Supply chain resilience
Industrial Momentum: Manufacturing Output in the USA

Driving Economic Engines: Manufacturing Output in the USA
The manufacturing sector serves as a barometer for a nation’s economic health, and understanding the nuances of manufacturing output in the USA is crucial. This article explores the dynamics, trends, and implications of manufacturing output, shedding light on its significance in the broader economic landscape.
Economic Pillar: Manufacturing’s Integral Role
Manufacturing holds a foundational role in the USA’s economic framework. Beyond creating products, it generates employment, fosters innovation, and contributes significantly to the country’s GDP. Analyzing manufacturing output provides insights into the overall economic pulse and the sector’s resilience.
Cyclical Nature: Manufacturing in Economic Cycles
Manufacturing output often mirrors economic cycles. During periods of expansion, production tends to rise, driving economic growth. Conversely, in downturns, reduced consumer demand may lead to production slowdowns. Recognizing the cyclical nature of manufacturing output is key for economic planners and businesses alike.
Global Interconnectedness: International Trade Impact
The USA’s manufacturing output is intricately linked to global trade. The demand for American-made goods on the international stage influences production levels. Trade policies, tariffs, and geopolitical shifts play a role in shaping the trajectory of manufacturing output and its contribution to the balance of trade.
Technological Advancements: Industry 4.0 Transformations
The advent of Industry 4.0, marked by technological advancements like automation, IoT, and artificial intelligence, has transformed manufacturing processes. Understanding how these technologies impact output efficiency, product innovation, and overall competitiveness is vital for staying abreast of industry trends.
Employment Landscape: Manufacturing Jobs and Skills
Changes in manufacturing output have direct implications for employment. While technological advancements may enhance productivity, they also impact labor requirements. Examining the evolving employment landscape within manufacturing sheds light on the skills needed in the industry and potential workforce challenges.
Supply Chain Resilience: Lessons from Disruptions
Recent global disruptions have underscored the importance of supply chain resilience. Manufacturing output can be significantly affected by disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, or unforeseen crises. Evaluating strategies to enhance supply chain resilience is paramount for the manufacturing sector.
Environmental Sustainability: Balancing Production and Impact
Manufacturing output has environmental implications, from resource consumption to waste generation. The industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Analyzing how manufacturers balance production needs with environmental impact and the adoption of eco-friendly initiatives is crucial for a sustainable future.
Government Policies: Shaping Manufacturing Landscape
Government policies play a substantial role in shaping the manufacturing landscape. Tax incentives, trade agreements, and regulations can influence output levels. Understanding the impact of policy changes provides insights into the potential trajectory of manufacturing output and its broader economic consequences.
Visit Manufacturing Output in the USA for In-Depth Insights
For those seeking in-depth insights into manufacturing output in the USA, visit Manufacturing Output in the USA. The curated analysis and information provided can empower businesses, policymakers, and individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the manufacturing sector.
In conclusion, manufacturing output is a multifaceted economic indicator that goes beyond production numbers. It reflects technological
Economic Resilience Amid Shifting Immigration Laws

Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of global affairs, changes in immigration laws can have a profound impact on the economic resilience of nations. This article explores the intricate relationship between economic stability and the evolving policies surrounding immigration.
Adaptation in Workforce Dynamics:
One key aspect of economic resilience lies in the adaptation of workforce dynamics. Changes in immigration laws often lead to shifts in labor availability. Businesses must navigate these changes strategically to ensure a resilient and capable workforce.
Innovation and Skill Diversification:
Immigration has historically been a source of innovation and skill diversification. Restrictive immigration laws can limit the influx of diverse talents, potentially stifling innovation. Economic resilience necessitates finding alternative avenues to foster creativity and skill diversity.
Impact on Industries and Economic Sectors:
Different industries are affected in varying degrees by changes in immigration laws. Some sectors rely heavily on immigrant labor. Understanding the sector-specific impact is crucial for devising resilient economic strategies that account for potential labor shortages or skill gaps.
Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth:
Immigrants often play a vital role in entrepreneurship and economic growth. Restrictive immigration policies can hamper the influx of entrepreneurial minds, impacting innovation and job creation. Building economic resilience requires fostering an environment that encourages immigrant entrepreneurs.
Global Competitiveness and Talent Retention:
Nations with flexible and welcoming immigration policies often attract top global talent. Changes in immigration laws can influence a country’s global competitiveness. To maintain economic resilience, countries must balance the need for talent retention with evolving immigration regulations.
