January 2024
Business News USA: Latest Developments and Market Trends

Introduction:
In the fast-paced world of business, staying informed about the latest developments and market trends is essential. This article serves as a comprehensive overview of recent business news in the USA, covering key sectors and noteworthy events shaping the economic landscape.
Technology and Innovation:
Business news in the USA has been buzzing with technological advancements and innovations. Tech giants continue to drive the industry forward, with breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and renewable energy. These developments not only impact the tech sector but also have ripple effects across various industries, influencing market dynamics and competitiveness.
Finance and Market Trends:
The financial landscape is a focal point in recent business news. From fluctuations in the stock market to changes in interest rates, businesses and investors closely monitor these trends. The evolving economic conditions, both domestically and globally, play a significant role in shaping investment strategies and business decisions.
E-commerce and Retail Dynamics:
The rise of e-commerce continues to reshape the retail landscape. Business news in the USA highlights the strategies adopted by traditional retailers and e-commerce giants alike to adapt to changing consumer behaviors. Innovations in logistics, customer experience, and omnichannel approaches are at the forefront of industry discussions.
Healthcare Industry Updates:
The healthcare sector is undergoing significant transformations, and recent business news in the USA reflects this evolution. From pharmaceutical breakthroughs to discussions on healthcare policies, these developments impact businesses within the healthcare industry and have broader implications for the economy as a whole.
Sustainable Business Practices:
Environmental and social responsibility have become integral to business strategies. Recent news highlights a growing emphasis on sustainable business practices. Companies are incorporating eco-friendly initiatives, diversity and inclusion programs, and ethical business standards, reflecting a shift in consumer preferences and societal expectations.
Startups and Entrepreneurship:
The entrepreneurial spirit is alive and well, with startups making waves in various industries. Business news in the USA features stories of innovation, funding rounds, and the challenges faced by emerging businesses. The startup ecosystem plays a crucial role in driving economic growth and fostering a culture of innovation.
Government Policies and Business Impact:
Changes in government policies have far-reaching effects on businesses. Recent news covers legislative developments, trade policies, and economic stimulus packages. The dynamic interplay between government decisions and business operations underscores the need for companies to stay informed and agile in their strategies.
Real Estate and Housing Market Trends:
The real estate market is a key indicator of economic health, and recent business news in the USA reflects trends in housing markets and commercial real estate. Factors such as remote work dynamics, interest rates, and urban migration influence property values and investment decisions.
Consumer Trends and Brand Strategies:
Understanding consumer behavior is paramount for businesses, and recent news sheds light on evolving trends. From shifts in purchasing preferences to the impact of social media on brand strategies, businesses are adapting their approaches to align with the ever-changing landscape of consumer expectations.
Global Economic Relations:
In an interconnected world, global economic relations play a vital
The Evolution of US Economic Fortunes
The Evolution of US Economic Fortunes
Exploring the rich tapestry of U.S. economic history unveils a narrative marked by resilience, innovation, and transformative shifts. This journey through time provides insights into the key epochs that have shaped the economic fortunes of the United States.
Founding Fathers and Early Economic Foundations
In the nascent years of the United States, the Founding Fathers laid the groundwork for economic prosperity. Alexander Hamilton’s financial system, encompassing a national bank and a robust credit system, set the stage for economic development. The young nation sought economic independence through initiatives like protective tariffs and infrastructure development, laying the foundation for future growth.
Westward Expansion and Economic Opportunities
The 19th century witnessed the westward expansion, a pivotal chapter in U.S. economic history. The acquisition of vast territories fueled economic opportunities, with the development of agriculture, mining, and transportation. The completion of the transcontinental railroad further interconnected the nation, spurring economic growth and urbanization.
Industrial Revolution and Economic Transformation
The late 19th and early 20th centuries marked the era of industrialization, a transformative period in U.S. economic history. The rise of manufacturing, technological innovations, and the growth of corporations propelled the nation into an industrial powerhouse. This era saw the emergence of iconic figures like John D. Rockefeller and Andrew Carnegie, shaping the landscape of American capitalism.
The Roaring Twenties and Economic Exuberance
The 1920s ushered in a period of economic exuberance known as the Roaring Twenties. The stock market soared, consumer spending surged, and technological advancements contributed to widespread prosperity. However, this economic euphoria was short-lived, culminating in the devastating crash of 1929 and the onset of the Great Depression.
New Deal and Economic Recovery
In response to the economic devastation of the Great Depression, President Franklin D. Roosevelt introduced the New Deal. This series of programs aimed to stimulate economic recovery, provide relief to the unemployed, and reform the financial system. The New Deal played a crucial role in shaping the social and economic landscape of the United States.
Post-War Economic Boom and Global Leadership
The aftermath of World War II witnessed a remarkable economic boom in the United States. The nation emerged as a global economic leader, experiencing rapid industrialization and technological advancements. The GI Bill, infrastructure development, and a growing middle class contributed to sustained economic growth, defining the mid-20th century as an era of unparalleled prosperity.
Challenges of the 1970s and Economic Restructuring
The 1970s brought economic challenges, including stagflation, oil shocks, and manufacturing decline. This tumultuous period prompted a shift in economic policies, with an emphasis on deregulation, free-market principles, and globalization. The restructuring of industries and the rise of the service sector marked a significant transformation in the U.S. economic landscape.
Technology Boom and the Information Age
The late 20th century witnessed a technology boom, catapulting the United States into the Information Age. The rise of Silicon Valley, the internet revolution, and advancements in communication technology transformed industries and created new economic opportunities. This era saw the emergence of tech giants
Migration’s Economic Influence: Balancing Impact and Policy
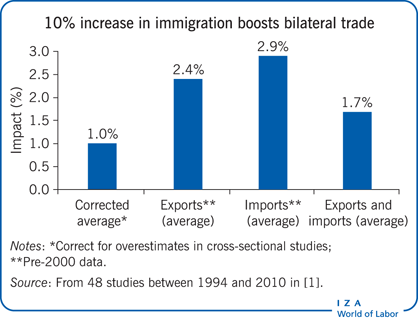
Migration’s Economic Influence: Balancing Impact and Policy
Immigration plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of nations, presenting both opportunities and challenges. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted impact of immigration on the economy and the importance of well-crafted policies to harness its benefits.
Contributions to Economic Growth
Immigrants contribute significantly to economic growth by bringing diverse skills, talents, and perspectives to the workforce. Their participation in various sectors, from technology to healthcare, fosters innovation and enhances productivity. A robust immigrant workforce often acts as a catalyst for economic expansion, driving industries forward and creating new opportunities.
Labor Market Dynamics and Job Creation
One of the key impacts of immigration on the economy is its influence on the labor market. Immigrant workers fill gaps in industries facing labor shortages, ensuring the smooth functioning of critical sectors. Moreover, their presence often complements the skills of the native workforce, leading to job creation rather than job displacement. This collaborative dynamic strengthens the overall labor market.
Entrepreneurship and Small Business Growth
Immigrants frequently play a pivotal role in entrepreneurship and small business growth. Many successful businesses are founded by immigrants, contributing to economic dynamism and job creation. Their entrepreneurial spirit not only enhances local economies but also diversifies business landscapes, fostering a more resilient and competitive economic environment.
Consumer Spending and Economic Stimulus
Immigrants contribute to consumer spending, driving demand for goods and services. As they integrate into communities, they become consumers themselves, supporting local businesses and contributing to economic stimulus. This cycle of increased spending has a ripple effect, positively impacting various sectors of the economy and promoting overall economic health.
Fiscal Contributions and Social Welfare
Contrary to some misconceptions, immigrants often make substantial fiscal contributions. They pay taxes, including income, property, and sales taxes, which contribute to public coffers. Studies indicate that, over time, immigrants tend to be net positive contributors to government finances. Responsible immigration policies can ensure that the fiscal benefits are maximized.
Challenges in Wage Dynamics and Low-Skilled Jobs
While immigration brings numerous benefits, it also poses challenges, particularly in wage dynamics and low-skilled job markets. In some cases, an influx of low-skilled immigrants can lead to wage suppression in certain sectors. Balancing the needs of the workforce and addressing potential disparities are crucial aspects of effective immigration policies.
Education and Skill-Level Considerations
A nuanced approach to immigration policies should consider education and skill levels. High-skilled immigrants often contribute to technological advancements and innovation, filling critical roles in STEM fields. Policies that attract and retain skilled professionals ensure that nations remain competitive in the global knowledge economy.
Social Integration and Cultural Diversity
Beyond economic impacts, immigration influences social dynamics and cultural diversity. Successful integration policies foster social cohesion, enriching societies with diverse perspectives and experiences. Embracing cultural diversity not only enhances the quality of life but also contributes to the overall vitality and resilience of communities.
