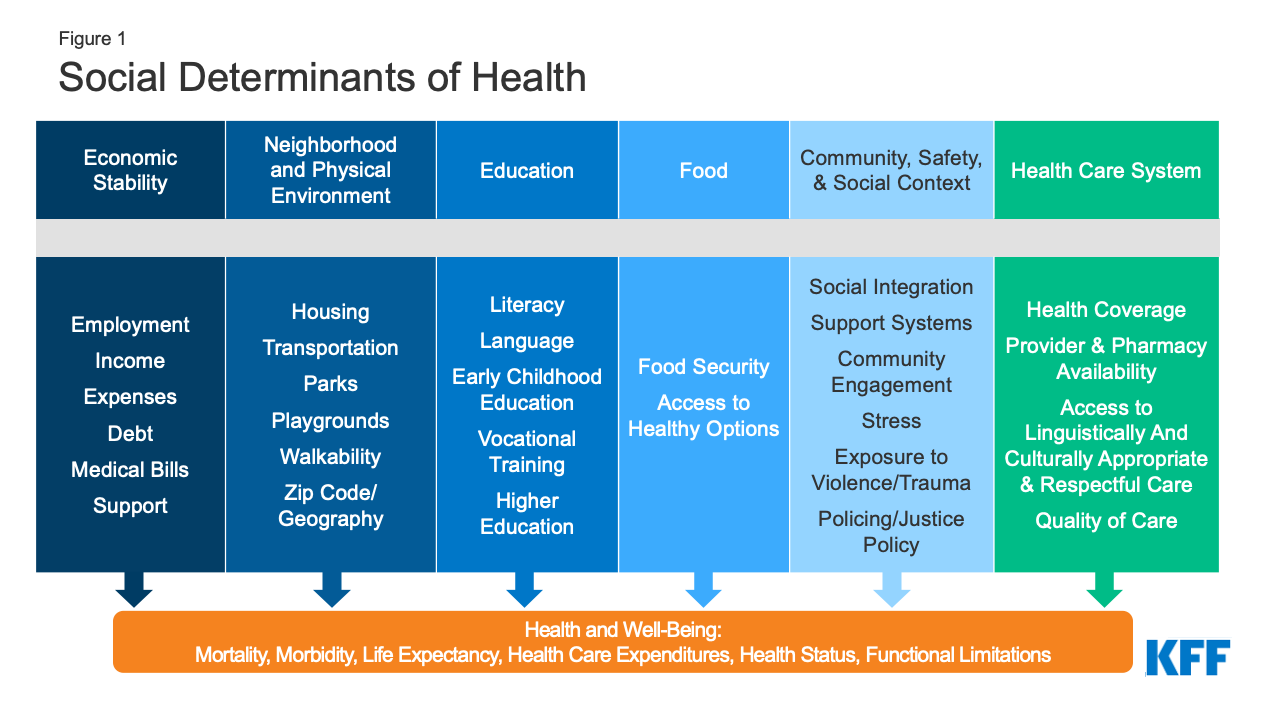
Social Determinants of Health and Economic Disparities
Healthcare policies play a crucial role in addressing social determinants of health, such as income, education, and housing. Policies that address these determinants not only improve health outcomes but also contribute to reducing economic disparities. By tackling root causes, healthcare policies become a tool for promoting a more equitable and economically inclusive society.
Global Healthcare Policies and Economic Competitiveness
On the global stage, healthcare policies influence economic competitiveness. Nations with robust healthcare systems are often more attractive to businesses and skilled professionals. A healthy population contributes to a more productive and stable workforce, enhancing a nation’s overall economic competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Economic Challenges of Healthcare Policy Implementation
While healthcare policies aim to improve overall well-being, their implementation can pose economic challenges. The cost of implementing new policies, potential resistance from various stakeholders, and the need for ongoing adjustments can strain financial resources. Effective policy implementation requires careful consideration of economic implications and strategies to mitigate potential challenges.
Pandemics and the Urgency of Adaptive Policies
The COVID-19 pandemic has
Economic Impact of Evolving Technology Laws
Introduction:
The rapidly evolving landscape of technology laws is reshaping the way societies interact with digital innovations. This article explores the profound economic impact resulting from changes in technology laws, delving into the intricate relationships between legislation, technology, and the economy.
Innovation Dynamics and Tech Sector Growth:
Changes in technology laws can significantly influence innovation dynamics and the growth of the tech sector. As regulations adapt to emerging technologies, they can either foster a conducive environment for innovation or pose challenges that stifle technological advancements. Understanding this interplay is vital for sustaining economic growth within the tech industry.