Supply Chain Resilience and Immigration Policies:
Supply chains are intricately connected to the labor force, and changes in immigration laws can disrupt these chains. Businesses need to assess and enhance supply chain resilience to mitigate potential economic shocks resulting from immigration policy changes.
Investor Confidence and Economic Stability:
Investors closely monitor immigration policies as they impact workforce stability and overall economic conditions. Maintaining investor confidence requires transparent policies that provide a sense of stability amid changing immigration laws.
Social and Cultural Contributions:
Beyond the economic aspects, immigrants often contribute significantly to the social and cultural fabric of a nation. Recognizing these contributions is essential for fostering a resilient and cohesive society that can adapt to changing immigration laws without compromising unity.
Linking Economic Resilience to Immigration Policy:
For a deeper exploration of the strategies to build economic resilience in the face of changing immigration laws, visit vexhibits.com. Understand the crucial interplay between immigration policies and economic stability, and discover proactive measures to fortify your nation’s economic resilience.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, economic resilience in the face of changing immigration laws requires a holistic approach. From workforce adaptation and innovation to sector-specific considerations and cultural contributions, nations must navigate these changes with foresight. By understanding the symbiotic relationship between immigration policies and economic stability, countries can forge a path that ensures resilience and sustainable growth in the evolving global landscape.
Economic Impact of Evolving Environmental Laws
Introduction:
The global landscape is witnessing a transformative shift in environmental laws, and this article delves into the consequential economic implications. As nations strive for sustainability, the evolving regulatory frameworks have profound effects on various sectors and financial landscapes.
Balancing Industry Compliance and Economic Viability:
The crux of economic implications lies in the delicate balance between industry compliance and economic viability. As environmental laws tighten, businesses must adapt to stringent regulations, often requiring significant investments in eco-friendly practices. Striking a balance is essential to ensure both environmental stewardship and economic sustainability.
Innovation as a Catalyst for Economic Growth:
Changes in environmental laws often act as a catalyst for innovation. Industries are compelled to explore new technologies and methods to meet environmental standards. This drive for innovation not only aligns with sustainability goals but also fosters economic growth by creating opportunities for technology-driven sectors.
Impact on Energy Markets and Renewable Investments:
The energy sector undergoes significant transformations in response to changes in environmental laws. The shift towards renewable energy sources gains momentum, influencing investments and market dynamics. The economic implications extend to job creation, infrastructure development, and the reconfiguration of traditional energy markets.
Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainable Sourcing:
Environmental laws influence supply chain resilience by emphasizing sustainable sourcing practices. Businesses are prompted to reevaluate their supply chains, considering the environmental impact of raw materials and production processes. Adapting to sustainable sourcing practices enhances resilience and aligns with evolving consumer preferences.
Consumer Behavior and Sustainable Markets:
As environmental consciousness grows, changes in environmental laws can reshape consumer behavior. Consumers increasingly favor eco-friendly products and services. This shift in demand not only drives market trends but also creates economic opportunities for businesses adopting sustainable practices.
Regulatory Compliance Costs and Financial Planning:
The economic implications extend to the financial planning of businesses. Meeting stringent environmental regulations often incurs compliance costs. Companies must strategically integrate these costs into their financial planning to ensure long-term sustainability without compromising profitability.
Economic Incentives and Green Investments:
Governments often introduce economic incentives to encourage businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices. These incentives, ranging from tax breaks to grants, influence investment decisions. Understanding and leveraging these incentives can enhance a company’s economic standing while contributing to environmental goals.
Tourism and Biodiversity Preservation:
Environmental laws play a crucial role in biodiversity preservation, especially in regions dependent on tourism. Stricter regulations to protect natural habitats can impact tourism, requiring destinations to strike a delicate balance between economic interests and environmental conservation.
International Trade Dynamics and Green Standards:
Changes in environmental laws influence international trade dynamics. Countries with stringent environmental standards may set the bar for green practices, affecting trade relationships. Understanding and aligning with these standards can impact a nation’s economic standing in the global market.