Addressing Challenges Through Policy Reforms
To explore innovative solutions at the intersection of the Impact of Immigration on
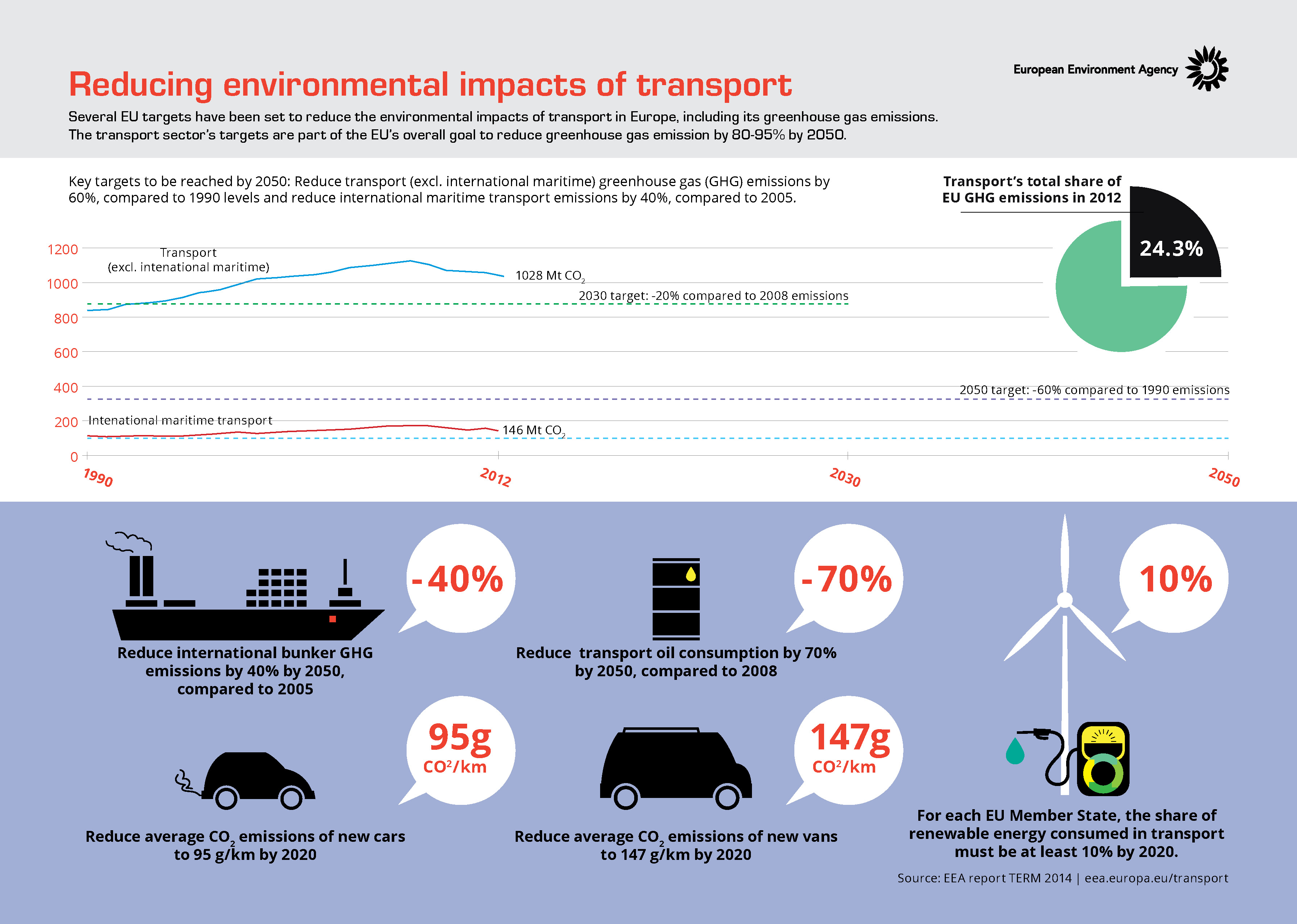
Economic Impact of Transportation Policy Changes
Navigating Economic Shifts: The Impact of Changes in Transportation Policies
Transportation policies play a pivotal role in shaping a nation’s economic landscape. This article delves into the intricate web of economic consequences brought about by shifts in transportation policies, exploring their effects on various sectors and the overall well-being of a country.
Enhancing Infrastructure and Economic Growth
A fundamental aspect of transportation policy changes is the impact on infrastructure development. Investments in modernizing transportation networks, such as roads, bridges, and public transit systems, can stimulate economic growth. Improved infrastructure not only enhances connectivity but also facilitates the movement of goods and people, fostering a conducive environment for economic activities.
Job Creation and Employment Opportunities
Changes in transportation policies often result in large-scale infrastructure projects, creating a demand for skilled labor. The construction and maintenance of new transportation systems lead to job creation, providing employment opportunities for a diverse workforce. These projects not only bolster the economy but also contribute to a reduction in unemployment rates.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
Efficient transportation is critical for a well-functioning supply chain. Policy changes that prioritize logistics and transportation efficiency can have a significant impact on the cost-effectiveness of moving goods. Streamlined supply chains contribute to overall economic efficiency, benefiting industries and consumers alike.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Transportation
In response to environmental concerns, transportation policies are increasingly focusing on sustainability. Embracing green transportation alternatives, such as electric vehicles and public transit, not only addresses environmental issues but also opens up economic opportunities in the growing green technology sector. The economic impact extends to job creation, technological innovation, and reduced healthcare costs associated with air pollution.
Urban Development and Real Estate Values
Transportation policies influence urban development patterns. Investments in public transit often lead to increased property values in well-connected areas. As accessibility improves, businesses and residents gravitate towards these regions, spurring economic activity and contributing to the growth of urban centers.
Global Trade and Economic Competitiveness
Transportation policies have a direct bearing on a nation’s ability to engage in global trade. Efficient transportation systems, including seaports and airports, enhance a country’s economic competitiveness. Policy changes that prioritize and modernize these crucial hubs facilitate smoother international trade, attracting investments and boosting the national economy.
Technological Integration and Innovation
Advancements in transportation technologies are often influenced by policy initiatives. Policies supporting research and development in transportation lead to innovations such as autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure. These technological advancements not only improve transportation efficiency but also contribute to economic growth through the emergence of new industries and job opportunities.
Social Equity and Accessibility
Transportation policies play a role in ensuring equitable access to opportunities. Policies that prioritize public transit and affordable transportation options contribute to social equity by ensuring that individuals from all socio-economic backgrounds can access education, employment, and essential services, thereby fostering an inclusive and economically vibrant society.
Challenges in Implementation and Economic Considerations
While the long-term economic benefits of transportation policy changes are evident, challenges in implementation can impact their immediate
Understanding Consumer Spending: Habits and Economic Impacts
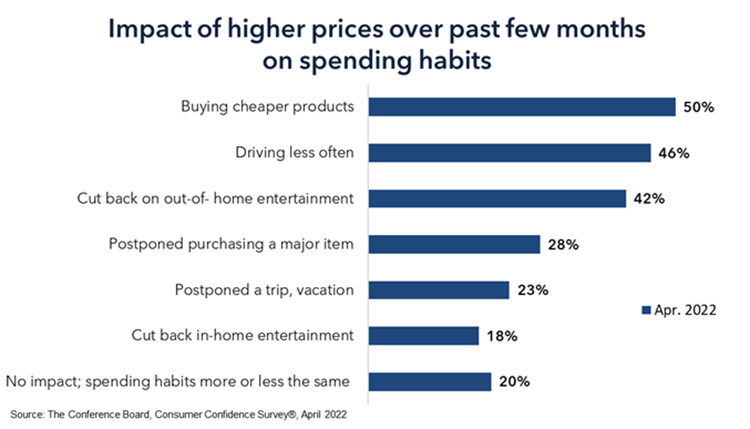
Decoding Consumer Spending: A Dive into Habits and Impacts
Consumer spending is a driving force in any economy, reflecting both individual choices and broader economic trends. This article delves into the intricacies of consumer spending habits, exploring their implications on individuals and the economy at large.
The Basics: What Drives Consumer Spending Habits?
Consumer spending habits are influenced by a myriad of factors. From personal income and financial stability to cultural influences and psychological factors, understanding the motivations behind spending choices is crucial. Examining these drivers provides insights into the dynamics of consumer behavior.
Trends and Patterns: Unraveling the Consumer Spending Landscape
Consumer spending is not uniform across demographics or time periods. Analyzing trends and patterns reveals shifts in consumer preferences, such as the rise of online shopping or changes in spending priorities during economic downturns. Keeping a pulse on these trends is essential for businesses and policymakers alike.
Economic Impact: The Ripple Effect of Consumer Choices
The collective impact of individual spending choices is profound. Consumer spending constitutes a significant portion of a nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Therefore, fluctuations in consumer spending can have cascading effects on overall economic health. Understanding this economic interdependence is crucial for stakeholders in various sectors.
Cyclical Nature: Consumer Spending in Economic Cycles
Consumer spending often follows economic cycles. During periods of economic prosperity, consumers tend to increase spending, driving economic growth. Conversely, in economic downturns, spending may contract as individuals become more cautious. Navigating the cyclical nature of consumer spending requires adaptability and strategic planning.
Psychological Influences: Emotions and Decision-Making
Consumer spending habits are not solely rational; emotions play a significant role in decision-making. Marketing strategies, peer influence, and the desire for status or comfort all tap into the emotional aspects of consumer behavior. Acknowledging these psychological influences is crucial for businesses crafting effective marketing campaigns.
Technological Shifts: The Impact of Digital Transformation
The advent of technology has reshaped consumer spending habits. E-commerce, mobile payments, and digital wallets have revolutionized how consumers make purchases. Adapting to these technological shifts is imperative for businesses aiming to stay relevant and meet the evolving preferences of modern consumers.
Societal Changes: Shifting Values and Preferences
Consumer spending habits often reflect broader societal changes. Shifts in values, such as a growing emphasis on sustainability or conscious consumerism, influence purchasing decisions. Businesses responsive to these changing preferences can forge stronger connections with their target audience.
Savings and Debt: Balancing Act for Consumers
Consumer spending habits are also intricately linked to saving and debt patterns. High levels of consumer debt can constrain spending, while a culture of saving can contribute to economic stability. Examining the delicate balance between savings and debt provides insights into the financial health of households.
The Future Landscape: Adapting to Consumer Trends
As consumer spending habits continue to evolve, businesses must proactively adapt to stay competitive. This involves leveraging data analytics, staying attuned to emerging trends, and embracing innovation. By anticipating and meeting the evolving needs of consumers, businesses can position themselves for sustained success.
Governance Excellence: Corporate Best Practices Unveiled
Governance Excellence: Corporate Best Practices Unveiled
Corporate governance is the bedrock of effective management and ethical business conduct. This article delves into the best practices that companies can adopt to ensure robust corporate governance, fostering transparency, accountability, and sustained success.
Defining Corporate Governance
At its core, corporate governance encompasses the mechanisms, processes, and relations by which companies are directed and controlled. It involves balancing the interests of a company’s many stakeholders, such as shareholders, management, customers, financiers, government, and the community. Defining the principles that guide these relationships is fundamental to good governance.
Transparency and Open Communication
One of the foundational pillars of corporate governance is transparency. Openly sharing information about a company’s strategies, financial performance, risks, and decision-making processes builds trust with stakeholders. Transparent communication fosters an environment where shareholders and other stakeholders feel informed and engaged in the company’s direction.
Board of Directors: Composition and Independence
A key aspect of effective corporate governance lies in the composition and independence of the board of directors. Having a diverse board with a mix of skills, experience, and backgrounds contributes to well-informed decision-making. Independence ensures that the board can act objectively in the best interests of the company without undue influence.
Ethical Leadership and Code of Conduct
Ethical leadership sets the tone for corporate culture. Establishing and promoting a strong code of conduct helps guide employees, management, and directors in making ethical decisions. Companies that prioritize ethical behavior not only foster a positive work environment but also enhance their reputation and credibility in the eyes of stakeholders.
Risk Management and Compliance
A robust corporate governance framework includes effective risk management and compliance measures. Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks are essential components of governance. Compliance with laws and regulations ensures that the company operates within legal boundaries, reducing the likelihood of legal issues that could impact its reputation and financial stability.
