Economic indicators
Navigating Stock Market Dynamics: Strategies for Optimal Performance
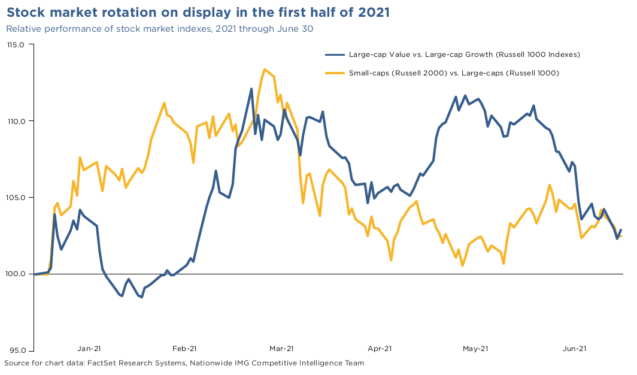
Unveiling the Intricacies of Stock Market Performance
Embarking on the journey of understanding stock market performance is akin to navigating a complex financial landscape. This article aims to unravel the intricacies, providing insights into strategies for optimal performance and informed decision-making.
The Dynamics of Stock Market Performance: A Primer
Stock market performance encapsulates the ebbs and flows of financial markets, reflecting the collective sentiment of investors. Understanding the dynamics involves delving into factors such as company earnings, economic indicators, and global events. This multifaceted approach is essential for grasping the nuances of stock market behavior.
Bull and Bear Markets: Riding the Waves
Stock markets are often characterized by bull and bear markets, representing periods of growth and decline, respectively. Recognizing the signs of these market cycles is crucial for investors. During bull markets, optimism prevails, and stocks generally rise. In contrast, bear markets witness pessimism, with stock prices falling. Strategic decision-making hinges on accurately identifying these market phases.
Market Indices: Gauging Overall Performance
Market indices, such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average, serve as benchmarks for assessing stock market performance. They provide a snapshot of how a broad section of the market is faring. Monitoring these indices aids investors in making informed decisions, offering insights into overall market trends.
Volatility and Risk Management: Navigating Uncertainties
Volatility is an inherent aspect of stock market performance. Prices can experience significant fluctuations, creating both opportunities and risks. Successful investors employ risk management strategies to mitigate potential downsides. Diversification, setting stop-loss orders, and staying informed about market news are essential components of effective risk management.
Economic Indicators and Their Impact: Connecting the Dots
The interplay between stock market performance and economic indicators is profound. Factors like GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation influence investor confidence and, consequently, stock prices. A comprehensive understanding of these economic indicators enhances the ability to anticipate market movements.
Company Fundamentals: Digging Deeper for Long-Term Gains
Examining the fundamentals of individual companies is a cornerstone of successful stock market investing. Factors such as earnings per share, revenue growth, and debt levels offer insights into a company’s financial health. Long-term investors often focus on strong fundamentals, aiming for sustained growth over time.
Market Timing vs. Time in the Market: A Strategic Dilemma
A perennial dilemma for investors is whether to focus on market timing or time in the market. Market timing involves trying to predict the best moments to buy or sell stocks, while time in the market emphasizes the benefits of long-term investing. Striking a balance that aligns with individual risk tolerance and financial goals is paramount.
Behavioral Finance: Understanding Investor Psychology
Stock market performance is not solely dictated by economic factors; it is also deeply intertwined with investor psychology. Behavioral finance explores how emotions and cognitive biases influence financial decisions. Awareness of these psychological factors empowers investors to make rational choices and avoid succumbing to market hysteria.
Technological Advancements and Algorithmic Trading: Shaping the Future
The advent of technology has revolutionized stock market dynamics. Algorithmic trading,
Industrial Momentum: Manufacturing Output in the USA

Driving Economic Engines: Manufacturing Output in the USA
The manufacturing sector serves as a barometer for a nation’s economic health, and understanding the nuances of manufacturing output in the USA is crucial. This article explores the dynamics, trends, and implications of manufacturing output, shedding light on its significance in the broader economic landscape.
Economic Pillar: Manufacturing’s Integral Role
Manufacturing holds a foundational role in the USA’s economic framework. Beyond creating products, it generates employment, fosters innovation, and contributes significantly to the country’s GDP. Analyzing manufacturing output provides insights into the overall economic pulse and the sector’s resilience.
Cyclical Nature: Manufacturing in Economic Cycles
Manufacturing output often mirrors economic cycles. During periods of expansion, production tends to rise, driving economic growth. Conversely, in downturns, reduced consumer demand may lead to production slowdowns. Recognizing the cyclical nature of manufacturing output is key for economic planners and businesses alike.