Linking Economic Implications to Strategic Decision-Making:
For an in-depth exploration of strategic decision-making amid changing environmental laws, visit vexhibits.com. Uncover insights into the economic implications of environmental regulations and discover strategies to navigate these changes for sustainable and resilient business operations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion,
Navigating Economic Impact: Technological Disruptions’ Ripple Effect
Navigating Economic Impact: The Ripple Effect of Technological Disruptions
In the ever-evolving landscape of global economies, technological disruptions have become a defining force, reshaping industries and influencing economic trajectories. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of technological disruptions on economies and businesses worldwide.
The Acceleration of Change in Industries
Technological disruptions are catalysts for rapid change within industries. From artificial intelligence to blockchain and automation, innovations are transforming the way businesses operate. Industries that embrace these changes experience heightened efficiency and productivity, but they also face the challenge of adapting to an accelerated pace of evolution.
Job Landscape and Workforce Dynamics
As technology automates routine tasks, the job landscape undergoes significant shifts. While new opportunities emerge in tech-related fields, traditional roles may become obsolete. Workforce dynamics are influenced by the need for upskilling and reskilling to match the demands of the evolving job market. Balancing the opportunities and challenges in the job landscape becomes a crucial aspect of navigating technological disruptions.
Small Businesses and Global Competition
Technological disruptions can level the playing field for small businesses, enabling them to compete on a global scale. Through digital platforms and e-commerce, small enterprises can reach a broader audience. However, this global reach also intensifies competition, requiring businesses to stay agile and innovative to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Investments in Innovation and Research
Economic growth is intricately tied to investments in innovation and research. Nations and businesses that prioritize technological advancements foster an environment conducive to growth. Governments, realizing the potential economic impact of technological disruptions, often incentivize research and development activities to stay at the forefront of global competitiveness.
Supply Chain Resilience and Vulnerabilities
Technological disruptions expose vulnerabilities in traditional supply chain models. From cybersecurity threats to global crises affecting manufacturing and distribution, businesses must reassess and fortify their supply chains. Achieving resilience involves integrating advanced technologies, data analytics, and contingency planning to mitigate risks and ensure continuity in a disruptive landscape.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
The digital transformation brought about by technological disruptions significantly influences consumer behavior. E-commerce, personalized experiences, and instant gratification have become the norm. Understanding these shifts is essential for businesses to align their strategies with evolving market trends, ensuring they meet consumer expectations and stay relevant in a dynamic economic environment.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the economic impact of technological disruptions through policies and regulations. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and addressing potential negative consequences is a delicate task. Policies that encourage responsible technological adoption while safeguarding societal interests contribute to a sustainable economic framework.
Challenges and Opportunities in Emerging Technologies
While technological disruptions present challenges, they also offer unprecedented opportunities. Emerging technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and biotechnology hold the potential to revolutionize industries. Businesses that strategically navigate these technologies can gain a competitive edge and contribute to the economic growth spurred by innovation.
Global Connectivity and Collaborations
In a world driven by technological connectivity, collaborations become essential for economic growth. Nations and businesses
Retail Industry Updates: Navigating Market Dynamics

Introduction:
The retail industry, a dynamic and ever-evolving sector, is undergoing significant transformations. In this exploration, we delve into the latest retail industry updates, highlighting key trends, innovations, and strategies that are reshaping the landscape.
E-commerce Integration: A Pivotal Shift in Retail Dynamics:
One of the noteworthy retail industry updates is the continued integration of E-commerce. As online shopping becomes increasingly prevalent, retailers are leveraging digital platforms to enhance customer experiences, expand market reach, and stay competitive in a digitally-driven market.
Omnichannel Retailing: Seamlessly Connecting the Dots:
Omnichannel retailing is another crucial update in the industry. The seamless integration of online and offline channels provides customers with a cohesive shopping experience. Retailers are adopting omnichannel strategies to create a unified journey, allowing customers to transition effortlessly between online and physical stores.
Contactless Payments and Digital Wallets: Redefining Transactions:
With a focus on safety and convenience, the adoption of contactless payments and digital wallets has surged. Retail industry updates include the implementation of secure and efficient payment options, reducing physical contact during transactions and meeting the preferences of tech-savvy consumers.
Retail Technology Innovations: Enhancing In-Store Experiences:
Retailers are embracing technology innovations to enhance in-store experiences. From augmented reality mirrors for virtual try-ons to smart shelves with inventory tracking, these updates aim to captivate customers and provide them with interactive and personalized shopping encounters.