Shareholder Rights and Engagement
Protecting shareholder rights is fundamental to good governance. Establishing mechanisms for shareholder engagement, such as regular meetings and voting opportunities, allows shareholders to voice their opinions and influence important decisions. Engaging with shareholders creates a sense of ownership and aligns their interests with the long-term success of the company.
Vexhibits: Exemplifying Corporate Governance
Explore how Vexhibits exemplifies corporate governance best practices. By prioritizing transparency, ethical leadership, and stakeholder engagement, Vexhibits showcases a commitment to effective governance, contributing to its success in the exhibition and events industry.
Performance Evaluation and Accountability
Regular performance evaluations of the board, executives, and committees are crucial for accountability. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting objective assessments ensures that individuals and teams are held accountable for their responsibilities. Accountability is a cornerstone of effective corporate governance.
Long-Term Strategic Planning
Corporate governance extends beyond day-to-day operations; it involves planning for the long-term sustainability of the company. Aligning strategic goals with the interests of stakeholders ensures that the company is well-positioned for future success. Long-term planning involves anticipating challenges, adapting to market trends, and staying agile in a dynamic business landscape.
Adaptability and Continuous
Crafting Success: Manufacturing Industry Insights
Crafting Success: Manufacturing Industry Insights
The manufacturing industry is a dynamic and evolving sector that plays a pivotal role in global economies. Delving into the insights of this multifaceted industry provides valuable perspectives for manufacturers, businesses, and professionals seeking to navigate its complexities.
Technological Advancements Reshaping Production
Technological advancements are revolutionizing manufacturing processes. From automation and robotics on the factory floor to the implementation of the Internet of Things (IoT) for predictive maintenance, technology is enhancing efficiency and precision. Manufacturers embracing these innovations are poised to stay competitive and streamline their production capabilities.
Supply Chain Resilience in a Global Context
Recent insights in the manufacturing industry emphasize the importance of building resilient supply chains. The global nature of manufacturing necessitates a robust and flexible supply chain strategy. Insights cover topics such as supply chain visibility, risk management, and the adoption of digital tools to enhance the agility and responsiveness of supply chain networks.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices on the Rise
Sustainability has become a focal point in manufacturing insights. Businesses are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, from implementing green manufacturing processes to incorporating sustainable materials. Manufacturers recognizing the importance of environmental stewardship not only contribute to a greener planet but also align with consumer preferences for sustainable products.
Data-Driven Decision-Making in Operations
Data analytics is playing a pivotal role in manufacturing insights. The ability to collect, analyze, and derive insights from data is transforming decision-making processes. Manufacturers are leveraging data to optimize production schedules, reduce downtime, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Data-driven insights empower manufacturers to make informed strategic choices.
Reskilling the Manufacturing Workforce
Insights into the manufacturing industry underscore the need for a skilled workforce. As technology advances, reskilling becomes imperative. Manufacturers are investing in training programs to equip their workforce with the necessary skills for operating and maintaining advanced machinery. This focus on reskilling not only ensures a competent workforce but also addresses the industry’s evolving demands.
Customization and Personalization Trends
Consumer preferences are evolving towards personalized products, and manufacturing insights reflect this trend. Manufacturers are adapting to the demand for customization by implementing flexible production processes. Insights cover strategies for mass customization, allowing manufacturers to meet individualized customer needs while maintaining operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Navigating regulatory landscapes is a constant in manufacturing insights. Adhering to industry standards and regulatory requirements is crucial for maintaining product quality, ensuring workplace safety, and upholding ethical practices. Manufacturers staying informed about compliance issues position themselves to navigate legal challenges and build trust with stakeholders.
Innovations in Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, continues to be a focal point in manufacturing insights. This innovative technology allows for the creation of complex and customized components with reduced waste. Insights cover advancements in materials, scalability, and applications of additive manufacturing, offering manufacturers new possibilities for efficient production.
Collaboration and Partnerships Driving Innovation
Insights reveal a shift towards collaboration and partnerships in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers are forming strategic alliances with technology providers, research institutions, and other industry players to
Navigating Business Travel Trends: A Modern Landscape

Navigating Business Travel Trends: A Modern Landscape
Business travel has undergone significant transformations in recent years, shaped by technological advancements, changing work cultures, and global events. Understanding and adapting to these evolving trends is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their travel strategies and enhance the overall travel experience for employees.
Technology Revolutionizing Travel Management
The integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized how businesses manage and streamline travel. From artificial intelligence-powered booking platforms to mobile travel apps, technology enhances efficiency, provides real-time updates, and ensures a seamless travel experience. Embracing these innovations is key to staying ahead in the dynamic landscape of business travel.
Flexible Work Arrangements Impacting Travel Patterns
The rise of flexible work arrangements, accelerated by the global shift to remote and hybrid work models, has significantly impacted business travel patterns. Employees are increasingly combining work and leisure travel, leading to a blurring of lines between business and leisure trips. This trend necessitates flexible travel policies that accommodate diverse needs and preferences.
Sustainability as a Driving Force
Sustainability has emerged as a central theme in business travel. Companies are becoming more conscious of their carbon footprint and adopting eco-friendly practices. This includes choosing sustainable transportation options, supporting green accommodations, and integrating environmentally responsible policies into their travel programs. Sustainable business travel is not just a trend; it’s a commitment to corporate social responsibility.
Focus on Employee Well-being During Travel
The well-being of employees during business travel is gaining prominence. Companies are recognizing the importance of ensuring that employees remain healthy, rested, and engaged while on the road. This involves offering wellness programs, providing access to mental health resources, and selecting travel options that prioritize comfort and convenience.
Rise of Bleisure Travel for Work-Life Balance
Bleisure travel, the combination of business and leisure trips, is on the rise. Employees are increasingly seeking opportunities to extend their business trips for personal exploration. This trend not only enhances work-life balance but also presents an opportunity for businesses to attract and retain top talent by offering a more holistic approach to business travel.
Enhanced Duty of Care Protocols
With an increased focus on employee well-being, companies are implementing enhanced duty of care protocols. This includes robust safety measures, real-time tracking of travelers, and comprehensive risk management strategies. Proactive duty of care ensures that employees feel secure during their travels, contributing to a positive overall travel experience.
Virtual Meetings Impacting Travel Frequency
The widespread adoption of virtual meeting platforms has altered the frequency and necessity of business travel. While certain engagements still demand in-person interactions, virtual meetings have become a viable alternative for routine discussions, reducing the need for frequent travel. Striking the right balance between virtual and physical engagements is crucial for optimizing travel budgets and resources.
Integration of Travel Technology for Personalization
Personalization is becoming a hallmark of modern business travel. Companies are leveraging travel technology to tailor experiences based on individual preferences. From personalized itineraries to automated expense management, integrating technology enhances the overall travel experience and contributes to employee
Fostering Economic Growth Through Education Initiatives

Fostering Economic Growth Through Education Initiatives
In today’s rapidly evolving global landscape, the intersection of education and economic development plays a pivotal role in shaping the future. As nations strive for progress and prosperity, investing in education emerges as a catalyst for sustainable economic growth. This article explores the intricate relationship between education and economic development, shedding light on the transformative power of well-crafted educational initiatives.
The Foundation of Prosperity
Education serves as the bedrock of a prosperous society. It empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate an increasingly complex world. A well-educated workforce is not only more adept at addressing contemporary challenges but also more capable of driving innovation and productivity, two key factors that fuel economic development.
Empowering the Workforce
One of the primary ways education contributes to economic development is by empowering the workforce. A highly skilled and knowledgeable workforce is essential for industries to thrive and remain competitive in the global marketplace. As technological advancements continue to reshape industries, a workforce equipped with up-to-date skills becomes a valuable asset, attracting investments and fostering economic sustainability.
Closing the Skills Gap
The ever-changing demands of the job market highlight the importance of education in addressing the skills gap. By aligning educational curricula with industry needs, educational institutions can play a crucial role in producing graduates with the skills required by the workforce. This proactive approach not only benefits individuals seeking employment but also strengthens the economic fabric by ensuring a skilled and adaptable workforce.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Education fosters an environment conducive to entrepreneurship and innovation, both integral components of economic development. A well-rounded education system encourages creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills—qualities essential for driving entrepreneurial ventures. By supporting an entrepreneurial culture, education becomes a catalyst for job creation and economic diversification.
Investment in Infrastructure
Robust education systems often attract investments in infrastructure. Nations recognizing the value of education are more likely to invest in schools, colleges, and research institutions. These investments not only enhance the quality of education but also create construction jobs and stimulate economic activity in the short term, laying the groundwork for long-term development.
Global Competitiveness
In an interconnected world, global competitiveness is a key driver of economic success. A nation’s education system plays a pivotal role in determining its standing in the global arena. A well-educated workforce enhances a country’s competitiveness by contributing to research, development, and innovation, ultimately attracting international investments and fostering economic growth.
The Role of Technology in Education
The integration of technology in education further amplifies its impact on economic development. Technologically literate individuals are better equipped to adapt to the evolving demands of the digital age. Educational initiatives that embrace technology not only prepare students for the future job market but also contribute to the growth of the technology sector, a potent driver of economic development.
Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of education on economic development are evident, challenges such as accessibility, affordability, and quality persist. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort
Tech Innovation: Catalyst for Economic Transformation
Driving Progress: The Interplay Between Technological Innovation and the Economy
Technological innovation is a driving force that continually shapes and transforms the economic landscape. This article delves into the intricate relationship between technological innovation and the economy, exploring how advancements in technology propel economic growth, reshape industries, and redefine the way we live and work.
Catalyst for Economic Growth: Fueling Productivity and Efficiency
Technological innovation acts as a catalyst for economic growth by enhancing productivity and efficiency across industries. From automation and artificial intelligence to advanced manufacturing processes, innovative technologies streamline operations, reduce costs, and contribute to overall economic output. Understanding this symbiotic relationship is key to grasping the dynamics of modern economies.
Industry Disruption: Reshaping Traditional Business Models
One of the hallmarks of technological innovation is its disruptive impact on traditional business models. New technologies often emerge, challenging established norms and reshaping entire industries. The rise of e-commerce, the sharing economy, and digital platforms exemplify how innovation can redefine market structures and create new economic opportunities.
Job Creation and Transformation: Navigating the Employment Landscape
While technological innovation may automate certain tasks, it also creates new job opportunities and transforms existing roles. The tech sector itself becomes a source of employment, and industries adapt to incorporate digital skills. Analyzing the evolving employment landscape sheds light on the dynamic relationship between technology and workforce trends.
Global Connectivity: Expanding Economic Boundaries
Technological innovation facilitates global connectivity, breaking down geographical barriers and expanding economic opportunities. Digital communication, e-commerce, and remote collaboration technologies enable businesses to operate on a global scale. Understanding how technological innovation fosters global economic interconnectedness is crucial for businesses navigating international markets.