Investment Climate and Startup Ecosystem:
The investment climate and the vibrancy of the startup ecosystem are deeply intertwined with technology laws. Reforms that create a favorable regulatory environment often attract more investments, nurturing a thriving startup culture. Conversely, restrictive laws can impede investment flow and hinder the growth of emerging tech companies.
Intellectual Property Protection and Market Competition:
Technology laws play a crucial role in shaping intellectual property protection and market competition. Striking the right balance ensures fair competition while safeguarding innovations. This balance is vital for sustaining economic growth, encouraging continuous technological advancements.
Consumer Trust and Data Privacy Regulations:
In an era dominated by digital interactions, consumer trust is paramount. Changes in technology laws that focus on data privacy regulations contribute to building and maintaining consumer trust. This trust, in turn, supports a healthy digital economy by encouraging online transactions and fostering a secure digital marketplace.
Global Trade Dynamics in the Tech Industry:
Technology laws also impact global trade dynamics, especially in the tech industry. Understanding and navigating international regulations are crucial for fostering global collaborations, enabling the exchange of technological expertise, and contributing to economic growth on a global scale.
Cybersecurity Standards and Economic Resilience:
As technology evolves, so do the threats in cyberspace. Technology laws that establish robust cybersecurity standards contribute to economic resilience. Safeguarding digital infrastructure is essential for maintaining trust, protecting critical systems, and ensuring the continuity of economic activities.
Workforce Adaptation and Skill Development:
Changes in technology laws influence the workforce by creating new skill requirements. Legal frameworks that address the impact of automation and digitalization on jobs can contribute to a more adaptable and skilled workforce, aligning with the evolving needs of the technology-driven economy.
Corporate Governance and Ethical Tech Practices:
The economic impact extends beyond technological advancements to corporate governance and ethical tech practices. Technology laws that promote ethical conduct contribute to building corporate trust and credibility. This, in turn, enhances long-term economic sustainability for tech companies.
Consumer Adoption of New Technologies:
Consumer adoption of new technologies is often influenced by legal frameworks. Technology laws that facilitate a smooth integration of innovations into daily life contribute to the widespread adoption of new technologies. This, in turn, drives economic growth by creating new markets and business opportunities.
Linking Economic Impact to Strategic Planning:
For a comprehensive understanding of the economic impact of changes in technology laws and strategies for strategic planning, explore vexhibits.com. Delve
Navigating Economic Impact: Technological Disruptions’ Ripple Effect
Navigating Economic Impact: The Ripple Effect of Technological Disruptions
In the ever-evolving landscape of global economies, technological disruptions have become a defining force, reshaping industries and influencing economic trajectories. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of technological disruptions on economies and businesses worldwide.
The Acceleration of Change in Industries
Technological disruptions are catalysts for rapid change within industries. From artificial intelligence to blockchain and automation, innovations are transforming the way businesses operate. Industries that embrace these changes experience heightened efficiency and productivity, but they also face the challenge of adapting to an accelerated pace of evolution.
Job Landscape and Workforce Dynamics
As technology automates routine tasks, the job landscape undergoes significant shifts. While new opportunities emerge in tech-related fields, traditional roles may become obsolete. Workforce dynamics are influenced by the need for upskilling and reskilling to match the demands of the evolving job market. Balancing the opportunities and challenges in the job landscape becomes a crucial aspect of navigating technological disruptions.
Small Businesses and Global Competition
Technological disruptions can level the playing field for small businesses, enabling them to compete on a global scale. Through digital platforms and e-commerce, small enterprises can reach a broader audience. However, this global reach also intensifies competition, requiring businesses to stay agile and innovative to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Investments in Innovation and Research
Economic growth is intricately tied to investments in innovation and research. Nations and businesses that prioritize technological advancements foster an environment conducive to growth. Governments, realizing the potential economic impact of technological disruptions, often incentivize research and development activities to stay at the forefront of global competitiveness.
Supply Chain Resilience and Vulnerabilities
Technological disruptions expose vulnerabilities in traditional supply chain models. From cybersecurity threats to global crises affecting manufacturing and distribution, businesses must reassess and fortify their supply chains. Achieving resilience involves integrating advanced technologies, data analytics, and contingency planning to mitigate risks and ensure continuity in a disruptive landscape.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
The digital transformation brought about by technological disruptions significantly influences consumer behavior. E-commerce, personalized experiences, and instant gratification have become the norm. Understanding these shifts is essential for businesses to align their strategies with evolving market trends, ensuring they meet consumer expectations and stay relevant in a dynamic economic environment.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the economic impact of technological disruptions through policies and regulations. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and addressing potential negative consequences is a delicate task. Policies that encourage responsible technological adoption while safeguarding societal interests contribute to a sustainable economic framework.