Personalization through Data Analytics: Tailoring the Retail Journey:
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in retail industry updates, enabling personalized experiences. Retailers leverage customer data to tailor recommendations, promotions, and marketing strategies. The result is a more customized retail journey that resonates with individual preferences.
Sustainability Initiatives: A Growing Focus in Retail:
Sustainability has become a central theme in retail industry updates. Consumers increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices, and retailers are responding with sustainable sourcing, packaging, and corporate responsibility initiatives. These efforts not only align with consumer values but also contribute to long-term brand loyalty.
Pop-Up Stores and Experiential Retail: Creating Unique Encounters:
Retailers are embracing the concept of pop-up stores and experiential retail as a strategy to create unique and memorable encounters for customers. These temporary and immersive spaces serve as an avenue for product launches, brand activations, and fostering a sense of exclusivity.
Supply Chain Resilience: Navigating Global Challenges:
Recent global challenges have underscored the importance of supply chain resilience. Retail industry updates include a focus on optimizing supply chains for flexibility, visibility, and responsiveness. Retailers are adopting technologies like blockchain to enhance transparency and mitigate risks.
Subscription Services: Nurturing Customer Loyalty:
The rise of subscription services is reshaping the retail landscape. Retailers are offering subscription boxes and services, providing customers with a curated and recurring shopping experience. This not only fosters customer loyalty but also creates predictable revenue streams for businesses.
Exploring Retail Industry Updates:
For a comprehensive exploration of the latest retail industry updates and insights, visit vexhibits.com. Discover curated content that delves into the trends, innovations, and strategies shaping the retail landscape, providing retailers with a roadmap for navigating these dynamic times.
Conclusion:
Resilient Enterprises: Strategies for Business Continuity
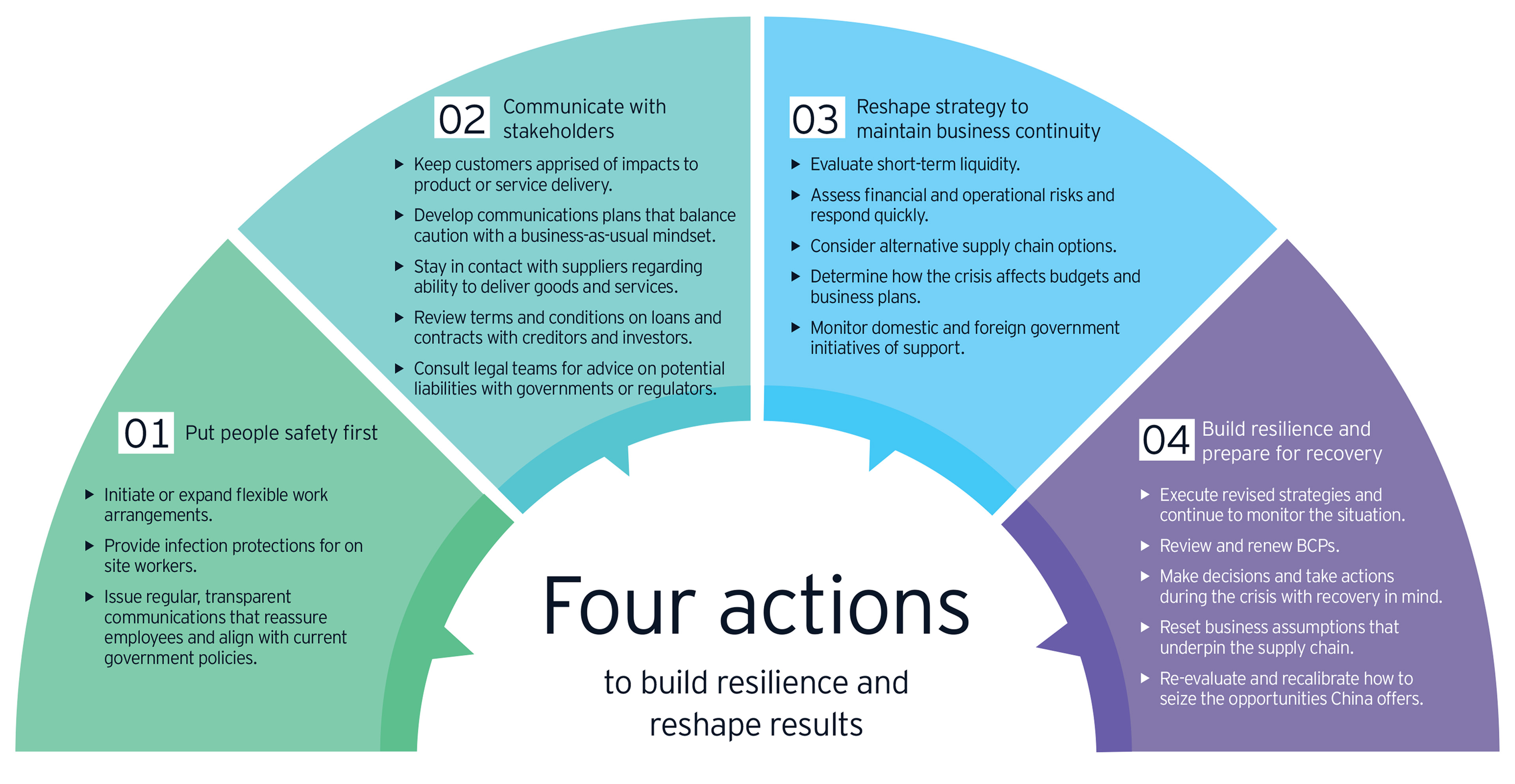
Introduction:
In an ever-changing business landscape, the ability to navigate challenges and disruptions is paramount. This article delves into the concept of business resilience and explores effective strategies that organizations can adopt to fortify their operations, ensure continuity, and emerge stronger in the face of uncertainties.
Business Resilience Strategies Link:
Discover essential Business Resilience Strategies here. Explore proven approaches to fortify your business and enhance continuity.
Risk Assessment and Preparedness:
The foundation of business resilience lies in a comprehensive risk assessment. Identifying potential risks, from natural disasters to economic downturns, allows organizations to prepare effectively. Preparedness involves developing contingency plans and ensuring that teams are well-equipped to respond promptly in times of crisis.
Diversification of Revenue Streams:
Relying on a single revenue stream can leave businesses vulnerable. Diversification involves expanding product or service offerings, entering new markets, or exploring alternative business models. This strategy not only enhances resilience but also positions the business to adapt to changing market dynamics.