Innovation Ecosystems: Collaboration and Entrepreneurship
Thriving technological innovation relies on robust innovation ecosystems that foster collaboration and entrepreneurship. Research institutions, startups, and established companies form interconnected networks, driving breakthroughs. Examining the components of innovation ecosystems provides insights into the factors that contribute to sustained technological advancement.
Government Policies: Nurturing Innovation Through Regulation
Government policies play a significant role in nurturing technological innovation. Regulations, incentives, and investments in research and development shape the innovation landscape. Analyzing the impact of government policies on technological innovation provides a broader understanding of the collaborative efforts needed to drive economic progress.
Consumer Behavior: Adapting to Tech-Driven Experiences
Technological innovation not only transforms industries but also influences consumer behavior. The adoption of new technologies creates shifts in consumer expectations and preferences. Businesses that understand and respond to these changes are better positioned to thrive in the evolving marketplace shaped by technological innovation.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Balancing Progress
While technological innovation brings about numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and ethical considerations. Issues such as job displacement, privacy concerns, and the digital divide require thoughtful consideration. Addressing these challenges is essential for creating a balanced and inclusive technological landscape that benefits society as a whole.
Visit Technological Innovation and the Economy for In-Depth Insights
For a comprehensive exploration of technological innovation and its impact on the economy, visit Technological Innovation and the Economy.
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges: Innovative Solutions
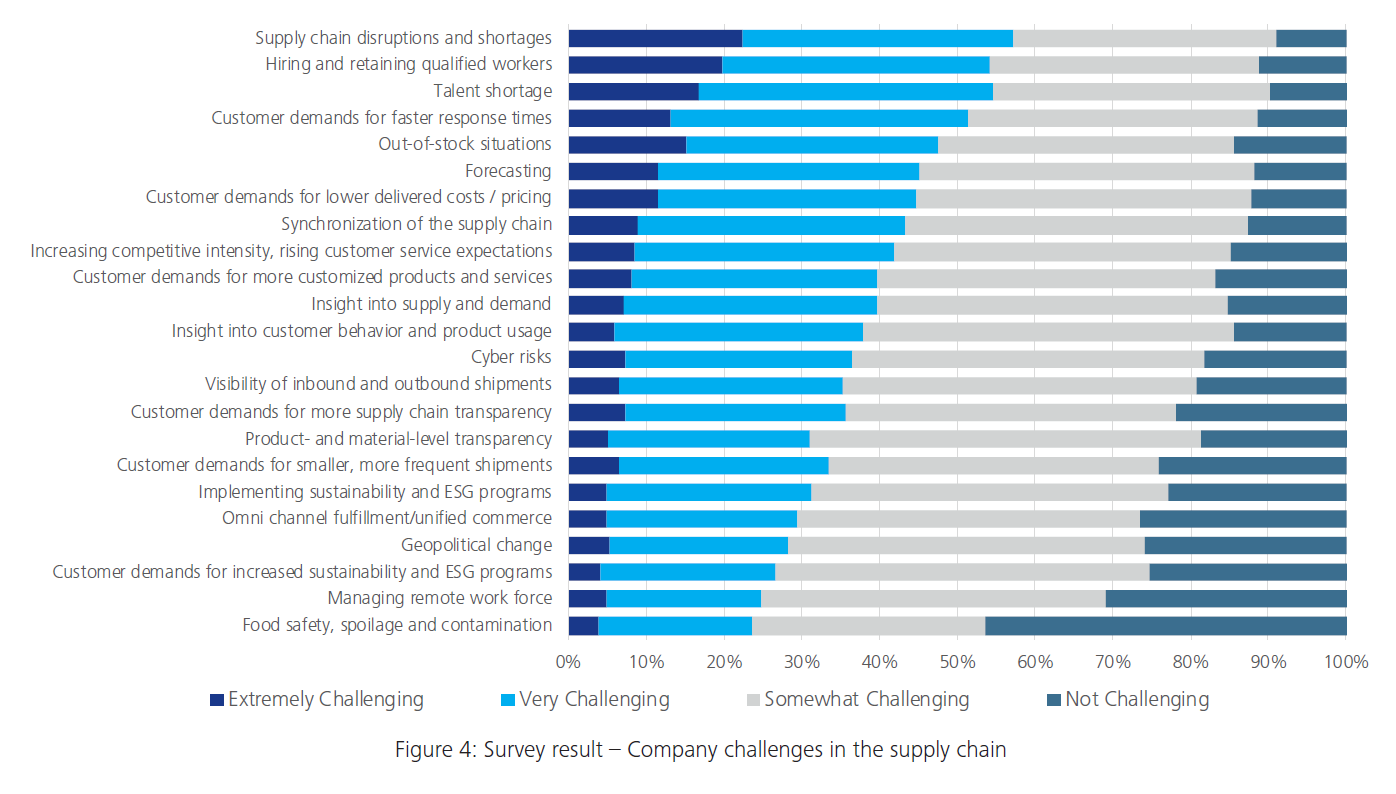
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges: Innovative Solutions
The global supply chain is facing unprecedented disruptions, requiring businesses to reassess and adapt to ensure continuity and resilience. In this article, we explore the challenges posed by supply chain disruptions and innovative solutions to navigate through these turbulent times.
Understanding Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions can arise from various factors, including natural disasters, geopolitical events, and unforeseen economic challenges. The interconnected nature of global supply chains means that a disruption in one part of the world can have cascading effects across industries. The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly highlighted the vulnerability of supply chains to unexpected shocks.
Impact on Businesses: From Delays to Shortages
The repercussions of supply chain disruptions are felt by businesses of all sizes. From delays in production and distribution to shortages of critical components, the disruptions can lead to increased costs, revenue loss, and potential damage to a company’s reputation. Businesses must proactively address these challenges to stay afloat in the face of uncertainty.
Technological Integration for Enhanced Visibility
One of the innovative solutions to supply chain disruptions is the integration of advanced technologies for enhanced visibility. Businesses are leveraging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, blockchain, and real-time analytics to gain insights into their supply chains. This increased visibility allows for better risk assessment, early detection of potential disruptions, and informed decision-making.
Diversification and Redundancy Strategies
To mitigate the impact of disruptions, businesses are adopting diversification and redundancy strategies. This involves diversifying supplier networks, sourcing materials from multiple regions, and maintaining safety stock levels. By spreading risk across different suppliers and geographic locations, businesses can enhance their resilience to unforeseen disruptions.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaboration
Collaboration is becoming a key component of supply chain resilience. Establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers, logistics providers, and other stakeholders creates a network of support. Collaborative efforts enable the sharing of information, resources, and expertise, fostering a more agile and responsive supply chain ecosystem.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making is paramount in navigating supply chain disruptions. Businesses are leveraging big data analytics to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential risks. The use of predictive analytics enables businesses to proactively respond to changes in market conditions and supply chain dynamics.
Supply Chain Transparency and Ethical Sourcing
Transparency in the supply chain is gaining prominence as companies and consumers alike prioritize ethical sourcing. Businesses are investing in technologies that provide end-to-end visibility, allowing consumers to trace the origins of products. Ethical sourcing practices not only build trust with consumers but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
Reskilling the Workforce for Agility
The human element plays a crucial role in navigating supply chain disruptions. Businesses are reskilling their workforce to enhance agility and adaptability. Cross-training employees, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and investing in skills relevant to supply chain management contribute to a more versatile and resilient workforce.
Investment in Robust Risk Management Strategies
Supply chain disruptions necessitate a reevaluation and enhancement of risk management strategies. Businesses
Harvesting Success: Agriculture Business Trends

Harvesting Success: Agriculture Business Trends
The agricultural landscape is undergoing transformative changes, driven by technological innovations, sustainability imperatives, and evolving consumer demands. Examining the current trends in agriculture business provides valuable insights into the strategies, practices, and innovations shaping the future of farming and agribusiness.
Precision Agriculture and Technology Integration
Agriculture business trends highlight the increasing adoption of precision agriculture practices. Technology integration, including GPS-guided tractors, drones for crop monitoring, and data analytics, is optimizing farm operations. Precision agriculture not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to resource conservation, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions for improved yields.
Sustainable Farming Practices and Agroecology
Sustainability is a cornerstone in agriculture business updates. Farmers are embracing agroecological practices that prioritize environmental stewardship. From organic farming and regenerative agriculture to water conservation techniques, sustainable practices are gaining traction. Agriculture business trends emphasize the importance of balancing productivity with long-term ecological resilience.
Smart Farming and IoT Solutions
The advent of smart farming, powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), is revolutionizing agriculture. Smart sensors, connected devices, and real-time monitoring systems enhance farm management. Agriculture business trends showcase how IoT solutions are improving crop yields, resource utilization, and overall farm efficiency. Smart farming is a key driver in the quest for a more sustainable and technologically advanced agriculture sector.
Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture
Urbanization and the demand for locally sourced produce are fueling trends in vertical farming and controlled environment agriculture. Agriculture business updates explore the rise of vertical farms, hydroponics, and aeroponics. These innovative methods allow for year-round production, reduced water usage, and the cultivation of crops in urban areas, addressing food security challenges.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localized Production
Recent agriculture business trends underscore the importance of supply chain resilience. Global events have highlighted vulnerabilities in traditional supply chains, prompting a shift towards localized production. Agriculture business updates discuss the rise of agribusinesses focused on regional markets, reducing dependency on long and complex supply chains.
Digital Platforms and Agricultural Marketplaces
Digital platforms and agricultural marketplaces are transforming the way farmers connect with buyers, suppliers, and consumers. Agriculture business trends highlight the emergence of online platforms facilitating direct-to-consumer sales, farm-to-table initiatives, and transparent supply chains. These digital solutions empower farmers to reach broader markets and enhance traceability.
Agtech Startups and Innovations
Agtech startups are at the forefront of driving innovations in agriculture. From AI-powered crop monitoring to blockchain applications for traceability, agriculture business updates delve into the diverse innovations introduced by startups. These technological advancements are reshaping traditional farming practices and contributing to increased efficiency and sustainability.
Climate-Resilient Agriculture and Adaptation Strategies
Climate change is a significant factor influencing agriculture business trends. Farmers are adopting climate-resilient agriculture practices and developing adaptation strategies. Agriculture business updates explore the integration of drought-resistant crops, water management solutions, and precision irrigation to mitigate the impact of climate variability on agricultural productivity.