Challenges and Opportunities in Emerging Technologies
While technological disruptions present challenges, they also offer unprecedented opportunities. Emerging technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and biotechnology hold the potential to revolutionize industries. Businesses that strategically navigate these technologies can gain a competitive edge and contribute to the economic growth spurred by innovation.
Global Connectivity and Collaborations
In a world driven by technological connectivity, collaborations become essential for economic growth. Nations and businesses
Economic Impact of Social Regulation Changes
Introduction:
In recent times, societies have witnessed a profound transformation in social regulations, prompting a ripple effect on the economic landscape. These changes, born out of evolving societal norms and governmental policies, carry substantial economic consequences that merit exploration.
Shifts in Employment Dynamics:
One of the primary facets of the economic impact revolves around alterations in employment dynamics. As social regulations adapt, businesses must reassess their workforce structures. These shifts can influence job creation, job security, and overall labor market stability.
Entrepreneurial Landscape:
Changes in social regulations often mold the entrepreneurial landscape. New regulations may either foster innovation or pose challenges to emerging businesses. Understanding the interplay between social regulations and entrepreneurship is crucial for predicting economic trends.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends:
Social regulations shape consumer behavior by influencing their preferences and values. This, in turn, has a direct impact on market trends. Businesses must stay attuned to these shifts to align their strategies with evolving consumer demands.
Government Expenditure and Social Welfare Programs:
As social regulations evolve, so does government expenditure. Changes in policies related to social welfare programs can significantly affect the allocation of public funds. Understanding these changes is essential for evaluating the broader economic impact on society.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Compliance:
The nexus between technological advancements and regulatory compliance is pivotal. Innovations may be driven by the need to adhere to new social regulations, presenting opportunities for growth in certain sectors. Conversely, industries lagging behind in compliance may face economic challenges.
Global Economic Integration:
Social regulations are not confined to national boundaries; they contribute to the broader trend of global economic integration. Understanding the global implications of these changes is imperative for businesses engaged in international trade.
Investor Confidence and Market Volatility:
Fluctuations in social regulations can impact investor confidence and market volatility. Investors keenly observe regulatory changes, as they can signal economic shifts. A transparent regulatory environment often enhances investor confidence and contributes to a more stable market.
Environmental Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility:
Modern social regulations increasingly emphasize environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility. Businesses aligning with these values may experience economic benefits through enhanced brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Linking Economic Impact to Social Responsibility:
Recognizing the symbiotic relationship between economic impact and social responsibility is crucial. Businesses that embrace social responsibility initiatives tend to fare better in the long run. For a deeper understanding of this interplay, explore the Economic impact of changes in social regulations at vexhibits.com.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the economic impact of changes in social regulations is multifaceted, influencing employment, entrepreneurship, consumer behavior, government expenditure, technology, global integration, investor confidence, and corporate responsibility. Navigating these dynamics requires a proactive approach from businesses and policymakers alike. As societal norms continue to evolve, understanding and adapting to the economic consequences of social regulatory changes will be integral to sustained growth and development.
Balancing Act: Navigating the US Trade Deficit Challenges
Understanding the Complexity: Navigating the US Trade Deficit Challenges
The US trade deficit has been a topic of discussion and debate, with its complexities requiring a nuanced understanding. This article delves into the intricacies of the trade deficit, exploring its implications and potential strategies for addressing challenges.
Defining the Trade Deficit: Unraveling the Numbers
The trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed its exports, leading to a negative balance in trade. For the United States, a consistent trade deficit raises questions about its economic relationships with other nations. Analyzing the trade balance involves exploring the factors contributing to this deficit.
Causes and Contributors: Unpacking the Dynamics
Several factors contribute to the US trade deficit. These include a high consumer demand for imported goods, a strong US dollar, and global supply chain intricacies. Distinguishing between structural and cyclical factors helps in formulating targeted strategies to address the root causes of the deficit.
Global Supply Chains: Interconnected Economies
In today’s interconnected world, global supply chains play a crucial role in shaping trade dynamics. The complexity of these supply chains contributes to the trade deficit as components of products may traverse multiple countries before reaching their final destination. Understanding this interconnectedness is vital for devising effective trade policies.