Investing in Technology and Innovation:
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in business resilience. Investing in cutting-edge technologies and fostering a culture of innovation enables organizations to streamline operations, adapt to market trends, and stay ahead of the competition. Embracing digital transformation is key to building resilience in the modern business landscape.
Supply Chain Resilience:
Global supply chains are susceptible to disruptions, as demonstrated by recent events. Building supply chain resilience involves mapping and diversifying suppliers, establishing backup plans, and leveraging technology for real-time visibility. A resilient supply chain ensures a consistent flow of goods and services, even during unforeseen disruptions.
Human Capital Development and Flexibility:
Empowering the workforce through continuous learning and development is fundamental to business resilience. A skilled and adaptable workforce is better equipped to handle challenges and contribute to innovative solutions. Flexibility in work arrangements and embracing remote work options further enhances organizational resilience.
Financial Preparedness and Risk Management:
Financial stability is a cornerstone of business resilience. Maintaining robust financial health involves prudent budgeting, building cash reserves, and implementing risk management strategies. Businesses with strong financial foundations can weather economic uncertainties and invest strategically in growth opportunities.
Effective Communication Strategies:
Clear and transparent communication is critical during times of crisis. Establishing effective communication channels with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, fosters trust and ensures that everyone is informed and aligned. Timely and honest communication helps manage expectations and reduces uncertainty.
Scenario Planning for Uncertainties:
Scenario planning involves envisioning various potential futures and developing strategies to address each scenario. By anticipating possible challenges and formulating response plans, organizations can navigate uncertainties more effectively. Scenario planning provides a roadmap for decision-making in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Collaboration and Partnerships:
Building collaborative relationships with other businesses, industry partners, and governmental agencies enhances resilience. Shared resources, information exchange, and collaborative problem-solving contribute to a collective resilience that extends beyond individual organizations. Strategic partnerships can provide support during challenging times.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
Business resilience is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. Regularly reassessing risks, updating
Economic Resilience Amid Energy Law Transformations
Introduction:
The global energy landscape is undergoing profound transformations, marked by dynamic changes in energy laws. In this article, we explore the imperative of economic resilience in the face of evolving energy regulations and how businesses can navigate the challenges posed by these shifts.