Rural Development and Agribusiness Opportunities
Agriculture business trends extend beyond the farm gate to encompass rural development and agribusiness opportunities. Initiatives promoting entrepreneurship, value addition,
Gaming Industry Business News: Trends, Updates, and Insights
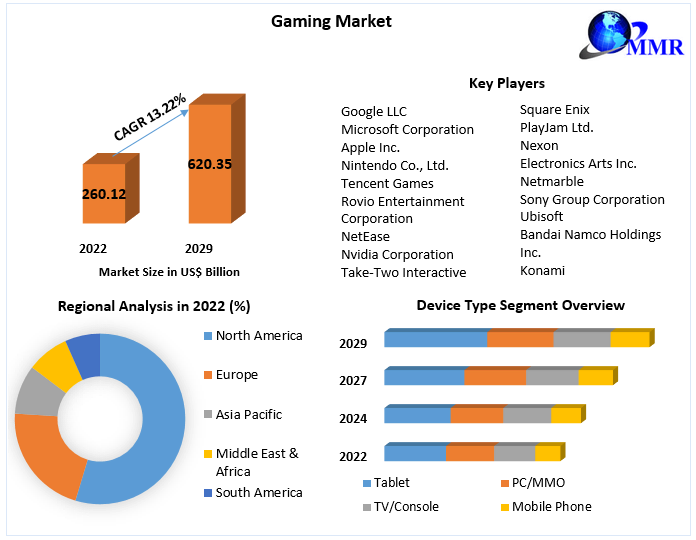
Introduction:
The gaming industry is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, constantly influenced by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. In this article, we delve into the latest business news, trends, and insights shaping the gaming landscape.
Rise of Cloud Gaming Services:
One of the prominent trends in the gaming industry is the rise of cloud gaming services. With platforms like Google Stadia, Microsoft xCloud, and NVIDIA GeForce Now, gamers can enjoy high-quality gaming experiences without the need for powerful hardware, marking a significant shift in accessibility and gameplay dynamics.
Gaming Industry Business News Link:
Stay updated on the latest Gaming Industry Business News here. Explore trends, updates, and insights into the dynamic world of gaming.
Esports’ Global Expansion:
Esports continues to gain traction globally, transforming competitive gaming into a mainstream phenomenon. The esports industry’s rapid growth has led to increased investments, sponsorships, and major tournaments, making it a lucrative market with a dedicated fan base.
Innovations in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):
Advancements in VR and AR technologies are enhancing the immersive gaming experience. From VR gaming headsets to AR-enabled mobile games, developers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, creating new dimensions for gamers to explore.
Mobile Gaming Dominance:
The mobile gaming sector remains a powerhouse within the industry. With the widespread availability of smartphones, developers are creating innovative and engaging mobile games, capturing a massive audience. Mobile gaming’s accessibility and convenience contribute significantly to its sustained popularity.
Gaming as a Social Experience:
The social aspect of gaming has become increasingly pronounced. With features like in-game chat, live streaming, and collaborative gameplay, gaming platforms are fostering communities, turning gaming into a shared experience that goes beyond the traditional solitary gaming sessions.
Integration of Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is making inroads into the gaming industry, introducing new possibilities for secure in-game transactions, ownership of virtual assets, and the creation of blockchain-based gaming ecosystems. This trend has the potential to revolutionize in-game economies.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Initiatives:
As environmental concerns grow, the gaming industry is taking steps towards sustainability. From eco-friendly packaging to energy-efficient gaming consoles, companies are incorporating eco-friendly practices, aligning with a broader global push for environmental responsibility.
Gaming Industry in the Metaverse:
The concept of the metaverse, a collective virtual shared space, is influencing the gaming industry’s future. Game developers are exploring ways to create interconnected virtual worlds, offering players immersive experiences and new dimensions of gameplay within a vast digital universe.
Challenges and Opportunities Amidst Business News:
The gaming industry faces challenges such as addressing diversity and inclusion, managing microtransactions, and adapting to rapidly changing technologies. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth, driving the industry forward.
Conclusion:
In a world where technology and entertainment intersect, the gaming industry continues to captivate audiences with innovation and business dynamics. Staying informed about the latest business news, trends, and insights is crucial for gaming enthusiasts, industry professionals, and anyone intrigued by the ever-evolving world of gaming.
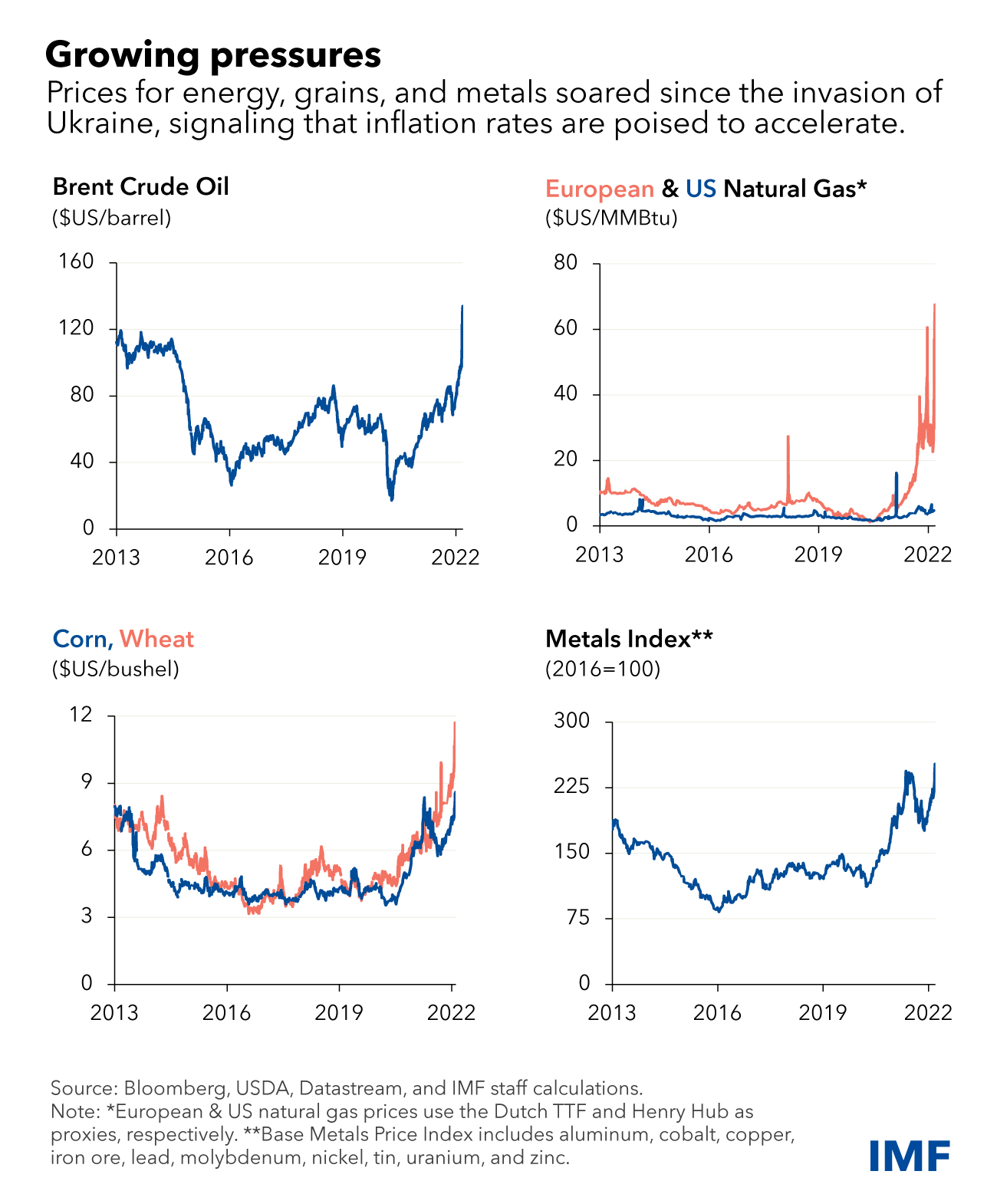
Economic Impact of Energy Regulation Changes

Navigating the Energy Landscape: Assessing the Economic Impact of Regulatory Changes
The energy sector plays a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes, and changes in energy regulations can send ripple effects throughout various industries. This article delves into the intricate economic impact stemming from shifts in energy regulations, shedding light on how these changes influence investment patterns, employment dynamics, and overall economic sustainability.
Renewable Energy Investments and Job Creation
Changes in energy regulations often influence the direction of investments in the energy sector. Policies that favor renewable energy sources may lead to increased investments in solar, wind, and other sustainable technologies. These investments, in turn, contribute to job creation in the renewable energy industry, stimulating economic growth while addressing environmental concerns.
Impact on Traditional Energy Sectors and Workforces
Conversely, regulatory changes may impact traditional energy sectors such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Stricter regulations on emissions and environmental standards may result in economic challenges for these industries, affecting employment dynamics in regions heavily reliant on traditional energy sources. Navigating this transition requires thoughtful policies to support affected workforces.
Electricity Pricing and Consumer Affordability
Energy regulations play a role in shaping electricity pricing, which directly affects consumers and businesses. Policies promoting renewable energy may impact pricing structures, with potential implications for consumer affordability. Balancing the transition to cleaner energy sources with the economic well-being of consumers is a key consideration for policymakers.
Grid Modernization and Infrastructure Investments
Changes in energy regulations often coincide with efforts to modernize energy grids and infrastructure. Policies that encourage grid modernization contribute to a more efficient and resilient energy system. These infrastructure investments not only enhance energy reliability but also stimulate economic activity through the creation of jobs in construction, technology, and related sectors.
Incentives for Energy Efficiency and Innovation
Regulatory changes may introduce incentives for energy efficiency and innovation. Policies that reward businesses and individuals for adopting energy-efficient practices contribute to sustainability goals while fostering innovation. This, in turn, has economic implications as businesses invest in new technologies and practices that align with evolving regulatory standards.
International Energy Trade and Geopolitical Impact
Energy regulations have implications for international energy trade and geopolitics. Policies that affect the export and import of energy resources influence global economic relationships. Shifts in energy regulations may alter the geopolitical landscape, impacting alliances, trade balances, and the economic standing of nations involved in the energy trade.
Energy Independence and National Security Considerations
Some energy regulations aim to enhance energy independence and address national security concerns. Policies promoting domestic energy production and reducing reliance on foreign sources contribute to economic stability and national security. However, these policies may also have economic consequences, affecting global energy markets and trade relationships.
Environmental Externalities and Economic Valuation
Regulations often aim to address environmental externalities associated with energy production. Policies that internalize the costs of environmental impacts, such as pollution and carbon emissions, contribute to more accurate economic valuation of energy sources. This shift can influence investment decisions, favoring cleaner and more sustainable options.