Impact on Industries: Winners and Losers
The US trade deficit has disparate impacts on various industries. While certain sectors benefit from access to cheaper imported goods, others face stiff competition and job losses. Examining the sector-specific implications helps in devising policies that balance the interests of different industries and promote overall economic growth.
Currency Exchange Rates: A Double-Edged Sword
Currency exchange rates play a pivotal role in trade balances. A strong US dollar can make exports more expensive and imports cheaper, contributing to the trade deficit. Addressing currency dynamics involves strategic interventions to maintain a competitive edge in international markets.
Trade Agreements: Shaping Economic Relationships
Trade agreements influence the patterns of international trade and, consequently, the trade deficit. Evaluating the terms of these agreements and exploring opportunities for renegotiation can be avenues for addressing imbalances. Crafting fair and mutually beneficial trade agreements is crucial for fostering sustainable economic relationships.
National Savings and Investment: A Macro Perspective
The trade deficit is closely linked to a nation’s savings and investment rates. Examining domestic savings and investment patterns provides insights into the broader economic context. Strategies to bolster national savings and investment can positively influence the trade balance over the long term.
Strategies for Mitigation: Balancing the Equation
Addressing the US trade deficit requires a multifaceted approach. This involves promoting exports, fostering domestic production, and strategically managing currency dynamics. Crafting policies that incentivize innovation, support industries with a comparative advantage, and enhance trade infrastructure can contribute to a more balanced trade equation.
Global Economic Dynamics: A Shifting Landscape
The US trade deficit is also influenced by global economic trends. Economic developments in major trading partners, geopolitical shifts, and global market conditions all contribute to the trade balance. Staying attuned to these global dynamics is essential for devising
Understanding Consumer Spending: Habits and Economic Impacts
Decoding Consumer Spending: A Dive into Habits and Impacts
Consumer spending is a driving force in any economy, reflecting both individual choices and broader economic trends. This article delves into the intricacies of consumer spending habits, exploring their implications on individuals and the economy at large.
The Basics: What Drives Consumer Spending Habits?
Consumer spending habits are influenced by a myriad of factors. From personal income and financial stability to cultural influences and psychological factors, understanding the motivations behind spending choices is crucial. Examining these drivers provides insights into the dynamics of consumer behavior.
Trends and Patterns: Unraveling the Consumer Spending Landscape
Consumer spending is not uniform across demographics or time periods. Analyzing trends and patterns reveals shifts in consumer preferences, such as the rise of online shopping or changes in spending priorities during economic downturns. Keeping a pulse on these trends is essential for businesses and policymakers alike.
Economic Impact: The Ripple Effect of Consumer Choices
The collective impact of individual spending choices is profound. Consumer spending constitutes a significant portion of a nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Therefore, fluctuations in consumer spending can have cascading effects on overall economic health. Understanding this economic interdependence is crucial for stakeholders in various sectors.
Cyclical Nature: Consumer Spending in Economic Cycles
Consumer spending often follows economic cycles. During periods of economic prosperity, consumers tend to increase spending, driving economic growth. Conversely, in economic downturns, spending may contract as individuals become more cautious. Navigating the cyclical nature of consumer spending requires adaptability and strategic planning.
Psychological Influences: Emotions and Decision-Making
Consumer spending habits are not solely rational; emotions play a significant role in decision-making. Marketing strategies, peer influence, and the desire for status or comfort all tap into the emotional aspects of consumer behavior. Acknowledging these psychological influences is crucial for businesses crafting effective marketing campaigns.
Technological Shifts: The Impact of Digital Transformation
The advent of technology has reshaped consumer spending habits. E-commerce, mobile payments, and digital wallets have revolutionized how consumers make purchases. Adapting to these technological shifts is imperative for businesses aiming to stay relevant and meet the evolving preferences of modern consumers.
Societal Changes: Shifting Values and Preferences
Consumer spending habits often reflect broader societal changes. Shifts in values, such as a growing emphasis on sustainability or conscious consumerism, influence purchasing decisions. Businesses responsive to these changing preferences can forge stronger connections with their target audience.
Savings and Debt: Balancing Act for Consumers
Consumer spending habits are also intricately linked to saving and debt patterns. High levels of consumer debt can constrain spending, while a culture of saving can contribute to economic stability. Examining the delicate balance between savings and debt provides insights into the financial health of households.
The Future Landscape: Adapting to Consumer Trends
As consumer spending habits continue to evolve, businesses must proactively adapt to stay competitive. This involves leveraging data analytics, staying attuned to emerging trends, and embracing innovation. By anticipating and meeting the evolving needs of consumers, businesses can position themselves for sustained success.