Adaptation in Energy Infrastructure:
One of the critical aspects of economic resilience amid changing energy laws is the adaptation of energy infrastructure. As regulations evolve to favor renewable sources and sustainability, businesses must invest in and adapt their energy infrastructure to align with the changing legal landscape. This adaptability ensures long-term resilience in the face of regulatory changes.
Investment Strategies and Energy Transition:
Economic resilience hinges on strategic investment decisions, particularly in the context of the energy transition. Companies that strategically invest in renewable energy sources and technologies can not only comply with changing energy laws but also position themselves as leaders in a sustainable and resilient future.
Impact on Energy Pricing and Affordability:
Changes in energy laws can have a direct impact on energy pricing and affordability. Economic resilience requires businesses to assess and manage the potential effects of regulatory changes on the cost of energy. Proactive measures, such as exploring energy-efficient technologies, can mitigate the impact on operational costs.
Diversification in Energy Sources:
To enhance economic resilience, businesses should consider diversifying their energy sources. Dependence on a single energy source may become a vulnerability as energy laws shift. A diversified energy portfolio, incorporating both traditional and renewable sources, provides a buffer against the uncertainties of changing regulations.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs:
Energy efficiency becomes a cornerstone of economic resilience. Changes in energy laws often incentivize energy-efficient practices. Companies that prioritize energy efficiency not only contribute to sustainability goals but also position themselves for cost savings, enhancing overall economic resilience.
Government Incentives and Economic Stimulus:
Governments often introduce incentives and economic stimulus packages to support businesses in adapting to changing energy laws. Understanding and leveraging these incentives can significantly contribute to economic resilience. Businesses should stay informed about available programs and strategically utilize them for sustainable growth.
Supply Chain Resilience and Energy Security:
Energy laws are intricately linked to supply chain resilience and energy security. Economic resilience requires businesses to assess the vulnerability of their supply chains to energy disruptions. Diversification of energy sources and strategic partnerships can enhance supply chain resilience in the face of evolving energy regulations.
Job Creation and Workforce Development:
The transition to new energy paradigms often creates opportunities for job creation and workforce development. Economic resilience involves aligning workforce skills with the emerging needs of the energy sector. Businesses can foster resilience by investing in training programs and ensuring a skilled workforce ready for the changing energy landscape.
Technological Innovation and Competitive Edge:
Economic resilience is closely tied to technological innovation. Companies that invest in innovative technologies aligned with changing energy laws can gain a competitive edge. Embracing innovation not only ensures compliance but also positions businesses as leaders in the evolving energy market.
Linking Economic Resilience to Strategic
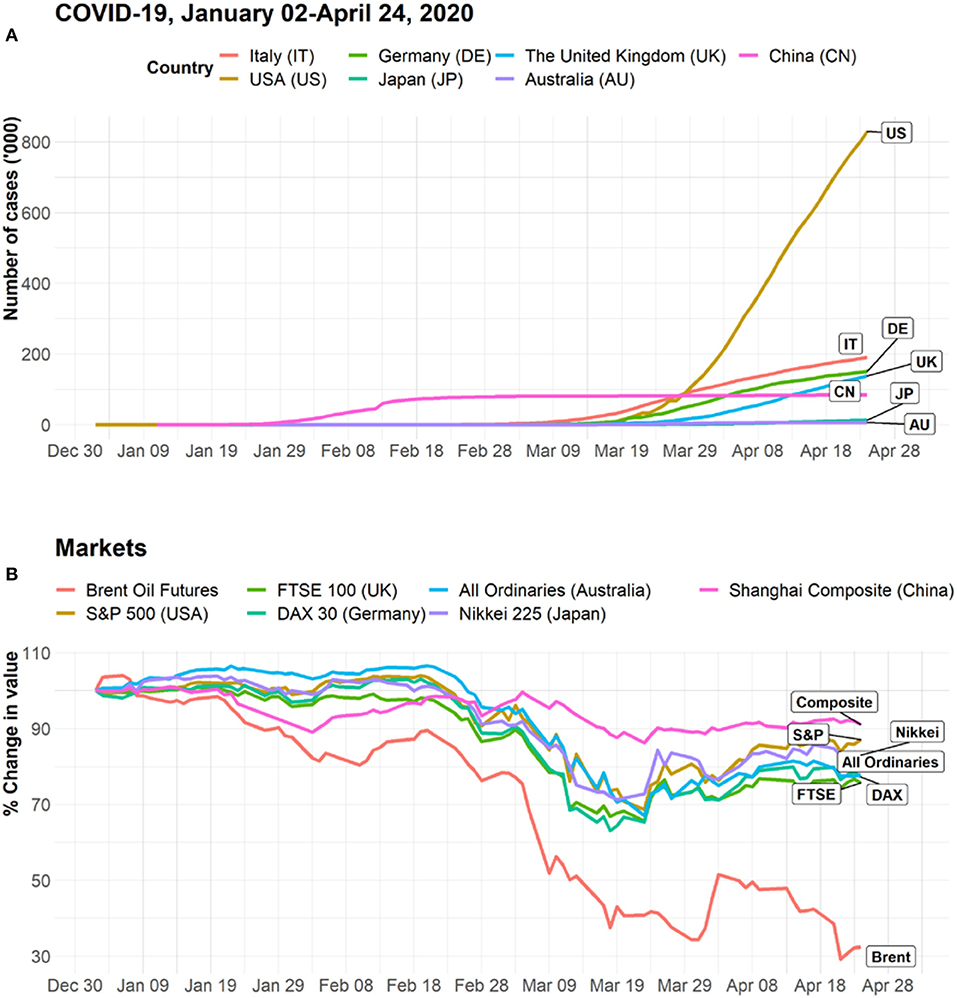
Navigating Post-Pandemic Economic Challenges: A Roadmap to Recovery

Navigating Post-Pandemic Economic Challenges: A Roadmap to Recovery
The global landscape has undergone significant transformations in the aftermath of the pandemic, presenting a myriad of economic challenges. In this exploration, we unravel the complexities and strategize a roadmap towards recovery in the post-pandemic era.