Social
Revitalizing Economies: Strategic Paths to Recovery
Revitalizing Economies: Strategic Paths to Recovery
The global landscape has been significantly impacted by economic challenges, prompting the need for innovative strategies to foster recovery. In this exploration, we delve into key economic recovery strategies that nations and businesses can employ to revitalize economies and promote sustainable growth.
Adapting Fiscal Policies for Resilience
One of the primary strategies for economic recovery involves adapting fiscal policies to promote resilience. Governments can implement targeted fiscal stimulus measures to boost demand, support businesses, and create jobs. By carefully calibrating these policies, authorities can lay the groundwork for a robust and sustainable economic rebound.
Investing in Infrastructure for Job Creation
A strategic focus on infrastructure investment becomes instrumental in generating employment opportunities and stimulating economic activity. Upgrading and expanding infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and technology, not only addresses immediate job creation needs but also lays the foundation for long-term economic growth.
Supporting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
Small and medium-sized enterprises form the backbone of many economies. Providing tailored support for SMEs, such as access to financing, training programs, and digitalization initiatives, can fuel their recovery and contribute significantly to overall economic resilience. Empowering these businesses aids in job retention and fosters entrepreneurship.
Embracing Digital Transformation for Innovation
In an increasingly digital world, embracing digital transformation is a key strategy for economic recovery. Encouraging businesses to innovate and adopt digital technologies enhances efficiency, competitiveness, and adaptability. Government initiatives to facilitate digitalization across sectors can position economies for sustained growth in the post-pandemic era.
Building Sustainable and Inclusive Economies
Sustainability and inclusivity are integral components of effective economic recovery. Investing in renewable energy, promoting environmentally friendly practices, and fostering social inclusiveness contribute to resilient economies. These strategies not only address immediate economic challenges but also lay the groundwork for a more sustainable and equitable future.
Facilitating International Trade and Collaboration
International trade plays a pivotal role in economic recovery. Governments can facilitate trade by removing barriers, negotiating favorable agreements, and promoting collaboration with global partners. Strengthening international ties fosters economic resilience and opens up new opportunities for businesses to expand their markets.
Investment in Education and Workforce Development
A skilled and adaptable workforce is crucial for economic recovery. Investing in education and workforce development programs ensures that individuals are equipped with the skills needed for emerging industries. This approach not only addresses immediate unemployment challenges but also positions nations for success in the evolving global economy.
Implementing Health and Wellness Initiatives
The ongoing global health challenges underscore the importance of health and wellness initiatives in economic recovery. Prioritizing public health measures, investing in healthcare infrastructure, and promoting wellness programs contribute to a healthier and more productive workforce. A healthy population is vital for sustained economic growth.
Strategic Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are powerful mechanisms for driving economic recovery. Collaboration between governments and private enterprises can leverage resources, expertise, and innovation. Strategic PPPs in areas such as infrastructure development, technology adoption, and research and development can accelerate economic revitalization.
Navigating Economic Recovery with Innovation
To
Balancing Profit and Purpose: Economic Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): A Paradigm Shift in Business Philosophy
Corporate Social Responsibility, once considered a philanthropic endeavor, has evolved into a strategic imperative for businesses. This paradigm shift reflects a broader recognition that economic success is intertwined with societal well-being. Exploring the economic effects of CSR unveils a nuanced relationship between profit and purpose.
Enhanced Reputation and Consumer Loyalty
Engaging in socially responsible practices contributes significantly to a company’s reputation. Consumers increasingly seek out businesses that align with their values, and companies with robust CSR initiatives often enjoy enhanced brand loyalty. This positive perception translates into economic benefits, fostering customer retention and attracting new clientele.
Stakeholder Relations: Building Trust and Long-Term Partnerships
Beyond consumer relations, CSR plays a pivotal role in cultivating strong ties with stakeholders. Whether employees, investors, or local communities, businesses that prioritize social responsibility build trust and foster long-term partnerships. These relationships, grounded in shared values, contribute to a stable and supportive business environment.
Cost Savings through Sustainability Initiatives
Many CSR initiatives focus on sustainability, not only benefiting the planet but also generating cost savings for businesses. Adopting eco-friendly practices, reducing waste, and optimizing energy consumption contribute to operational efficiency. These sustainable efforts often lead to direct economic advantages, aligning environmental responsibility with financial prudence.
Employee Productivity and Retention
Investing in CSR positively impacts the workplace, influencing employee morale, productivity, and retention. Companies that prioritize social responsibility attract top talent and create a positive work culture. Engaged and satisfied employees contribute to increased productivity, innovation, and a reduction in recruitment and training costs.
Access to Capital and Investment Opportunities
The financial community increasingly considers CSR performance when making investment decisions. Companies with strong social responsibility credentials often find it easier to access capital and secure favorable lending terms. Sustainable and ethical business practices are seen as indicators of long-term financial viability, attracting socially conscious investors.
Mitigating Risks and Enhancing Resilience
CSR acts as a risk mitigation strategy for businesses. By addressing social and environmental issues proactively, companies can prevent reputational damage and legal complications. Additionally, a robust CSR framework enhances organizational resilience, helping businesses navigate unforeseen challenges with greater adaptability.
Regulatory Compliance and Long-Term Viability
The regulatory landscape is evolving, with a growing emphasis on ethical and sustainable business practices. Companies that integrate CSR into their operations stay ahead of regulatory changes, ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties. Long-term viability in the ever-changing business environment is closely tied to responsible and adaptive practices.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
CSR fosters innovation as companies seek sustainable and socially responsible solutions to business challenges. This innovation, in turn, provides a competitive advantage. Businesses that pioneer ethical and sustainable practices position themselves as industry leaders, attracting a customer base that values innovation and responsibility.
Community Development and Economic Impact
CSR initiatives often extend beyond business operations to contribute to community development. Whether through philanthropy, education programs, or local partnerships, businesses can positively impact the economic well-being of the communities they serve. This community engagement creates a reciprocal relationship, benefiting both
Economic Impact of Tax Policy Changes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-fiscal-policy-types-objectives-and-tools-3305844-final-5b4e4a59c9e77c005bbfde3a.png)
Navigating Fiscal Landscapes: Unraveling the Economic Impact of Tax Policy Changes
Tax policies play a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes, and alterations in tax regulations can have profound effects on various sectors. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate economic impact stemming from changes in tax policies, examining how these shifts influence government revenue, business operations, and overall economic well-being.
Government Revenue and Fiscal Policy
One of the primary economic impacts of changes in tax policies is their effect on government revenue. Taxation is a key source of funding for public services and government initiatives. Alterations in tax policies, whether through rate changes or structural adjustments, directly impact the revenue available to governments. Assessing the economic impact involves understanding how changes in tax policies influence fiscal policy decisions and government budgeting.
Business Operations and Investment Patterns
Changes in tax policies can significantly influence business operations and investment patterns. Policies that alter corporate tax rates, investment incentives, or depreciation schedules impact the financial decisions of businesses. Understanding the economic impact involves analyzing how businesses adapt their operations, investment strategies, and expansion plans in response to changes in tax policies.
Consumer Spending and Disposable Income
Tax policies directly influence the disposable income of individuals and households. Changes in income tax rates, deductions, and credits impact how much money consumers have available for spending. The economic impact involves assessing how alterations in tax policies influence consumer behavior, saving patterns, and overall levels of disposable income.
Small Businesses and Entrepreneurship
The economic impact of changes in tax policies extends to small businesses and entrepreneurship. Policies that provide tax relief or incentives for small businesses can stimulate entrepreneurship and business growth. Conversely, changes that introduce additional tax burdens may pose challenges for small enterprises. Evaluating the economic impact involves understanding how tax policies shape the landscape for small businesses.
International Competitiveness and Global Investment
Tax policies also contribute to a nation’s international competitiveness. Policies that create a favorable tax environment may attract foreign investment and enhance the competitiveness of domestic industries on the global stage. Analyzing the economic impact involves assessing how changes in tax policies influence global investment patterns and the overall competitiveness of a country’s economy.
Wealth Distribution and Social Equity
Tax policies are instrumental in shaping wealth distribution and social equity within societies. Progressive tax systems aim to distribute the tax burden based on income levels. Changes in tax policies can impact income disparities and contribute to or mitigate wealth inequality. Understanding the economic impact involves examining how tax policies align with broader social and economic equity goals.
Real Estate Markets and Property Values
Tax policies have implications for real estate markets and property values. Policies related to property taxes, deductions for mortgage interest, and capital gains taxes influence the real estate landscape. Economic impact assessments involve evaluating how changes in tax policies affect housing affordability, property values, and the overall stability of real estate markets.
Retirement Planning and Pension Systems
Changes in tax policies can affect retirement planning and
Strategies for Business Scalability Success

Unlocking Growth: Strategies for Business Scalability Success
In the dynamic landscape of business, the ability to scale is often the key differentiator between success and stagnation. Implementing effective scalability strategies empowers businesses to expand their operations, reach new markets, and thrive in ever-evolving industries.
Understanding the Foundations of Scalability
At the heart of business scalability is a solid foundation. Companies must build scalable processes, systems, and infrastructure from the outset. This ensures that as demand increases or market conditions change, the business can seamlessly adjust without facing bottlenecks or operational constraints.
Embracing Technological Advancements
In the digital age, leveraging technological advancements is crucial for scalability. Integrating scalable software solutions, cloud-based infrastructure, and automation tools can streamline operations and provide the flexibility needed to adapt to changing business requirements. Technological scalability is not just an option but a necessity for modern businesses.
Flexible and Scalable Financial Management
Financial agility is a linchpin for business scalability. Adopting flexible financial management practices allows businesses to allocate resources efficiently, respond to market fluctuations, and make strategic investments in expansion. Scalable financial models enable companies to navigate growth without compromising stability.
Talent Acquisition and Development Strategies
A scalable workforce is essential for sustained growth. Businesses should focus on acquiring and developing talent that aligns with their long-term objectives. Implementing scalable training programs and fostering a culture of continuous learning ensures that the workforce evolves alongside the business, ready to take on new challenges.
Strategic Partnerships for Scalable Growth
Collaborating with strategic partners can significantly enhance scalability. Partnerships provide access to complementary resources, expertise, and customer bases. By forming alliances with like-minded businesses, companies can navigate expansion more effectively and tap into new opportunities without shouldering the entire burden alone.