Global Interconnectedness: International Trade Impact
The USA’s manufacturing output is intricately linked to global trade. The demand for American-made goods on the international stage influences production levels. Trade policies, tariffs, and geopolitical shifts play a role in shaping the trajectory of manufacturing output and its contribution to the balance of trade.
Technological Advancements: Industry 4.0 Transformations
The advent of Industry 4.0, marked by technological advancements like automation, IoT, and artificial intelligence, has transformed manufacturing processes. Understanding how these technologies impact output efficiency, product innovation, and overall competitiveness is vital for staying abreast of industry trends.
Employment Landscape: Manufacturing Jobs and Skills
Changes in manufacturing output have direct implications for employment. While technological advancements may enhance productivity, they also impact labor requirements. Examining the evolving employment landscape within manufacturing sheds light on the skills needed in the industry and potential workforce challenges.
Supply Chain Resilience: Lessons from Disruptions
Recent global disruptions have underscored the importance of supply chain resilience. Manufacturing output can be significantly affected by disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, or unforeseen crises. Evaluating strategies to enhance supply chain resilience is paramount for the manufacturing sector.
Environmental Sustainability: Balancing Production and Impact
Manufacturing output has environmental implications, from resource consumption to waste generation. The industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Analyzing how manufacturers balance production needs with environmental impact and the adoption of eco-friendly initiatives is crucial for a sustainable future.
Government Policies: Shaping Manufacturing Landscape
Government policies play a substantial role in shaping the manufacturing landscape. Tax incentives, trade agreements, and regulations can influence output levels. Understanding the impact of policy changes provides insights into the potential trajectory of manufacturing output and its broader economic consequences.
Visit Manufacturing Output in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For those seeking in-depth insights into manufacturing output in the USA, visit Manufacturing Output in the USA. The curated analysis and information provided can empower businesses, policymakers, and individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the manufacturing sector.
In conclusion, manufacturing output is a multifaceted economic indicator that goes beyond production numbers. It reflects technological
Navigating Financial Waters: Interest Rates in the USA

Decoding Economic Signposts: Interest Rates in the USA
Understanding interest rates in the USA is pivotal for both financial markets and everyday consumers. This article explores the multifaceted aspects of interest rates, their role in the economy, and the impact they have on various sectors.
Fundamentals of Interest Rates: The Building Blocks
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment. Controlled by central banks, they serve as a lever for economic management. Analyzing the fundamental principles of interest rates provides a foundation for grasping their broader implications.
Central Bank Dynamics: The Federal Reserve’s Role
The Federal Reserve, the USA’s central bank, plays a central role in setting and influencing interest rates. Through mechanisms like the federal funds rate, the Fed regulates borrowing costs and shapes monetary policy. Understanding the dynamics of the Federal Reserve is crucial for interpreting interest rate movements.
Economic Indicators: Interest Rates as Barometers
Interest rates act as barometers for economic health. The Federal Reserve adjusts rates based on economic indicators such as inflation, employment, and GDP growth. Examining how interest rates respond to these indicators provides insights into the overall economic climate.
Consumer Impact: Borrowing Costs and Spending Habits
For consumers, interest rates directly influence borrowing costs. Whether obtaining a mortgage, car loan, or using credit cards, changes in interest rates impact spending and saving habits. Monitoring interest rate trends allows individuals to make informed financial decisions.
Business Investments: Capitalizing on Rate Environments
Interest rates influence corporate decisions on investments and expansions. Lower rates may encourage businesses to borrow for growth, while higher rates may lead to more conservative financial strategies. Analyzing the relationship between interest rates and business investments provides a glimpse into economic vitality.
Real Estate Dynamics: Mortgages and Property Markets
The real estate sector is particularly sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. Mortgage rates, influenced by broader interest rate trends, impact homebuyers’ affordability. Understanding how interest rates affect real estate dynamics is crucial for homeowners, buyers, and industry professionals.
Stock Market Reactions: Investors’ Sentiment and Strategies
Interest rates play a significant role in shaping investors’ sentiment in the stock market. As rates change, stock prices may respond accordingly. Investors often adjust their portfolios based on interest rate expectations, making the analysis of this relationship integral for investment decisions.
Inflationary Pressures: Balancing Act for Monetary Policy
Interest rates also serve as a tool to control inflation. By adjusting rates, central banks aim to strike a balance between stimulating economic growth and preventing excessive inflation. Examining how interest rates contribute to this delicate balancing act provides insights into monetary policy.
Global Influences: Interest Rates in a Connected World
Interest rates in the USA have implications beyond its borders. Global economic interconnectedness means that rate changes can affect international trade, currency values, and financial markets worldwide. Understanding the global influences on interest rates is crucial for businesses and policymakers.
Visit Interest Rates in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For a comprehensive exploration of interest rates in the USA, visit Interest Rates in