The Unprecedented Disruption and Economic Fallout
The onset of the pandemic unleashed unprecedented disruption across industries, resulting in economic fallout worldwide. Lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and reduced consumer spending sent shockwaves through the global economy. Understanding the depth of these challenges is crucial in formulating effective recovery strategies.
Impact on Small Businesses and Employment Dynamics
Small businesses bore a disproportionate brunt during the pandemic, facing closures, financial strains, and operational hurdles. The repercussions extended to employment dynamics, with job losses and shifts in labor markets. Addressing the specific challenges faced by small businesses and revitalizing employment opportunities are integral components of the recovery process.
Supply Chain Resilience and Global Dependencies
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, emphasizing the need for increased resilience. Dependency on specific regions for crucial supplies became evident as disruptions reverberated globally. The post-pandemic era calls for a reevaluation of supply chain strategies, focusing on resilience, diversification, and adaptability.
Digital Transformation as a Catalyst for Recovery
Amid challenges, the pandemic accelerated digital transformation across industries. Remote work, e-commerce, and digital communication became the new norm. Leveraging technology as a catalyst for recovery involves further integration, upskilling the workforce, and capitalizing on digital platforms to enhance business resilience and efficiency.
Government Stimulus and Economic Policies
Governments worldwide responded to the economic challenges with stimulus packages and policy interventions. The post-pandemic recovery hinges on the effectiveness of these measures. Governments must strike a balance between stimulating economic activity, addressing social disparities, and ensuring long-term fiscal sustainability.
The Evolution of Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
Consumer behavior underwent a paradigm shift during the pandemic, influencing market trends. E-commerce, remote services, and health-related industries experienced significant growth. Understanding the evolving landscape of consumer preferences is essential for businesses to realign strategies and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Healthcare System Strengthening and Preparedness
The pandemic exposed weaknesses in healthcare systems globally. Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, investing in research and development, and enhancing preparedness for future health crises are vital components of post-pandemic recovery. Collaborations between public and private sectors are crucial for building robust healthcare systems.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Considerations
The post-pandemic recovery provides an opportunity to embed sustainability in economic practices. Emphasizing environmental considerations, adopting sustainable business models, and integrating eco-friendly practices contribute to long-term resilience and align with global efforts towards a greener future.
Global Cooperation and Collaborative Solutions
Post-pandemic challenges transcend borders, emphasizing the need for global cooperation. Collaborative solutions, information sharing, and joint efforts in research and development foster a collective approach to recovery. International partnerships are instrumental in addressing challenges that require coordinated responses.
To explore comprehensive insights into the economic challenges in the post-pandemic era and strategies for recovery, visit Vexhibits.com. This platform provides valuable resources and trends, offering a