Customer-Centric Scalability Approaches
Understanding and meeting customer needs are paramount for scalability. Scalable businesses prioritize customer-centric strategies, such as personalized experiences, efficient customer support, and scalable product offerings. Aligning scalability with customer satisfaction creates a foundation for sustainable growth.
Scalability Through Diversification
Diversifying products, services, or markets is a classic strategy for scalability. It reduces reliance on a single revenue stream and opens avenues for expansion. However, strategic diversification requires careful planning and analysis to ensure that it aligns with the overall business strategy.
Data-Driven Decision-Making for Scalability
In the era of big data, leveraging analytics for decision-making is a game-changer for scalability. Businesses that harness data insights can make informed choices, identify growth opportunities, and optimize processes. Data-driven scalability ensures that decisions are rooted in real-time information, mitigating risks associated with uncertainty.
Agility as a Core Scalability Principle
Scalable businesses are inherently agile. They can swiftly adapt to market changes, embrace innovation, and pivot when necessary. Building an agile organizational culture fosters resilience and responsiveness, enabling businesses to navigate challenges and seize opportunities as they arise.
Navigating the Future with Business Scalability Strategies
In conclusion, the journey to business scalability is a dynamic and strategic undertaking. By understanding the foundations, embracing technology, nurturing talent, forming partnerships, and staying customer-centric, businesses can position themselves for sustained
Global Conflicts’ Economic Fallout: Navigating Consequences
Global Conflicts’ Economic Fallout: Navigating Consequences
The echoes of global conflicts reverberate far beyond the battlefield, leaving a lasting imprint on the economic landscape. This exploration delves into the intricate web of economic consequences triggered by global conflicts and the challenges nations face in navigating their aftermath.
Destruction of Infrastructure and Economic Assets
One of the immediate economic consequences of global conflicts is the widespread destruction of infrastructure and economic assets. Wars often result in the bombing of vital transportation networks, factories, and communication systems. Rebuilding these structures requires significant financial resources, diverting funds that could be invested in economic development and growth.
Displacement and Humanitarian Costs
Global conflicts force millions to flee their homes, creating a massive refugee crisis with profound economic implications. The displaced population often strains resources in host countries, leading to increased demand for humanitarian aid. The costs of providing shelter, healthcare, and basic necessities to refugees contribute to a significant economic burden on both the affected and assisting nations.
Impact on Global Trade and Commerce
Global conflicts disrupt the flow of international trade and commerce, affecting economies worldwide. Trade routes may be compromised, and sanctions imposed on belligerent nations can lead to economic isolation. The resulting decline in global trade adversely impacts businesses, disrupts supply chains, and hampers economic growth in both conflict zones and beyond.
Shifts in Geopolitical Alliances and Trade Relationships
The aftermath of global conflicts often reshapes geopolitical alliances and trade relationships. Former allies may become adversaries, leading to realignments in international trade partnerships. Nations may need to adapt their economic strategies to navigate changing political dynamics, potentially leading to economic isolation or the forging of new alliances.
Debt Accumulation and Economic Strain
Financing global conflicts frequently involves taking on substantial amounts of debt. The accumulation of war-related debt places a severe strain on a nation’s economy. Servicing this debt diverts funds from essential public services, infrastructure development, and social programs, hindering long-term economic stability and growth.
Economic Inequality and Social Disparities
The economic consequences of global conflicts exacerbate existing inequalities and contribute to social disparities. War disrupts employment opportunities, leading to increased unemployment rates. Disruptions in education and healthcare further deepen societal divides, creating lasting economic challenges that persist long after the conflict has ended.
Environmental Degradation and Economic Impact
Global conflicts often result in environmental degradation due to factors like pollution, deforestation, and the use of destructive weaponry. The long-term economic impact of environmental damage is substantial, affecting agriculture, biodiversity, and public health. Mitigating these environmental consequences requires significant investment and poses additional economic challenges.
Reconstruction Efforts and Economic Recovery
Post-conflict reconstruction efforts are crucial for economic recovery. Rebuilding infrastructure, restoring social services, and creating a stable environment for businesses are essential components of recovery plans. The effectiveness of these efforts influences the speed and success of economic recovery in the aftermath of global conflicts.
Psychological Impact and Productivity Challenges
Beyond the physical destruction, global conflicts leave a lasting psychological impact on individuals and societies. Mental health challenges, trauma, and
Navigating Economic Consequences: Cybersecurity Threats

Navigating Economic Consequences: Cybersecurity Threats
In an interconnected digital era, the economic landscape is increasingly shaped by the pervasive impact of cybersecurity threats. This exploration delves into the intricate web of economic consequences triggered by cyber threats, unraveling the complex dynamics that businesses and nations must navigate in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges.
Rising Financial Costs of Cybersecurity Incidents
Cybersecurity threats inflict a substantial financial toll on businesses and economies. The costs associated with data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cyber incidents include not only immediate financial losses but also long-term repercussions. From restoring compromised systems to addressing reputational damage, businesses bear the burden of significant financial costs in the aftermath of cybersecurity incidents.
Impact on Business Operations and Productivity
Cybersecurity threats disrupt the normal flow of business operations, leading to downtime, decreased productivity, and operational inefficiencies. Businesses must divert resources to address and mitigate the impact of cyber incidents, hindering their ability to focus on core activities. The pervasive nature of cyber threats poses a constant challenge to maintaining seamless business operations.
Loss of Intellectual Property and Innovation Setbacks
The theft of intellectual property through cyber espionage poses a direct threat to innovation and competitiveness. Cyber attackers, often state-sponsored or cybercriminal groups, target proprietary information, trade secrets, and research and development data. The loss of intellectual property not only hampers innovation but can also lead to setbacks in global competitiveness as businesses struggle to protect their valuable assets.
Erosion of Customer Trust and Reputation Damage
The fallout from cybersecurity incidents extends beyond immediate financial and operational impacts to the realm of customer trust and reputation. Breaches that compromise sensitive customer data erode trust, and the resulting reputational damage can be long-lasting. Rebuilding trust is a formidable task, often requiring significant investments in communication, transparency, and enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Ramifications
Cybersecurity threats trigger a cascade of regulatory and legal challenges. Governments and regulatory bodies impose stringent requirements on businesses to safeguard sensitive information. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe legal ramifications and financial penalties. Navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity regulations becomes a critical aspect of business operations in an era marked by increasing data protection concerns.
Economic Impact on Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
While large enterprises may have the resources to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face disproportionate economic consequences. Cyber threats that disrupt the operations of SMEs can lead to financial distress, business closures, and job losses. Bridging the cybersecurity gap for SMEs becomes essential for fostering economic resilience.
Escalation of Cybersecurity Insurance Costs
As the frequency and sophistication of cyber threats increase, the demand for cybersecurity insurance has surged. However, the economic consequences of cyber threats extend to the insurance sector. Insurers are grappling with the rising costs of cyber claims, leading to an escalation in cybersecurity insurance premiums. This dynamic further underscores the economic ripple effect of cybersecurity threats across various industries.
Cybersecurity Threats in Critical Infrastructure
The targeting of
Navigating Post-Pandemic Economic Challenges: A Roadmap to Recovery

Navigating Post-Pandemic Economic Challenges: A Roadmap to Recovery
The global landscape has undergone significant transformations in the aftermath of the pandemic, presenting a myriad of economic challenges. In this exploration, we unravel the complexities and strategize a roadmap towards recovery in the post-pandemic era.
The Unprecedented Disruption and Economic Fallout
The onset of the pandemic unleashed unprecedented disruption across industries, resulting in economic fallout worldwide. Lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and reduced consumer spending sent shockwaves through the global economy. Understanding the depth of these challenges is crucial in formulating effective recovery strategies.
Impact on Small Businesses and Employment Dynamics
Small businesses bore a disproportionate brunt during the pandemic, facing closures, financial strains, and operational hurdles. The repercussions extended to employment dynamics, with job losses and shifts in labor markets. Addressing the specific challenges faced by small businesses and revitalizing employment opportunities are integral components of the recovery process.
Supply Chain Resilience and Global Dependencies
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, emphasizing the need for increased resilience. Dependency on specific regions for crucial supplies became evident as disruptions reverberated globally. The post-pandemic era calls for a reevaluation of supply chain strategies, focusing on resilience, diversification, and adaptability.
Digital Transformation as a Catalyst for Recovery
Amid challenges, the pandemic accelerated digital transformation across industries. Remote work, e-commerce, and digital communication became the new norm. Leveraging technology as a catalyst for recovery involves further integration, upskilling the workforce, and capitalizing on digital platforms to enhance business resilience and efficiency.
Government Stimulus and Economic Policies
Governments worldwide responded to the economic challenges with stimulus packages and policy interventions. The post-pandemic recovery hinges on the effectiveness of these measures. Governments must strike a balance between stimulating economic activity, addressing social disparities, and ensuring long-term fiscal sustainability.
The Evolution of Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
Consumer behavior underwent a paradigm shift during the pandemic, influencing market trends. E-commerce, remote services, and health-related industries experienced significant growth. Understanding the evolving landscape of consumer preferences is essential for businesses to realign strategies and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Healthcare System Strengthening and Preparedness
The pandemic exposed weaknesses in healthcare systems globally. Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, investing in research and development, and enhancing preparedness for future health crises are vital components of post-pandemic recovery. Collaborations between public and private sectors are crucial for building robust healthcare systems.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Considerations
The post-pandemic recovery provides an opportunity to embed sustainability in economic practices. Emphasizing environmental considerations, adopting sustainable business models, and integrating eco-friendly practices contribute to long-term resilience and align with global efforts towards a greener future.
Global Cooperation and Collaborative Solutions
Post-pandemic challenges transcend borders, emphasizing the need for global cooperation. Collaborative solutions, information sharing, and joint efforts in research and development foster a collective approach to recovery. International partnerships are instrumental in addressing challenges that require coordinated responses.
To explore comprehensive insights into the economic challenges in the post-pandemic era and strategies for recovery, visit Vexhibits.com. This platform provides valuable resources and trends, offering a
Economic Impact of Infrastructure Policy Changes
Economic Impact of Infrastructure Policy Changes
In recent times, the economic landscape has been shaped by dynamic shifts in infrastructure policies. These changes have far-reaching consequences, influencing various sectors and impacting the overall economic health of nations.
The Ripple Effect on Industries
Infrastructure policy alterations send ripples across industries, affecting manufacturing, construction, and technology. Investments in modernizing transportation or upgrading energy grids create a demand for specialized goods and services. For instance, improved transportation infrastructure necessitates more vehicles and advanced logistics solutions, stimulating economic activity within these sectors.
Job Creation and Unemployment Rates
One of the direct consequences of changes in infrastructure policies is the creation of jobs. Large-scale projects often require a substantial workforce, leading to increased employment rates. Conversely, alterations in policy can also lead to job displacement, particularly in industries facing a decline due to outdated infrastructure.
Investor Confidence and Economic Growth
Changes in infrastructure policies significantly impact investor confidence. Clear and strategic policies signal stability, attracting investments that spur economic growth. On the flip side, uncertainty or frequent policy changes may deter investors, leading to capital flight and hindering economic development.
Environmental Sustainability and Green Infrastructure
As nations increasingly focus on sustainability, changes in infrastructure policies often align with environmental goals. Investments in green infrastructure, such as renewable energy projects and eco-friendly transportation, not only contribute to environmental conservation but also open up new economic opportunities in the burgeoning green sector.
Challenges in Implementation
While the long-term benefits of updated infrastructure policies are evident, the implementation phase poses challenges. Delays, budget overruns, and logistical issues can arise, impacting the anticipated economic benefits. Policymakers must navigate these challenges to ensure successful execution.
Global Competitiveness and Trade Dynamics
Infrastructure plays a pivotal role in a nation’s global competitiveness. Well-developed transportation networks and efficient logistics enhance a country’s ability to engage in international trade. Changes in infrastructure policies can thus have a direct impact on a nation’s standing in the global economic landscape.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Infrastructure policy changes often catalyze technological advancements and innovation. Investments in smart infrastructure, digital connectivity, and research and development drive progress. This not only enhances the overall quality of life but also stimulates economic growth through the creation of cutting-edge industries.
Public-Private Partnerships and Funding Mechanisms
Many infrastructure projects rely on collaboration between the public and private sectors. Changes in policy may affect the dynamics of these partnerships and influence funding mechanisms. Ensuring a conducive environment for public-private collaboration is crucial for the successful implementation of infrastructure projects.
Social Equity and Inclusive Development
Infrastructure policies play a role in shaping social equity and inclusive development. Access to basic amenities, such as reliable transportation and energy, can bridge socio-economic gaps. Conversely, neglecting certain regions or demographics in infrastructure planning can exacerbate disparities.
Linking Economic Consequences to Policy Changes
Amidst these economic considerations, the need for a balanced and informed approach to infrastructure policy changes becomes apparent. Stakeholders must be mindful of the broader economic implications as decisions are made. To explore further insights
Tech Business Developments: Navigating the Digital Frontier

Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, businesses find themselves navigating a dynamic digital frontier. This article explores the latest trends and transformative shifts in tech business developments, shedding light on the innovations shaping industries and redefining the future.
Digital Transformation: The Core of Tech Business Evolution:
At the heart of contemporary tech business developments is the concept of digital transformation. Companies across diverse sectors are leveraging advanced technologies to revamp their operations, enhance customer experiences, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: Shaping Smart Business Strategies:
AI continues to be a driving force in tech business developments. From predictive analytics to machine learning algorithms, businesses are integrating AI into their operations to gain insights, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions. The result is smarter, more efficient business strategies.
5G Revolution: Accelerating Connectivity and Innovation:
The rollout of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in tech business developments. With faster and more reliable connectivity, businesses are exploring new possibilities, from enhanced mobile experiences to the Internet of Things (IoT). The 5G revolution is reshaping how businesses operate and deliver services.
Cybersecurity Imperative: Safeguarding the Digital Landscape:
As technology advances, the importance of cybersecurity becomes paramount. Tech business developments include robust measures to safeguard digital assets and customer data. From encryption protocols to advanced threat detection systems, businesses are investing in cybersecurity to build trust and resilience.
E-commerce Innovations: Redefining Online Retail Experiences:
The intersection of technology and commerce is undergoing a revolution. E-commerce innovations are transforming the way businesses sell and consumers shop. From augmented reality in product visualization to personalized shopping experiences, tech developments are reshaping the online retail landscape.
Cloud Computing: Flexible Infrastructures for Scalable Growth:
Cloud computing remains a cornerstone of tech business developments. The flexibility and scalability offered by cloud solutions empower businesses to adapt to changing demands. From data storage to software as a service (SaaS), the cloud is a catalyst for innovation and efficient resource utilization.
Blockchain Applications: Beyond Cryptocurrencies:
While often associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology extends far beyond. In tech business developments, blockchain finds applications in secure supply chain management, transparent financial transactions, and even the verification of digital identities. The decentralized nature of blockchain brings trust and transparency to various business processes.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Immersive Experiences Take Center Stage:
AR and VR technologies are elevating user experiences across industries. From virtual product try-ons in retail to immersive training simulations in healthcare, these tech developments are creating new dimensions of interaction. Businesses are leveraging AR and VR to engage audiences in innovative and impactful ways.
Edge Computing: Enhancing Speed and Efficiency:
As data processing needs grow, edge computing emerges as a critical tech development. By bringing computation closer to the source of data, businesses enhance speed and reduce latency. This is particularly crucial for applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous systems.
Exploring the Tech Business Landscape:
For a comprehensive exploration of the latest tech business developments and their
Corporate Trends: Navigating the Shifting Business Landscape

Introduction:
The corporate landscape is in a perpetual state of evolution, shaped by various factors ranging from technological advancements to societal shifts. In this exploration, we delve into the currents of corporate trends, dissecting the nuances that define the modern business environment.
Tech-Driven Transformations:
Corporate trends in recent years have been undeniably influenced by technological advancements. From artificial intelligence and automation to data analytics, businesses are navigating a landscape where embracing and adapting to these tech-driven transformations is not merely an option but a strategic imperative. The integration of technology enhances efficiency, drives innovation, and often delineates success in today’s corporate arena.
Remote Work Revolution:
The global response to unprecedented events has accelerated the remote work revolution. Corporate trends now reflect a paradigm shift in traditional work models. Companies are reevaluating office spaces, embracing flexible work arrangements, and leveraging digital tools to ensure productivity. This evolution brings challenges but also opens doors to new possibilities for talent acquisition and employee satisfaction.
Evolving Corporate Culture:
Corporate culture is no longer confined to office walls. As businesses embrace remote work and diverse teams, the definition and cultivation of corporate culture undergo significant changes. Companies are placing increased emphasis on fostering inclusivity, diversity, and employee well-being. The evolution of corporate culture is becoming a key factor in attracting and retaining top talent.
Sustainability as a Core Value:
In an era marked by environmental consciousness, corporate trends are pivoting towards sustainability. Businesses are integrating eco-friendly practices into their operations, driven not only by a sense of social responsibility but also recognizing the economic benefits of sustainable practices. This shift towards environmental sustainability is increasingly becoming a core value for corporate entities.
Agile Business Models:
The fast-paced, ever-changing business landscape demands agility. Corporate trends highlight the importance of adopting flexible and adaptive business models. The ability to pivot quickly in response to market dynamics, consumer preferences, and external factors is becoming a defining characteristic of successful businesses.
Emphasis on Employee Development:
Investing in employee development is emerging as a cornerstone of corporate success. Beyond traditional training programs, businesses are focusing on continuous learning, skill development, and creating pathways for career growth. This not only enhances workforce capabilities but also contributes to employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Data Security and Privacy Compliance:
With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, data security and privacy have become paramount. Corporate trends underscore the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and adherence to privacy regulations. Businesses are investing in secure technologies and implementing stringent measures to protect sensitive information, building trust with both clients and employees.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations:
Collaboration is a key driver in contemporary corporate strategies. Businesses are increasingly forming strategic partnerships to leverage complementary strengths, expand market reach, and foster innovation. The era of siloed operations is giving way to a collaborative ecosystem where partnerships play a pivotal role in achieving corporate objectives.
Consumer-Centric Approaches:
Corporate trends recognize the power of the consumer. Businesses are adopting customer-centric approaches, utilizing data analytics to understand consumer behavior, and tailoring products
Unraveling Economies: Political Instability’s Economic Consequences

Unraveling Economies: The Far-Reaching Effects of Political Instability
Political instability is a disruptive force that reverberates beyond the realm of governance, significantly impacting economic landscapes worldwide. This article explores the multifaceted economic consequences that unfold when political stability is compromised.
Trade Disruptions and Investment Uncertainty
One of the immediate economic consequences of political instability is the disruption of international trade. Uncertainty surrounding a nation’s political climate can deter foreign investments and lead to a decline in exports and imports. The unpredictability of policies and potential trade barriers create an environment where businesses hesitate to commit resources, hindering economic growth.
Currency Volatility and Inflationary Pressures
Political instability often translates into currency volatility, affecting exchange rates and triggering inflationary pressures. Investors may lose confidence in a nation’s currency, leading to depreciation. The ensuing inflation erodes the purchasing power of citizens, causing a ripple effect on consumer spending, business investments, and overall economic stability.
Impact on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Foreign Direct Investment, a crucial driver of economic growth, is particularly sensitive to political stability. Countries facing political turmoil may experience a sharp decline in FDI, as investors seek safer and more predictable markets. This reduction in foreign investments hampers infrastructure development, job creation, and the overall economic progress of the nation.
Erosion of Public Trust and Consumer Confidence
Political instability erodes public trust and confidence in government institutions. This lack of trust extends to the economic sphere, affecting consumer confidence and spending behaviors. When citizens are uncertain about their country’s political future, they tend to cut back on non-essential expenses, leading to a slowdown in economic activity.
Government Spending and Fiscal Policy Challenges
Stable political environments enable governments to formulate and implement consistent fiscal policies. In times of political instability, the continuity of such policies becomes challenging. Governments may struggle to maintain fiscal discipline, leading to budgetary imbalances, increased public debt, and constraints on essential public services.
Social Unrest and Disruptions to Productive Activities
Political instability often manifests in social unrest and protests. These disturbances disrupt productive activities, causing a decline in productivity and economic output. Businesses may face challenges in maintaining regular operations, and the uncertainty may prompt some to relocate or scale back their activities.
Impact on Financial Markets and Investor Sentiment
Financial markets are highly responsive to political developments. Political instability introduces an element of uncertainty that can lead to increased market volatility. Investors may adopt a risk-averse stance, resulting in capital flight and a downturn in stock markets. The interconnectedness of global financial markets means that political turbulence in one region can have widespread consequences.
Long-Term Economic Stagnation and Development Setbacks
Persistent political instability can result in long-term economic stagnation. The inability to implement consistent economic policies, attract investments, and foster a conducive business environment hampers a nation’s development. The repercussions extend to education, healthcare, and infrastructure, impeding progress on multiple fronts.
International Repercussions and Global Economic Spillover
The economic consequences of political instability are not confined within national borders. Globalization means that disruptions in one country can